Abstract
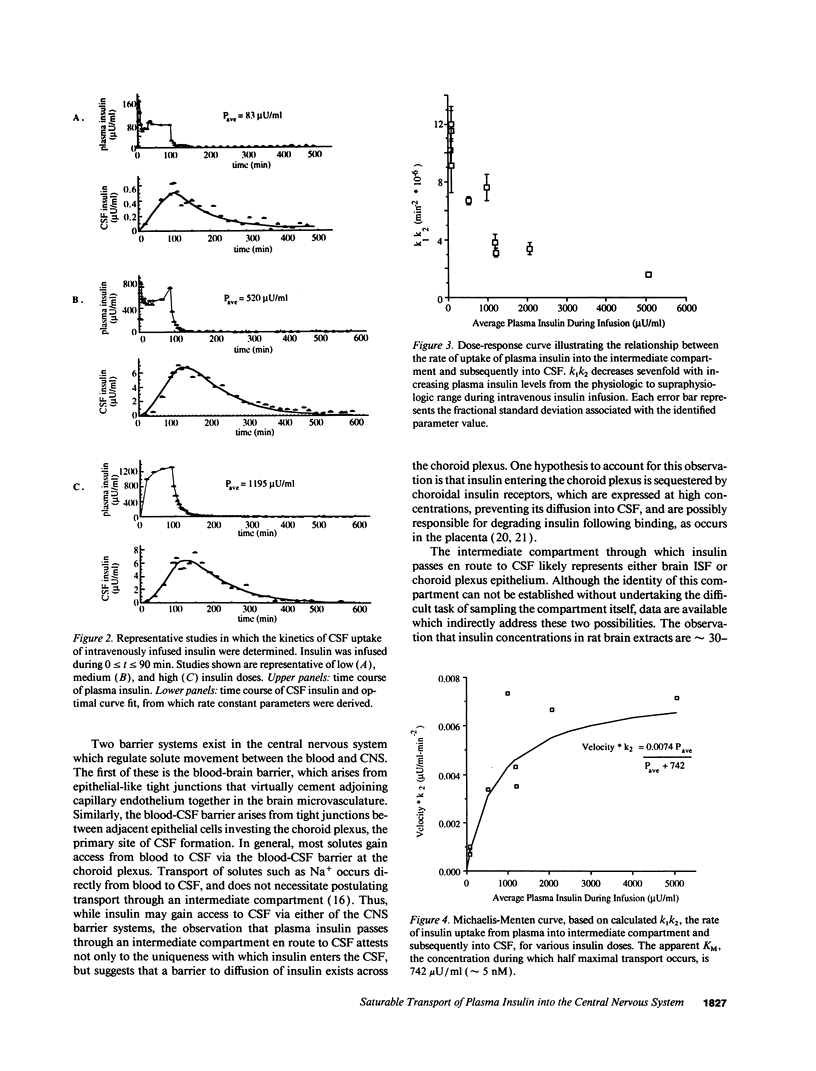
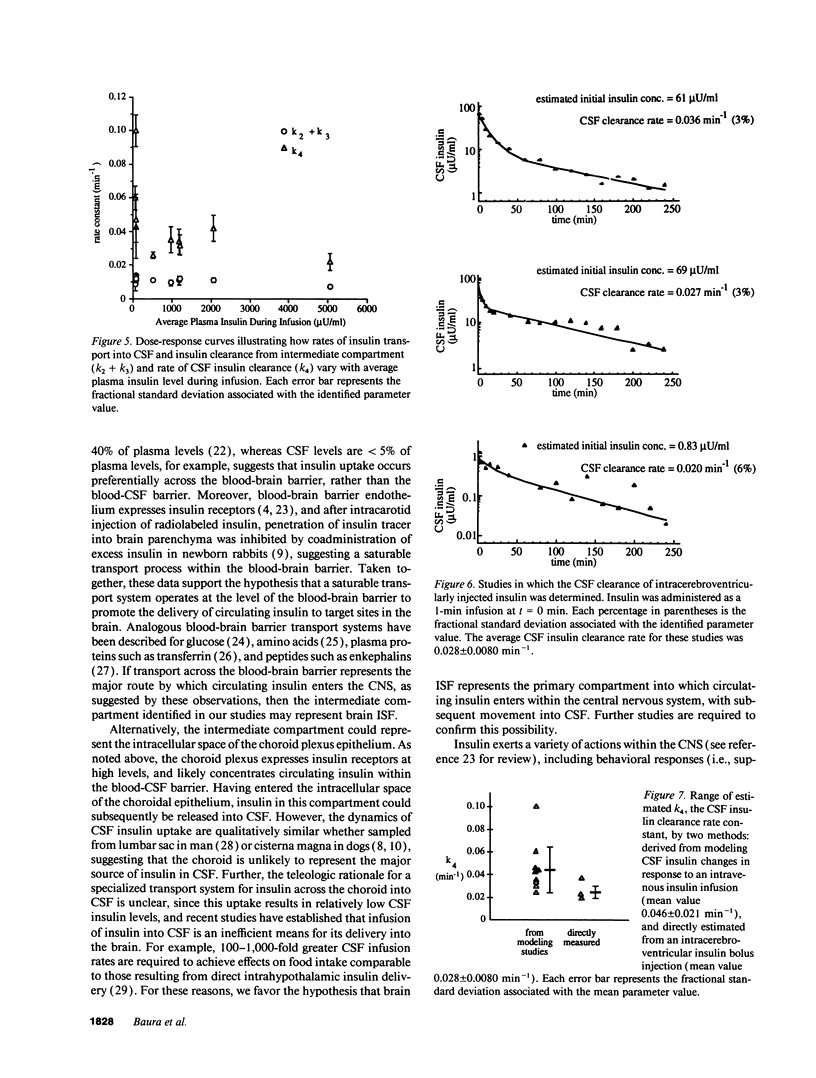
By acting in the central nervous system, circulating insulin may regulate food intake and body weight. We have previously shown that the kinetics of insulin uptake from plasma into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can best be explained by passage through an intermediate compartment. To determine if transport kinetics into this compartment were consistent with an insulin receptor-mediated transport process, we subjected overnight fasted, anesthetized dogs to euglycemic intravenous insulin infusions for 90 min over a wide range of plasma insulin levels (69-5,064 microU/ml) (n = 10). Plasma and CSF samples were collected over 8 h for determination of immunoreactive insulin levels, and the kinetics of insulin uptake from plasma into CSF were analyzed using a compartmental model with three components (plasma-->intermediate compartment-->CSF). By sampling frequently during rapid changes of plasma and CSF insulin levels, we were able to precisely estimate three parameters (average standard deviation 14%) characterizing the uptake of insulin from plasma, through the intermediate compartment and into CSF (k1k2); insulin entry into CSF and insulin clearance from the intermediate compartment (k2 + k3); and insulin clearance from CSF (k4). At physiologic plasma insulin levels (80 +/- 7.4 microU/ml), k1k2 was determined to be 10.7 x 10(-6) +/- 1.3 x 10(-6) min-2. With increasing plasma levels, however, k1k2 decreased progressively, being reduced sevenfold at supraphysiologic levels (5,064 microU/ml). The apparent KM of this saturation curve was 742 microU/ml (approximately 5 nM). In contrast, the rate constants for insulin removal from the intermediate compartment and from CSF did not vary with plasma insulin (k2 + k3 = 0.011 +/- 0.0019 min-1 and k4 = 0.046 +/- 0.021 min-1). We conclude that delivery of plasma insulin into the central nervous system is saturable, and is likely facilitated by an insulin-receptor mediated transport process.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Sandra A. Vascular transport of insulin to rat cardiac muscle. Central role of the capillary endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1225–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI113439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. G., Woods S. C., West D. B., van Houten M., Posner B. I., Dorsa D. M., Porte D., Jr Immunocytochemical detection of insulin in rat hypothalamus and its possible uptake from cerebrospinal fluid. Endocrinology. 1983 Nov;113(5):1818–1825. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-5-1818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challier J. C., Hauguel S., Desmaizieres V. Effect of insulin on glucose uptake and metabolism in the human placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 May;62(5):803–807. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-5-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. Facilitated transfer of glucose from blood into brain tissue. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(1):103–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Argenio D. Z. Optimal sampling times for pharmacokinetic experiments. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981 Dec;9(6):739–756. doi: 10.1007/BF01070904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy K. R., Pardridge W. M. Blood-brain barrier transcytosis of insulin in developing rabbits. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 8;420(1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J. B., Rubin J. B., Handrahan J. V., Connor J. R., Fine R. E. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of transferrin across the blood-brain barrier. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(2):299–304. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank H. J., Pardridge W. M. A direct in vitro demonstration of insulin binding to isolated brain microvessels. Diabetes. 1981 Sep;30(9):757–761. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.9.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank H. J., Pardridge W. M. Insulin binding to brain microvessels. Adv Metab Disord. 1983;10:291–302. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027310-2.50016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Krohmer J. S. Insulin transfer in the isolated human placenta. Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Jul;32(1):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Johnson S. M. Receptor-mediated transport of insulin across endothelial cells. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1583–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.3883490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manin M., Broer Y., Balage M., Rostene W., Grizard J. Metabolic clearance of insulin from the cerebrospinal fluid in the anesthetized rat. Peptides. 1990 Jan-Feb;11(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90102-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan M. K., Andrews K. M., Kelly J., Grossman S. P. Effects of chronic intrahypothalamic infusion of insulin on food intake and diurnal meal patterning in the rat. Behav Neurosci. 1990 Apr;104(2):373–385. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.104.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M. Receptor-mediated peptide transport through the blood-brain barrier. Endocr Rev. 1986 Aug;7(3):314–330. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-3-314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED D. J., WOODBURY D. M. KINETICS OF MOVEMENT OF IODIDE, SUCROSE, INULIN AND RADIO-IODINATED SERUM ALBUMIN IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM AND CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:816–850. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. W., Bergman R. N., Kahn S. E., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Fisher L. D., Sipols A. J., Woods S. C., Steil G. M., Porte D., Jr Evidence for entry of plasma insulin into cerebrospinal fluid through an intermediate compartment in dogs. Quantitative aspects and implications for transport. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1272–1281. doi: 10.1172/JCI115431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. W., Figlewicz D. P., Baskin D. G., Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Insulin in the brain: a hormonal regulator of energy balance. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):387–414. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. W., Sipols A., Kahn S. E., Lattemann D. F., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Bergman R. N., Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Kinetics and specificity of insulin uptake from plasma into cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):E378–E383. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.3.E378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderWeele D. A., Haraczkiewicz E., Van Itallie T. B. Elevated insulin and satiety in obese and normal-weight rats. Appetite. 1982 Jun;3(2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6663(82)80003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallum B. J., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Porte D., Jr, Figlewicz D. P., Jacobson L., Beard J. C., Ward W. K., Dorsa D. Cerebrospinal fluid insulin levels increase during intravenous insulin infusions in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jan;64(1):190–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-1-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Lotter E. C., McKay L. D., Porte D., Jr Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of insulin reduces food intake and body weight of baboons. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):503–505. doi: 10.1038/282503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr, Bobbioni E., Ionescu E., Sauter J. F., Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin: its relationship to the central nervous system and to the control of food intake and body weight. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Nov;42(5 Suppl):1063–1071. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.5.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Eng J. Insulin in the central nervous system. Adv Metab Disord. 1983;10:341–354. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027310-2.50018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Hope I. D., Ader M., Bergman R. N. Insulin transport across capillaries is rate limiting for insulin action in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1620–1628. doi: 10.1172/JCI114339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Hope I., Ader M., Poulin R. A., Bergman R. N. Dose-response relationship between lymph insulin and glucose uptake reveals enhanced insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues. Diabetes. 1992 Feb;41(2):241–253. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.41.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zloković B. V., Lipovac M. N., Begley D. J., Davson H., Rakić L. Transport of leucine-enkephalin across the blood-brain barrier in the perfused guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):310–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



