Abstract
To elucidate the effects of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) on fuel oxidation and insulin sensitivity, eight healthy subjects were treated with saline and recombinant human (IGF-I (10 micrograms/kg.h) during 5 d in a crossover, randomized fashion, while receiving an isocaloric diet (30 kcal/kg.d) throughout the study period. On the third and fourth treatment days, respectively, an L-arginine stimulation test and an intravenous glucose tolerance test were performed. A euglycemic, hyperinsulinemic clamp combined with indirect calorimetry and a glucose tracer infusion were performed on the fifth treatment day. IGF-I treatment led to reduced fasting and stimulated (glucose and/or L-arginine) insulin and growth hormone secretion. Basal and stimulated glucagon secretion remained unchanged. Intravenous glucose tolerance was unaltered despite reduced insulin secretion. Resting energy expenditure and lipid oxidation were both elevated, while protein oxidation was reduced, and glucose turnover rates were unaltered on the fifth treatment day with IGF-I as compared to the control period. Enhanced lipolysis was reflected by elevated circulating free fatty acids. Moreover, insulin-stimulated oxidative and nonoxidative glucose disposal (i.e., insulin sensitivity) were enhanced during IGF-I treatment. Thus, IGF-I treatment leads to marked changes in lipid and protein oxidation, whereas, at the dose used, carbohydrate metabolism remains unaltered in the face of reduced insulin levels and enhanced insulin sensitivity.
Full text
PDF

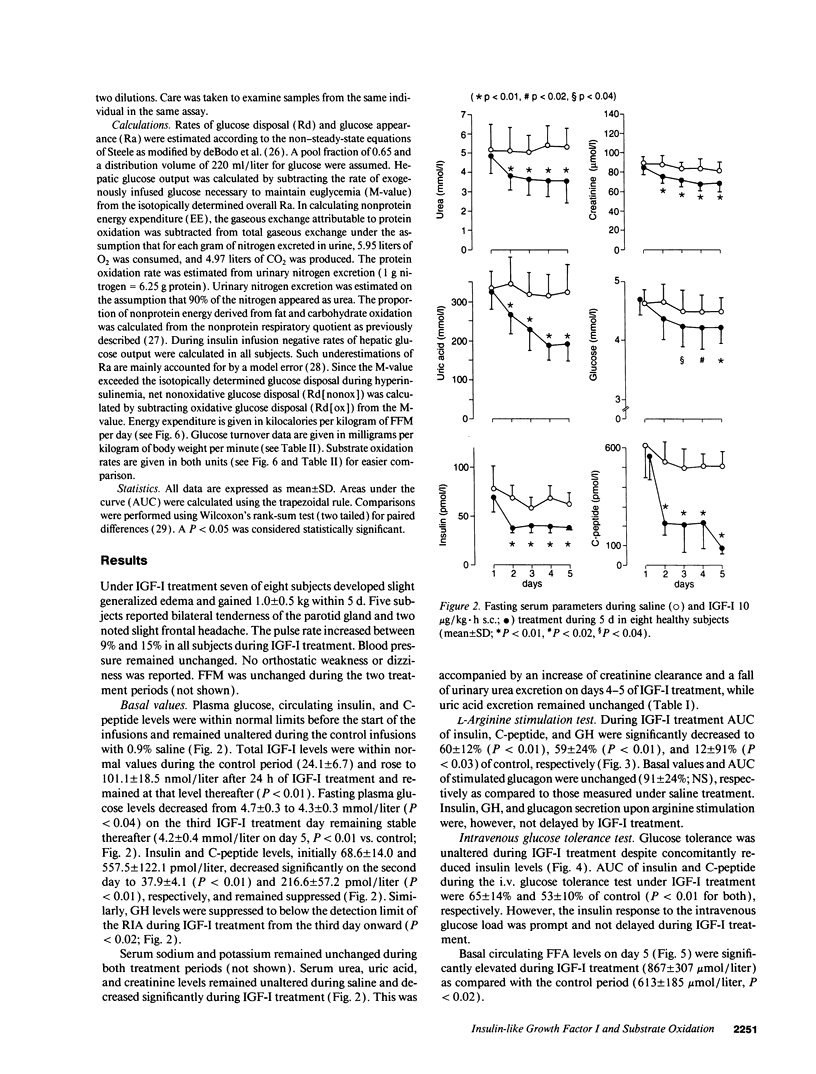





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak J. F., Møller N., Schmitz O. Effects of growth hormone on fuel utilization and muscle glycogen synthase activity in normal humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):E736–E742. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.5.E736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Clemmons D. R., Boes M., Busby W. H., Booth B. A., Dake B. L., Sandra A. Transcapillary permeability and subendothelial distribution of endothelial and amniotic fluid insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the rat heart. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1078–1086. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Harrison L. C., Muggeo M., Gorden P., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors in normal and abnormal physiology in humans. Adv Intern Med. 1979;24:23–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berelowitz M., Szabo M., Frohman L. A., Firestone S., Chu L., Hintz R. L. Somatomedin-C mediates growth hormone negative feedback by effects on both the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6262917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratusch-Marrain P. R., Smith D., DeFronzo R. A. The effect of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):973–982. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Poulos J., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Sinha M. K. Insulin-like growth factor I binding in hepatocytes from human liver, human hepatoma, and normal, regenerating, and fetal rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):976–981. doi: 10.1172/JCI113451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Smith-Banks A., Underwood L. E. Reversal of diet-induced catabolism by infusion of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):234–238. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Mari A., Ferrannini E. Non-steady state: error analysis of Steele's model and developments for glucose kinetics. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E679–E689. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBODO R. C., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S. ON THE HORMONAL REGULATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM; STUDIES WITH C14 GLUCOSE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1963;19:445–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahn M. S., Lange M. P., Jacobs L. A. Insulinlike growth factor 1 production is inhibited in human sepsis. Arch Surg. 1988 Nov;123(11):1409–1414. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400350123019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Gluckman P. D., Ball K., Breier B., Shaw J. H. The effects of infusion of insulinlike growth factor (IGF) I, IGF-II, and insulin on glucose and protein metabolism in fasted lambs. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):614–622. doi: 10.1172/JCI115346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elia M., Livesey G. Theory and validity of indirect calorimetry during net lipid synthesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Apr;47(4):591–607. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.4.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Tsalikian E., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of physiologic levels of glucagon and growth hormone on human carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Studies involving administration of exogenous hormone during suppression of endogenous hormone secretion with somatostatin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):875–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI108364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacca A., Gupta R., Efendic S., Hall K., Skottner A., Lickley L., Vranic M. Differential effects of IGF-I and insulin on glucoregulation and fat metabolism in depancreatized dogs. Diabetes. 1990 Mar;39(3):340–347. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Schmid C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I on insulin secretion and renal function in normal human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2868–2872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Scheiwiller E., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth and has distinct effects on organ size in hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Barrett E., Plewe G., Fagin K. D., Sherwin R. S. Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1717–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI114072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlander S., Vranić M., Efendić S. Increased glucose turnover and glucose cycling in acromegalic patients with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 1986 Nov;29(11):778–783. doi: 10.1007/BF00873216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Tamborlane W. V., Rife F., Sherwin R. S. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 on the responses to and recognition of hypoglycemia in humans. A comparison with insulin. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):141–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI116163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer S. R., Underwood L. E., Baxter R. C., Clemmons D. R. Enhancement of the anabolic effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I by use of both agents simultaneously. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):391–396. doi: 10.1172/JCI116212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Anin S., Klipper-Aurbach Y., Klinger B. Effects of insulin-like growth factor on linear growth, head circumference, and body fat in patients with Laron-type dwarfism. Lancet. 1992 May 23;339(8804):1258–1261. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91594-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Vandekerkhove K. M. Insulin-like growth factor-I at physiological concentrations is a potent inhibitor of insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1593–1598. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller J., Jørgensen J. O., Møller N., Christiansen J. S., Weeke J. Effects of growth hormone administration on fuel oxidation and thyroid function in normal man. Metabolism. 1992 Jul;41(7):728–731. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller N., Schmitz O., Jøorgensen J. O., Astrup J., Bak J. F., Christensen S. E., Alberti K. G., Weeke J. Basal- and insulin-stimulated substrate metabolism in patients with active acromegaly before and after adenomectomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):1012–1019. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1569148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi C., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Freychet P. Effects and binding of insulin-like growth factor I in the isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice: comparison with insulin. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert N. J., Caprio S., Sherwin R. S. Insulin-like growth factor I inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion but does not impair glucose metabolism in normal humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Mar;76(3):804–806. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.3.8445040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Effects of growth hormone on insulin action in man. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, impaired suppression of glucose production, and impaired stimulation of glucose utilization. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):663–669. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Smith D., Shulman G. I., Papachristou D., DeFronzo R. A. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1510–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI112981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMON W. D., Jr, DAUGHADAY W. H. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon F., Cuneo R. C., Hesp R., Sönksen P. H. The effects of treatment with recombinant human growth hormone on body composition and metabolism in adults with growth hormone deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 28;321(26):1797–1803. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912283212605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S., Yang H., Ney D. M., DiMarchi R. D. Infusion of human insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) into malnourished rats reduces hepatic IGF-I mRNA abundance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):795–800. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92503-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiwiller E., Guler H. P., Merryweather J., Scandella C., Maerki W., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth restoration of insulin-deficient diabetic rats by recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):169–171. doi: 10.1038/323169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwander J. C., Hauri C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Synthesis and secretion of insulin-like growth factor and its binding protein by the perfused rat liver: dependence on growth hormone status. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):297–305. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal K. R., Van Loan M., Fitzgerald P. I., Hodgdon J. A., Van Itallie T. B. Lean body mass estimation by bioelectrical impedance analysis: a four-site cross-validation study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Jan;47(1):7–14. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sestoft L. Metabolic aspects of the calorigenic effect of thyroid hormone in mammals. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1980 Nov;13(5):489–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1980.tb03415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Schulman G. A., Hendler R., Walesky M., Belous A., Tamborlane W. Effect of growth hormone on oral glucose tolerance and circulating metabolic fuels in man. Diabetologia. 1983 Mar;24(3):155–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00250154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Greenwood F. C., Ellis J. P., Lowy C., Rutherford A., Nabarro J. D. Changes of carbohydrate tolerance in acromegaly with progress of the disease and in response to treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Oct;27(10):1418–1430. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-10-1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkalj I., Keller U., Ninnis R., Vosmeer S., Stauffacher W. Effect of increasing doses of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose, lipid, and leucine metabolism in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Nov;75(5):1186–1191. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.5.1430077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. L., Ginalska-Malinowska M., Romer T. E., Pucilowska J. B., Underwood L. E. Effects of the infusion of insulin-like growth factor I in a child with growth hormone insensitivity syndrome (Laron dwarfism). N Engl J Med. 1991 May 23;324(21):1483–1488. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105233242107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1768–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI112500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Guler H. P., Waldvogel M., Hauri C., Futo E., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M., Froesch E. R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):952–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Guler H. P., Waldvogel M., Hauri C., Futo E., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M., Froesch E. R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):952–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Waldvogel M., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Effect of trypsin treatment of rat adipocytes on biological effects and binding of insulin and insulin-like growth factors: further evidence for the action of insulin-like growth factors through the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenobi P. D., Graf S., Ursprung H., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose tolerance, insulin levels, and insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1908–1913. doi: 10.1172/JCI115796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul-Offers S., Ueda I., Van den Brande J. L. Biosynthetic somatomedin C (SM-C/IGF-I) increases the length and weight of Snell dwarf mice. Pediatr Res. 1986 Sep;20(9):825–827. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198609000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]