Abstract
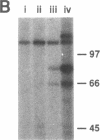
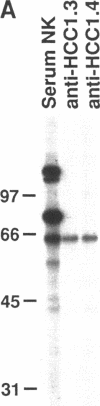
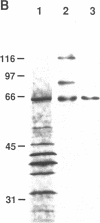
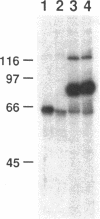
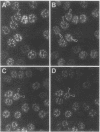
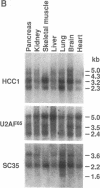
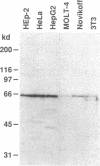
A patient with liver cirrhosis who progressed to hepatocellular carcinoma was found to develop novel antinuclear antibodies. The serum was used to isolate full-length cDNA clones encoding related proteins of 530 amino acids (representative clone HCC1.4) and 524 amino acids (representative clone HCC1.3). Affinity-purified antibodies eluted from recombinant proteins recognized a 64-kD nuclear protein in Western blotting and decorated the nucleoplasm in a speckled-network fashion in immunofluorescence, colocalizing with antibodies to pre-mRNA splicing factor SC35 and uridine-rich small nuclear RNAs. The deduced amino acid sequence contained an arginine/serine-rich (RS) domain and three-ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence domains, two classes of motifs present in several splicing factors. A repeating octapeptide of Arg-Ser-Arg-Ser-Arg(Lys)-Glu(Asp)-Arg-Lys(Arg) was present in RS region of HCC1. This octapeptide sequence called RS-ERK motif was also found in splicing factors U2AF 35- and 65-kD proteins and 70-kD U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. The molecular features and immunolocalization data suggest that the HCC1 autoantigen may be associated with splicing activities and are consistent with observations that autoantibody responses frequently target molecules involved in important cellular biosynthetic functions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein H., Gorman M., Nöthiger R. The sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encodes a putative RNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. A putative homolog of U2AF65 in S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4663–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs R. T., Gregor P., Idriss S., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Regulation of sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster via alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):739–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Hamel J. C., Buyon J. P., Tan E. M. Molecular definition and sequence motifs of the 52-kD component of human SS-A/Ro autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):68–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI115003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Imai H., Hamel J. C., Tan E. M. Human autoantibody to RNA polymerase I transcription factor hUBF. Molecular identity of nucleolus organizer region autoantigen NOR-90 and ribosomal RNA transcription upstream binding factor. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1239–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Developmental expression of a regulatory gene is programmed at the level of splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein N., Chan P. K., Mond J. J. Identification of numatrin, the nuclear matrix protein associated with induction of mitogenesis, as the nucleolar protein B23. Implication for the role of the nucleolus in early transduction of mitogenic signals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10608–10612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1373910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goralski T. J., Edström J. E., Baker B. S. The sex determination locus transformer-2 of Drosophila encodes a polypeptide with similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1011–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb T. M., Jackson S. P. The DNA-dependent protein kinase: requirement for DNA ends and association with Ku antigen. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90057-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
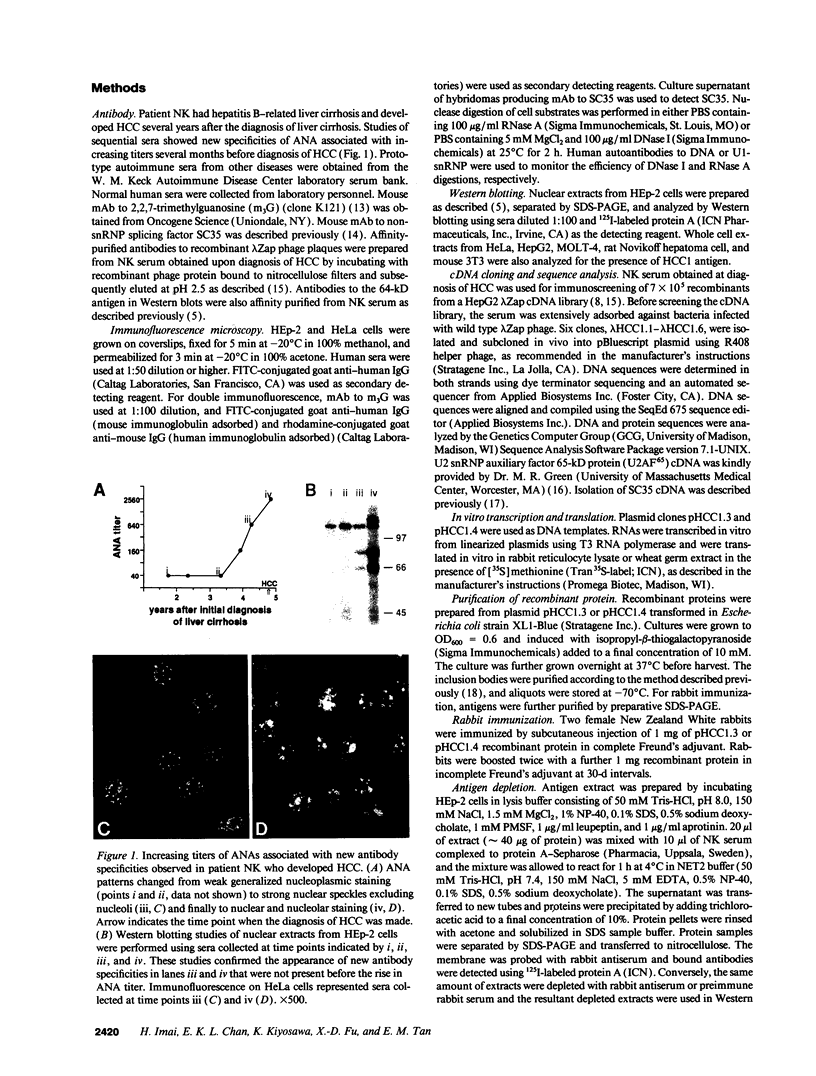
- Imai H., Nakano Y., Kiyosawa K., Tan E. M. Increasing titers and changing specificities of antinuclear antibodies in patients with chronic liver disease who develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1993 Jan 1;71(1):26–35. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930101)71:1<26::aid-cncr2820710106>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
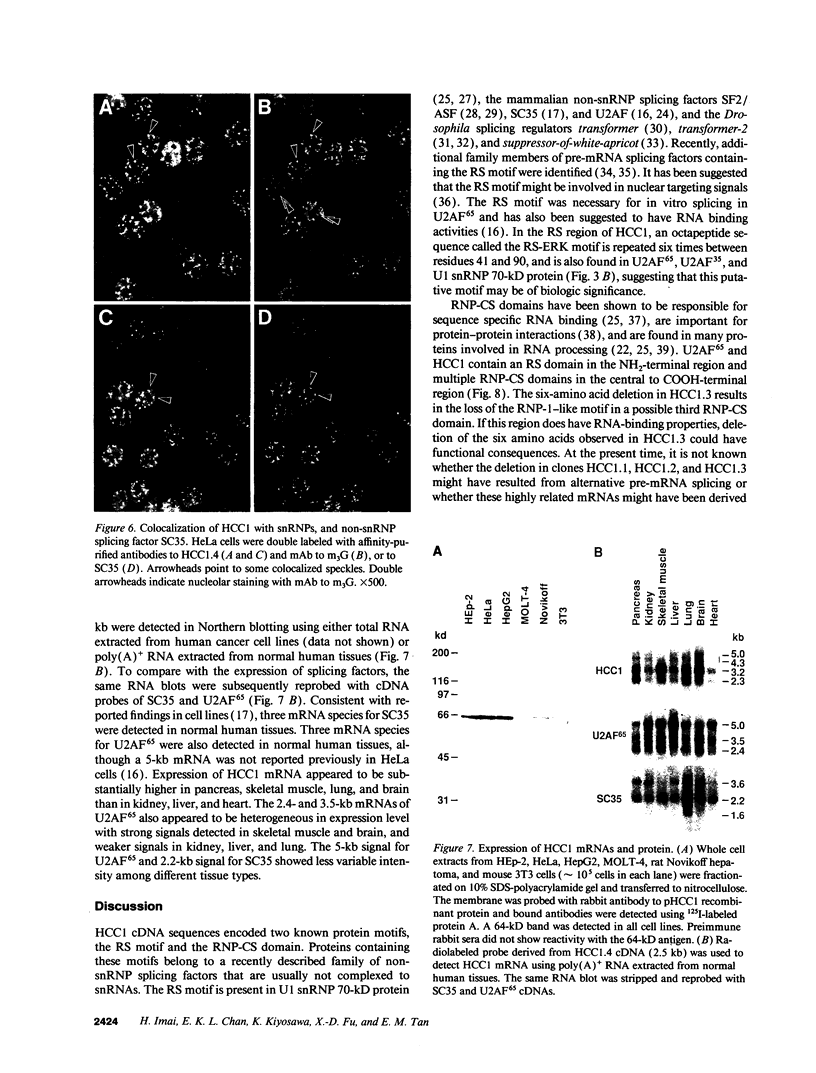
- Imai H., Ochs R. L., Kiyosawa K., Furuta S., Nakamura R. M., Tan E. M. Nucleolar antigens and autoantibodies in hepatocellular carcinoma and other malignancies. Am J Pathol. 1992 Apr;140(4):859–870. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Tyc K., Steitz J. A., Sollner-Webb B. The U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein functions in the first step of preribosomal RNA processing. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):897–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90338-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Mayeda A., Kozak D., Binns G. Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, and Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90627-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R. Pre-mRNA splicing by complementation with purified human U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9415–9429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancebo R., Lo P. C., Mount S. M. Structure and expression of the Drosophila melanogaster gene for the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle 70K protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2492–2502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Zahler A. M., Krainer A. R., Roth M. B. Two members of a conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1301–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Dathan N. A., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. The U2B'' RNP motif as a site of protein-protein interaction. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3675–3681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3467–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies in pathology and cell biology. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):841–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toschi L., Bravo R. Changes in cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen distribution during DNA repair synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1623–1628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Blum H. E. Primary hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 5;325(10):729–731. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109053251010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Patton J. G., Green M. R. Cloning and domain structure of the mammalian splicing factor U2AF. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):609–614. doi: 10.1038/355609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M., Zamore P. D., Carmo-Fonseca M., Lamond A. I., Green M. R. Cloning and intracellular localization of the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor small subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8769–8773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]