Abstract
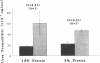
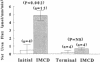
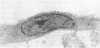
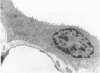
Low protein diets reverse the urea concentration gradient in the renal inner medulla. To investigate the mechanism(s) for this change, we studied urea transport and cell ultrastructure in initial and terminal inner medullary collecting ducts (IMCD) from rats fed 18% protein or an isocaloric, 8% protein diet for 4 wk. Serum urea, aldosterone, and albumin were significantly lower in rats fed 8% protein, but total protein and potassium were unchanged. Vasopressin stimulated passive urea permeability (Purea) threefold (P < 0.05) in initial IMCDs from rats fed 8% protein, but not from rats fed 18% protein. Luminal phloretin reversibly inhibited vasopressin-stimulated Purea. However, in terminal IMCDs from rats fed either diet, vasopressin stimulated Purea. Net transepithelial urea flux (measured with identical perfusate and bath solutions) was found only in initial IMCDs from rats fed 8% protein. Reducing the temperature reversibly inhibited it, but phloretin did not. Electron microscopy of initial IMCD principal cells from rats fed 8% protein showed expanded Golgi bodies and prominent autophagic vacuoles, and morphometric analysis demonstrated a marked increase in the surface density and boundary length of the basolateral plasma membrane. These ultrastructural changes were not observed in the terminal IMCD. Thus, 8% dietary protein causes two new urea transport processes to appear in initial but not terminal IMCDs. This is the first demonstration that "active" urea transport can be induced in a mammalian collecting duct segment.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAY G. A., PRESTON A. S. Effect of urea on urine concentration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1952–1960. doi: 10.1172/JCI104420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. D., DOYLE A. P., PROBST J. H. Service of urea in renal water conservation. Am J Physiol. 1959 Mar;196(3):545–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.3.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. L., Knepper M. A. Inhibition of urea transport in inner medullary collecting duct by phloretin and urea analogues. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F359–F365. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp J. R. Renal tubular reabsorption of urea in normal and protein-depleted rats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1304–1308. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp W. L., Madsen K. M., Verlander J. W., Tisher C. C. Intercalated cells of the rat inner medullary collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1987 May;31(5):1080–1087. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp W. L., Madsen K. M., Verlander J. W., Tisher C. C. Morphologic heterogeneity along the rat inner medullary collecting duct. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):219–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson R. A., Schmidt-Nielsen B. Recirculation of urea analogs from renal collecting ducts of high- and low-protein-fed rats. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jul;223(1):130–137. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feehally J., Baker F., Walls J. Dietary protein manipulation in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Nephron. 1988;50(3):247–252. doi: 10.1159/000185167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorotto M. L., Sheng H. P., Evans H. J., Leblanc A. D., Johnson P. C., Nichols B. L. Specific effects of weight loss, protein deficiency and energy deprivation on the water and electrolyte composition of young rats. J Nutr. 1987 May;117(5):933–940. doi: 10.1093/jn/117.5.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin A. G., Sands J. M. Characteristics of osmolarity-stimulated urea transport in rat IMCD. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):F1061–F1067. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.6.F1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joppich R., Deetjen P. The relation between the reabsorption of urea and of water in the distal tubule of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;329(2):172–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00586991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper M. A., Danielson R. A., Saidel G. M., Johnston K. H. Effects of dietary protein restriction and glucocorticoid administration on urea excretion in rats. Kidney Int. 1975 Nov;8(5):303–315. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper M. A., Good D. W., Burg M. B. Ammonia and bicarbonate transport by rat cortical collecting ducts perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 2):F870–F877. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.6.F870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper M. A. Urea transport in isolated thick ascending limbs and collecting ducts from rats. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):F634–F639. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.5.F634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Rector F. C., Jr Countercurrent multiplication system without active transport in inner medulla. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):214–223. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Imai M. Effects of glutaraldehyde fixation on renal tubular function. I. Preservation of vasopressin-stimulated water and urea pathways in rat papillary collecting duct. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):479–483. doi: 10.1007/BF00585072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSITER W. E., GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of net transtubular movement of water and urea in nondiuretic mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1139–1147. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., BERLINER R. W. The role of urea in the urine concentrating mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):741–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassiter W. E., Mylle M., Gottschalk C. W. Micropuncture study of urea transport in rat renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):965–970. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng L., Szanyiová M., Boda K. The renal response of sheep to a low dietary nitrogen intake. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1985;34(2):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURDAUGH H. V., Jr, SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., DOYLE E. M., O'DELL R. Renal tubular regulation of urea excretion in man. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Sep;13(2):263–268. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Sands J. M., Knepper M. A. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits vasopressin-stimulated osmotic water permeability in rat inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1172/JCI113742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peil A. E., Stolte H., Schmidt-Nielsen B. Uncoupling of glomerular and tubular regulations of urea excretion in rat. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):F1666–F1674. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.6.F1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell J. P., Sanjana V., Frey N. R., Jamison R. L. The effect of urea infusion on the urinary concentrating mechanism in protein-depleted rats. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):399–409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz L., Gunther R. A., Shoji E. S., Freedland R. A., Avery E. H. Effects of high and low protein diets on sheep renal function and metabolism. Kidney Int. 1973 Sep;4(3):188–207. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., OSAKI H., MURDAUGH H. V., Jr, O'DELL R. Renal regulation of urea excretion in sheep. Am J Physiol. 1958 Aug;194(2):221–228. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., SCHMIDT-NIELSEN K., HOUPT T. R., JARNUM S. A. Urea excretion in the camel. Am J Physiol. 1957 Mar;188(3):477–484. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.188.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Knepper M. A. Urea permeability of mammalian inner medullary collecting duct system and papillary surface epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):138–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI112774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Nonoguchi H., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin effects on urea and H2O transport in inner medullary collecting duct subsegments. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F823–F832. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Schrader D. C. An independent effect of osmolality on urea transport in rat terminal inner medullary collecting ducts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):137–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI115269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D., Mason G. D. Renal tubular reabsorption of urea in sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1970 Oct;55(4):275–283. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1970.sp002079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. L. Concentration of urine in a central core model of the renal counterflow system. Kidney Int. 1972 Aug;2(2):85–94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUNIGER B., SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B. INTRARENAL DISTRIBUTION OF UREA AND RELATED COMPOUNDS: EFFECTS OF NITROGEN INTAKE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:971–978. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Schmidt-Nielsen B. Urea transport in the collecting duct of rats on normal and low protein diet. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00362746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler A. S., Kalaba R. E., Marsh D. J. Three-dimensional anatomy and renal concentrating mechanism. I. Modeling results. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):F368–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.3.F368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Sonnenberg H. Urea reabsorption in the medullary collecting duct of protein-depleted young rats before and after urea infusion. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):302–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00581414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Sonnenberg H. Urea secretion in medullary collecting duct of the rat kidney during water and mannitol diuresis. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F165–F171. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]