Abstract
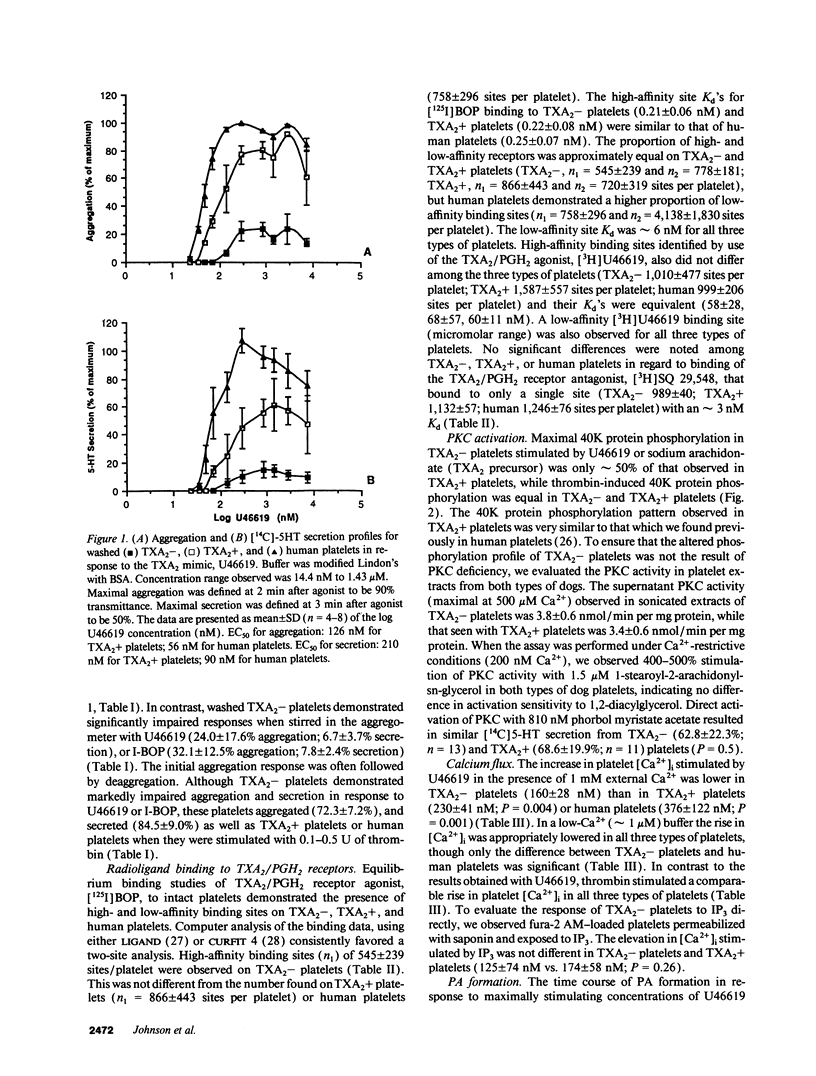
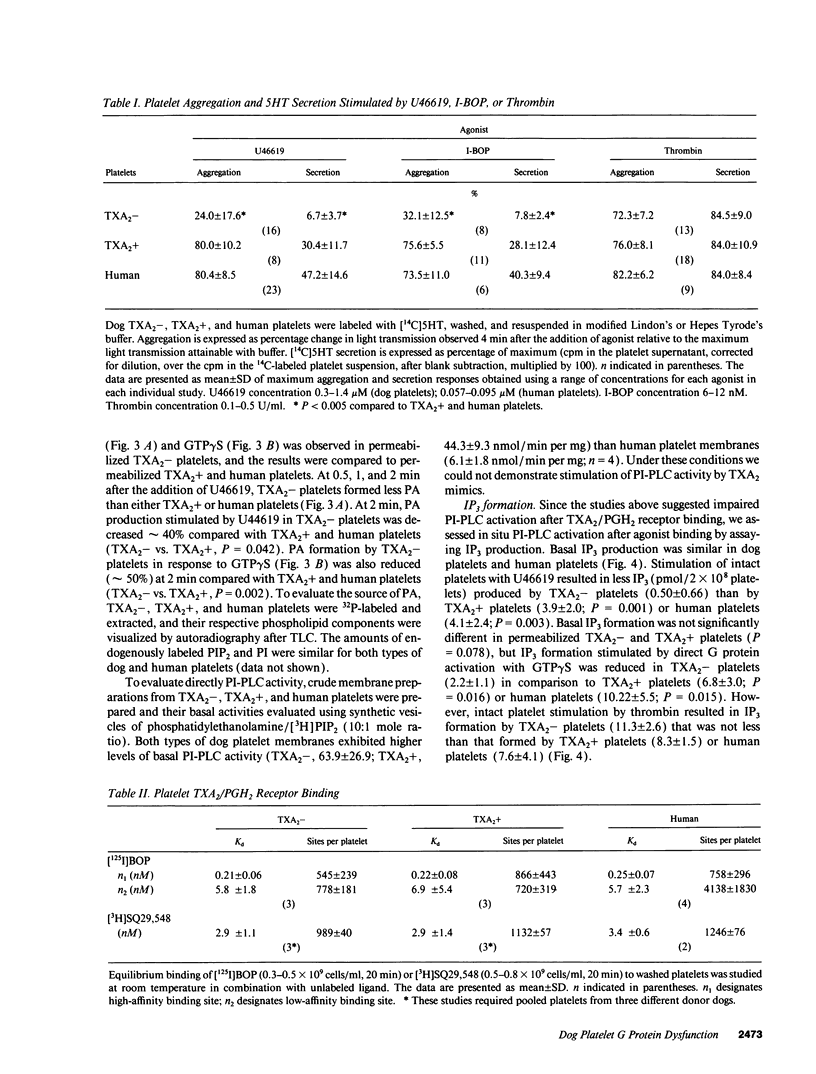
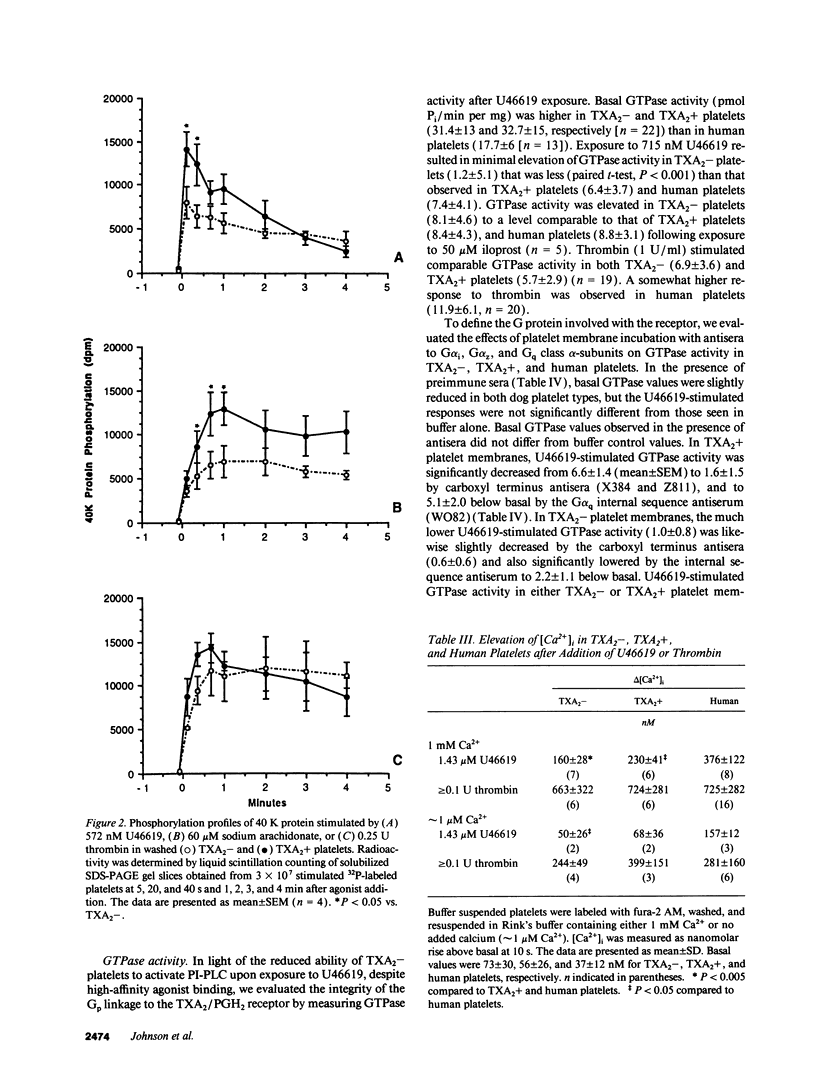
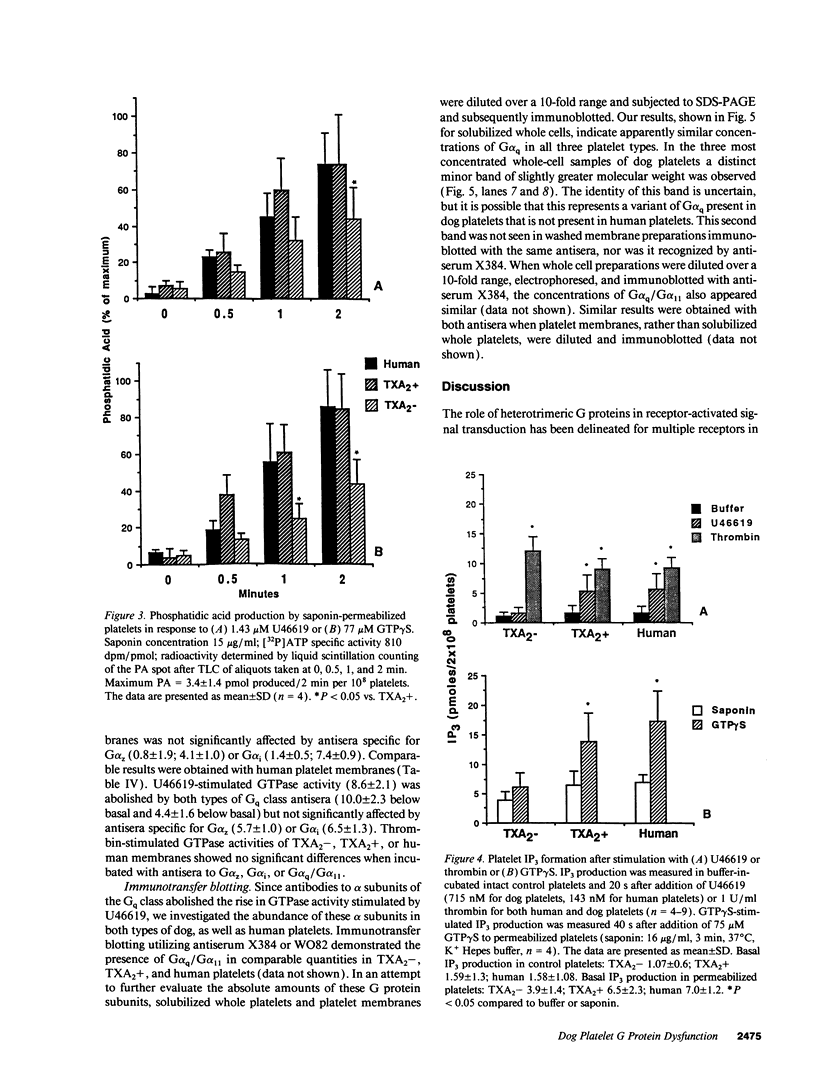
Human platelet thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 (TXA2/PGH2) receptors are linked to phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) via a G protein tentatively identified as a member of the Gq class. In contrast, platelet thrombin receptors appear to activate PI-PLC via other unidentified G proteins. Platelets from most dogs are TXA2 insensitive (TXA2-); i.e., they do not aggregate irreversibly or secrete although they bind TXA2, but they respond normally to thrombin. In contrast, a minority of dogs have TXA2-sensitive (TXA2+) platelets that are responsive to TXA2. To determine the mechanism responsible for TXA2- platelets, we evaluated receptor activation of PI-PLC. Equilibrium binding of TXA2/PGH2 receptor agonists, [125I]BOP and [3H]U46619, and antagonist, [3H]SQ29,548, revealed comparable high-affinity binding to TXA2-, TXA2+, and human platelets. U46619-induced PI-PLC activation was impaired in TXA2- platelets as evidenced by reduced (a) phosphorylation of the 47-kD substrate of protein kinase C, (b) phosphatidic acid (PA) formation, (c) rise in cytosolic calcium concentration, and (d) inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate (IP3) formation, while thrombin-induced PI-PLC activation was not impaired. GTPase activity stimulated by U46619, but not by thrombin, was markedly reduced in TXA2- platelets. Antisera to Gq class alpha subunits abolished U46619-induced GTPase activity in TXA2-, TXA2+, and human platelets. Direct G protein stimulation by GTP gamma S yielded significantly less PA and IP3 in TXA2- platelets. Immunotransfer blotting revealed comparable quantities of Gq class alpha-subunits in all three platelet types. Thus, TXA2- dog platelets have impaired PI-PLC activation in response to TXA2/PGH2 receptor agonists secondary to G protein dysfunction, presumably involving a member of the Gq class.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldassare J. J., Henderson P. A., Fisher G. J. Plasma membrane associated phospholipase C from human platelets: synergistic stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by thrombin and guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):56–60. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga H. S., Walker R. K., Winberry L. K., Rittenhouse S. E. Platelet adenylate cyclase and phospholipase C are affected differentially by ADP-ribosylation. Effects on thrombin-mediated responses. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2520297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno Y., Yada Y., Nozawa Y. Purification and characterization of membrane-bound phospholipase C specific for phosphoinositides from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11459–11465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Waldo G. L., Evans T., Northup J. K., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Modification of AlF-4- and receptor-stimulated phospholipase C activity by G-protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13917–13922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Shaller C. C., Belmonte E. J. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced granule secretion in platelets. Evidence that the activation of phospholipase C mediated by platelet thromboxane receptors involves a guanine nucleotide binding protein-dependent mechanism distinct from that of thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1269–1275. doi: 10.1172/JCI112947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Hou C., Sidiropoulos D., Stock J. B., Jakobs K. H., Gierschik P. Stimulation of phospholipase C by guanine-nucleotide-binding protein beta gamma subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. E., Brass L. F., Manning D. R. Thrombin and phorbol esters cause the selective phosphorylation of a G protein other than Gi in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13298–13305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Feinman R. D., Detwiler T. C., Smith J. B., Ingerman C. M., Silver M. J. Prostaglandin endoperoxides and thromboxane A2 can induce platelet aggregation in the absence of secretion. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):66–69. doi: 10.1038/269066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignard M., Vargaftig B. B. Synthesis of thromboxane A2 by non-aggregating dog platelets challenged with arachidonic acid or with prostaglandin H2. Prostaglandins. 1977 Aug;14(2):222–240. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignard M., Vargaftig B. Dog platelets fail to aggregate when they form aggregating substances upon stimulation with arachidonic acid. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;38(1):7–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons R. M., Meyers K. M. Acquisition and aggregation of canine blood platelets: basic mechanisms of function and differences because of breed origin. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):137–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. W., 2nd, DeJesus A. Human platelet aggregation and shape change are coupled to separate thromboxane A2-prostaglandin H2 receptors. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):H327–H334. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.2.H327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. W., 2nd Distinct platelet thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor subtypes. A radioligand binding study of human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1883–1891. doi: 10.1172/JCI114375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman A. M., Tena R. G., Kessler P. D., Weisman H. F., Schulman S. P., Blumenthal R. S., Jackson D. G., Van Dop C. Diminished beta-adrenergic receptor responsiveness and cardiac dilation in hearts of myopathic Syrian hamsters (BIO 53.58) are associated with a functional abnormality of the G stimulatory protein. Circulation. 1990 Apr;81(4):1341–1352. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.4.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse I., Mito M., Hattori A., Higuchi W., Shibata A., Ushikubi F., Okuma M., Yahata K. Defective signal transduction induced by thromboxane A2 in a patient with a mild bleeding disorder: impaired phospholipase C activation despite normal phospholipase A2 activation. Blood. 1993 Feb 15;81(4):994–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M., Sekiguchi K., Nomura H., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Further studies on the specificity of diacylglycerol for protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):598–605. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandt R., Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Evidence for two GTPases activated by thrombin in membranes of human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2370669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S., Smrcka A., Nowak L., Wu D. G., Simon M., Sternweis P. C. Antibodies to the alpha q subfamily of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunits attenuate activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by hormones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20519–20524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg A., Hall S. E., Ogletree M. L., Harris D. N., Liu E. C. Characterization of [5,6-3H]SQ 29,548 as a high affinity radioligand, binding to thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2-receptors in human platelets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):786–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Kozasa T., Smrcka A. V., Simon M. I., Rhee S. G., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Purification from Sf9 cells and characterization of recombinant Gq alpha and G11 alpha. Activation of purified phospholipase C isozymes by G alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14367–14375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M. Diversity of structure, signaling and regulation within the family of muscarinic cholinergic receptors. FASEB J. 1992 Feb 1;6(3):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Gawler D., O'Hagan S., Wilson A. Thrombin, unlike vasopressin, appears to stimulate two distinct guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2380109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Wilson A. Platelet activating factor and U44069 stimulate a GTPase activity in human platelets which is distinct from the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins, Ns and Ni. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):737–740. doi: 10.1042/bj2340737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Wong Y. H., Vu T. K., Coughlin S. R. The cloned platelet thrombin receptor couples to at least two distinct effectors to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20831–20834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. J., Dunlop P. C., Leis L. A., From A. H. Dihydropyridine agonist Bay K 8644 inhibits platelet activation by competitive antagonism of thromboxane A2-prostaglandin H2 receptor. Circ Res. 1988 Mar;62(3):494–505. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. J., Leis L. A., King R. A. Thromboxane responsiveness of dog platelets is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):578–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. J., Leis L. A., Rao G. H., White J. G. Arachidonate-induced platelet aggregation in the dog. Thromb Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. J., Rao G. H., Leis L. A., White J. G. Effect of agents that alter cyclic AMP on arachidonate-induced platelet aggregation in the dog. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):722–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler P. D., Cates A. E., Van Dop C., Feldman A. M. Decreased bioactivity of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase in hearts from cardiomyopathic Syrian hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):244–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI114147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E., Taussig R., Gilman A. G. The G226A mutant of Gs alpha highlights the requirement for dissociation of G protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1212–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mais D. E., Kochel P. J., Saussy D. L., Jr, Halushka P. V. Binding of an 125I-labeled thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor antagonist to washed canine platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mais D. E., Saussy D. L., Jr, Chaikhouni A., Kochel P. J., Knapp D. R., Hamanaka N., Halushka P. V. Pharmacologic characterization of human and canine thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptors in platelets and blood vessels: evidence for different receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Brass L. F. The role of GTP-binding proteins in platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Oct 1;66(4):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGoff M. A., Allen B. T., Der T., Sicard G. A., Santoro S. A. Mechanisms of vascular graft thrombosis: role of altered canine platelet sensitivity to thromboxane. Thromb Res. 1989 Sep 15;55(6):695–707. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A., Beiderman B., Bourne H. R. A mutation that prevents GTP-dependent activation of the alpha chain of Gs. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):712–715. doi: 10.1038/334712a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinelli T. A., Niewiarowski S., Daniel J. L., Smith J. B. Receptor-mediated effects of a PGH2 analogue (U 46619) on human platelets. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):H1035–H1043. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.5.H1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinelli T. A., Oatis J. E., Jr, Okwu A. K., Mais D. E., Mayeux P. R., Masuda A., Knapp D. R., Halushka P. V. Characterization of an 125I-labeled thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):557–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates J. A., FitzGerald G. A., Branch R. A., Jackson E. K., Knapp H. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd Clinical implications of prostaglandin and thromboxane A2 formation (1). N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 15;319(11):689–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809153191106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates J. A., FitzGerald G. A., Branch R. A., Jackson E. K., Knapp H. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd Clinical implications of prostaglandin and thromboxane A2 formation (2). N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 22;319(12):761–767. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809223191206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C. Purification of unique alpha subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) by affinity chromatography with immobilized beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18707–18712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Goldsmith P., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. The G protein coupled to the thromboxane A2 receptor in human platelets is a member of the novel Gq family. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9309–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of purified subtypes of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C beta by G protein alpha and beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9667–9674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara K., Murray R., FitzGerald G. A., Fitzgerald D. J. The response to thromboxane A2 analogues in human platelets. Discrimination of two binding sites linked to distinct effector systems. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6836–6844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Ishibashi T., Narumiya S., Okuma M. Analysis of the defective signal transduction mechanism through the platelet thromboxane A2 receptor in a patient with polycythemia vera. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jan 23;67(1):144–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Okuma M., Kanaji K., Sugiyama T., Ogorochi T., Narumiya S., Uchino H. Hemorrhagic thrombocytopathy with platelet thromboxane A2 receptor abnormality: defective signal transduction with normal binding activity. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Apr 7;57(2):158–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]