Abstract
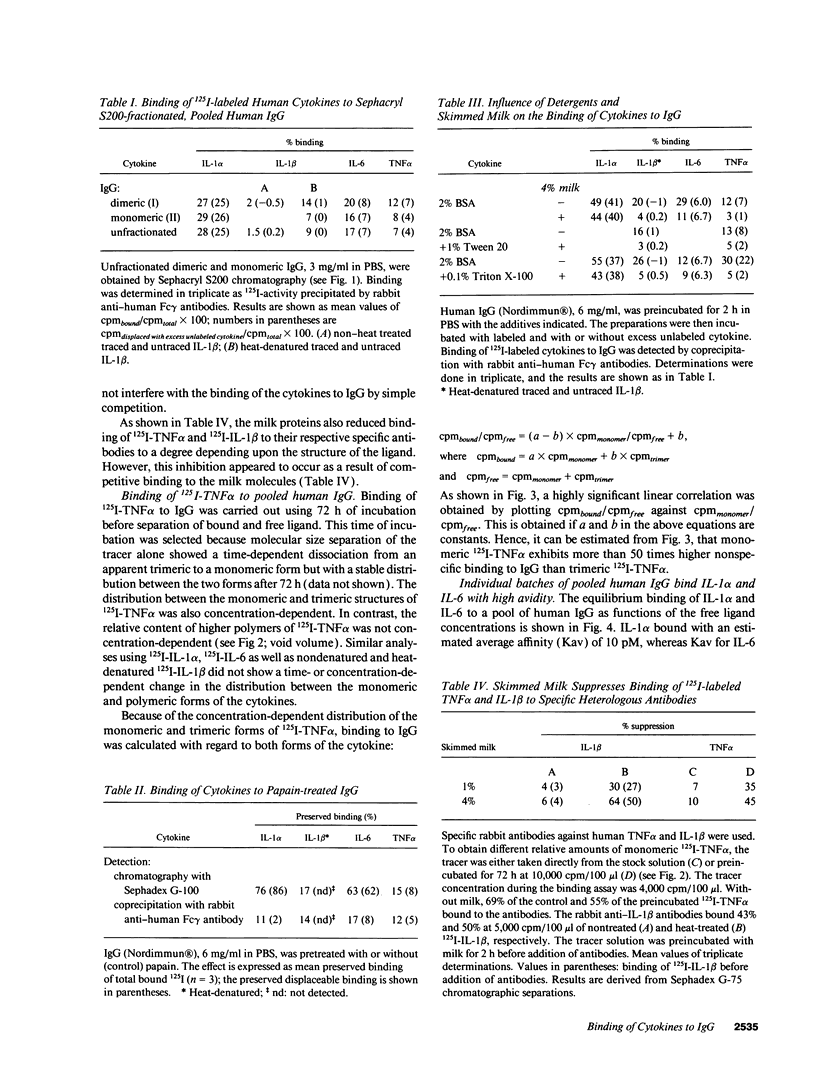
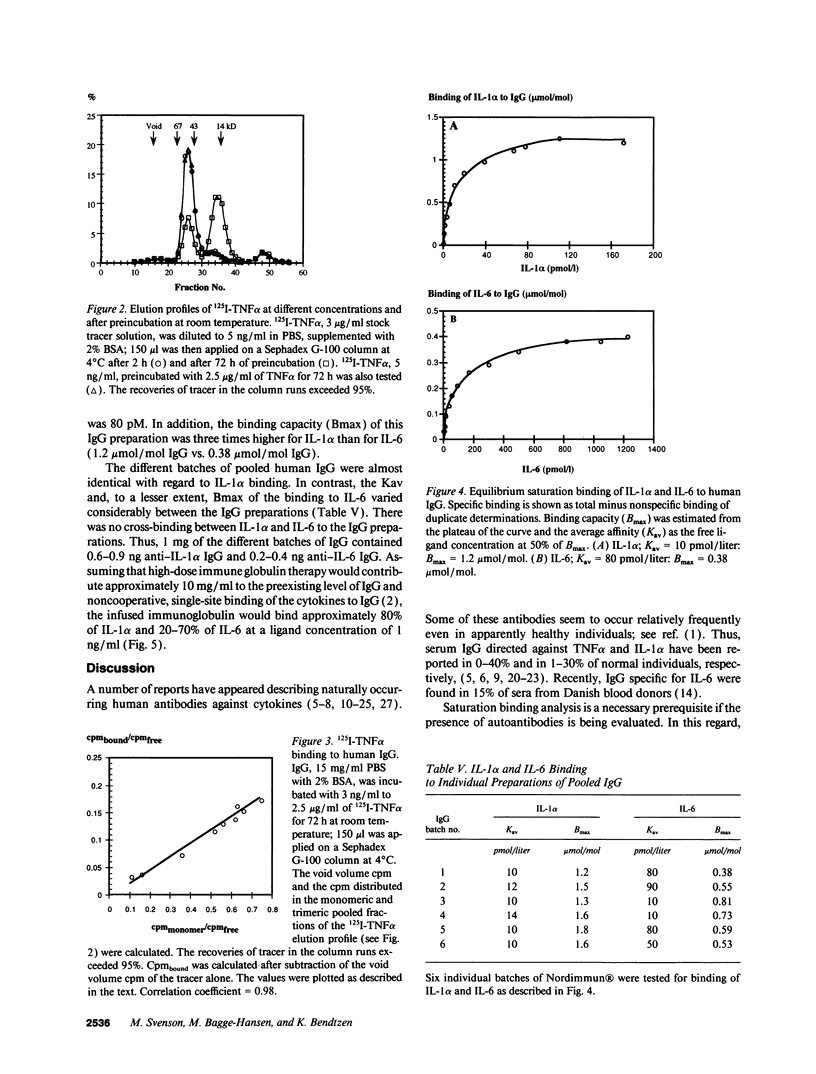
Pharmaceutically prepared IgG, pooled from sera of over 2,000 normal individuals, contained both monomeric and dimeric IgG. Each type of IgG bound 125I-labeled interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Increased binding to IgG was observed if 125I-IL-1 beta was denatured by heating to 39 degrees C. However, the binding of both nondenatured and denatured 125I-IL-1 beta was not inhibited by unlabeled IL-1 beta. In contrast, binding of 125I-IL-1 alpha, 125I-IL-6, and 125I-TNF alpha was inhibited by the corresponding unlabeled cytokine. Papain-digestion of IgG abolished binding of 125I-TNF alpha but failed to influence the displaceable binding of 125I-IL-1 alpha and 125I-IL-6. 125I-TNF alpha was a mixture of trimeric and monomeric forms, the latter being the predominant form at lower concentrations. The apparent saturability of 125I-TNF alpha was explained by a higher nonspecific binding of monomeric than of trimeric 125I-TNF alpha to IgG. The amounts of cytokine antibodies in IgG preparations would contribute approximately 2 micrograms anti-IL-1 alpha IgG and 1 microgram anti-IL-6 IgG per kg body wt during high dose immune globulin therapy. In conclusion, pharmaceutical preparations of human IgG contain specific and neutralizing, high affinity antibodies against IL-1 alpha and IL-6, but not against TNF alpha or IL-1 beta. There are significant methodological pitfalls that hamper detection of IgG autoantibodies against cytokines.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendtzen K., Svenson M., Jønsson V., Hippe E. Autoantibodies to cytokines--friends or foes? Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90068-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Vandekerckhove F. Cytokines and their interactions with other inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of sepsis and septic shock. Eur J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;21(6):559–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Hahn B. H., Saag M. S., Shaw G. M., Weigent D. A., Blalock J. E. Individuals infected with HIV possess antibodies against IL-2. Immunology. 1988 Dec;65(4):611–615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen E. C., Rezai A. R., Nakajima K., Beall G. N., Mitsuyasu R. T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Martinez-Maza O. Infection with HIV is associated with elevated IL-6 levels and production. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capper S. J., Kalinka S., Mander T. H. Specific radioimmunoassays for IL 1 alpha and IL 1 beta in plasma at physiological and acidic pH: determination of immunoreactive forms by gel filtration and radioligand binding studies. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):182–189. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90014-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso A., Bonfanti C., Colombrita D., De Francesco M., De Rango C., Foresti I., Gargiulo F., Gonzales R., Gribaudo G., Landolfo S. Natural antibodies to IFN-gamma in man and their increase during viral infection. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damas P., Ledoux D., Nys M., Vrindts Y., De Groote D., Franchimont P., Lamy M. Cytokine serum level during severe sepsis in human IL-6 as a marker of severity. Ann Surg. 1992 Apr;215(4):356–362. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199204000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Remick D. G. Sandwich ELISA for detection of picogram quantities of interleukin-8. Immunol Invest. 1991 Feb;20(1):89–97. doi: 10.3109/08820139109054928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M. Manipulating the immune system with immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 9;326(2):107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201093260206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastgate J. A., Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Capper S. J., Duff G. W. Plasma levels of interleukin-1-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1991 Aug;30(4):295–297. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/30.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figlin R. A., Itri L. M. Anti-interferon antibodies: a perspective. Semin Hematol. 1988 Jul;25(3 Suppl 3):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Svenson M., Bendtzen K. Auto-antibodies to tumour necrosis factor alpha in healthy humans and patients with inflammatory diseases and gram-negative bacterial infections. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Aug;30(2):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlbrigge R. C., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Chaplin D. D., Unanue E. R. Monoclonal antibodies to murine IL-1 alpha. Production, characterization, and inhibition of membrane-associated IL-1 activity. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2643–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Svenson M., Bendtzen K. Serum-induced suppression of interferon (IFN) activity. Lack of evidence for the presence of specific autoantibodies to IFN-alpha in normal human sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):559–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Svenson M., Diamant M., Bendtzen K. Anti-interleukin-6 antibodies in normal human serum. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):777–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Svenson M., Diamant M., Bendtzen K. High-affinity IgG autoantibodies to IL-6 in sera of normal individuals are competitive inhibitors of IL-6 in vitro. Cytokine. 1993 Jan;5(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(93)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogquist K. A., Nett M. A., Sheehan K. C., Pendleton K. D., Schreiber R. D., Chaplin D. D. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to murine IL-1 beta and demonstration of IL-1 in vivo. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1534–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Toda G., Hashimoto N., Umeda N., Miyake K., Yamanaka M., Kurokowa K. Naturally occurring anti-interferon-alpha 2a antibodies in patients with acute viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):80–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffes E. W., 3rd, Ininns E. K., Schmitz K. L., Yamamoto R. S., Dett C. A., Granger G. A. The presence of antibodies to lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in normal serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Sep;32(9):1148–1152. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesmok G., Lindsey C., Duerr M., Fournel M., Emerson T., Jr Efficacy of monoclonal antibody against human recombinant tumor necrosis factor in E. coli-challenged swine. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1197–1207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Stuart D. I., Walker N. P. Structure of tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):225–228. doi: 10.1038/338225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W. Native interleukin 1 inhibitors. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leusch H. G., Sitzler G., Markos-Pusztai S. Failure to demonstrate TNF alpha-specific autoantibodies in human sera by ELISA and western blot. J Immunol Methods. 1991 May 17;139(1):145–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90361-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mae N., Liberato D. J., Chizzonite R., Satoh H. Identification of high-affinity anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies in normal human serum as an interfering substance in a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IL-1 alpha. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991 Apr;10(1-2):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Kurlac L., Gallagher A., Hawkey C. J. High circulating concentrations of interleukin-6 in active Crohn's disease but not ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1531–1534. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Daubas P., Gresser I., Sereni D., Varet B. Patient with circulating antibodies to alpha-interferon. Lancet. 1981 Nov 28;2(8257):1227–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonen P., Gaffner R., Wingfield P. Native cytokines do not bind to uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein). FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81446-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. D., Mills K. C., Lefkowitz D. L., Lefkowitz S. S. An improved colorimetric assay for tumor necrosis factor using WEHI 164 cells cultured on novel microtiter plates. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90336-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller A., Emling F., Blohm D., Schlick E., Schollmeier K. Monoclonal antibodies to human tumor necrosis factor alpha: in vitro and in vivo application. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):162–169. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90011-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panem S., Check I. J., Henriksen D., Vilcek J. Antibodies to alpha-interferon in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. M., Nykjaer A., Christiansen B. S., Heickendorff L., Mogensen S. C., Møller B. Bioactive human recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha: an unstable dimer? Eur J Immunol. 1989 Oct;19(10):1887–1894. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C., Hansen M. B., Schyberg T., Berg K. Autoantibodies to crude human leucocyte interferon (IFN), native human IFN, recombinant human IFN-alpha 2b and human IFN-gamma in healthy blood donors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux K. H., Tankersley D. L. A view of the human idiotypic repertoire. Electron microscopic and immunologic analyses of spontaneous idiotype-anti-idiotype dimers in pooled human IgG. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1387–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saurat J. H., Schifferli J., Steiger G., Dayer J. M., Didierjean L. Anti-interleukin-1 alpha autoantibodies in humans: characterization, isotype distribution, and receptor-binding inhibition--higher frequency in Schnitzler's syndrome (urticaria and macroglobulinemia). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Aug;88(2):244–256. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90335-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld H. J., Poeschl B., Frey J. R., Loetscher H., Hunziker W., Lustig A., Zulauf M. Efficient purification of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor beta from Escherichia coli yields biologically active protein with a trimeric structure that binds to both tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3863–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunder-Plassmann G., Sedlacek P. L., Sunder-Plassmann R., Derfler K., Swoboda K., Fabrizii V., Hirschl M. M., Balcke P. Anti-interleukin-1 alpha autoantibodies in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1991 Oct;40(4):787–791. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Akama T., Okane M., Kono I., Matsui Y., Yamane K., Kashiwagi H. Interleukin-1-inhibitory IgG in sera from some patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1528–1538. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Ayabe T., Kamimura J., Kashiwagi H. Anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies in patients with rheumatic diseases and in healthy subjects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Sep;85(3):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Bagge Hansen M., Bendtzen K. Distribution and characterization of autoantibodies to interleukin 1 alpha in normal human sera. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):695–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Hansen M. B., Kayser L., Rasmussen A. K., Reimert C. M., Bendtzen K. Effects of human anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies on receptor binding and biological activities of IL-1. Cytokine. 1992 Mar;4(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90047-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Poulsen L. K., Fomsgaard A., Bendtzen K. IgG autoantibodies against interleukin 1 alpha in sera of normal individuals. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Apr;29(4):489–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Preston M. S., Finlayson J. S. Immunoglobulin G dimer: an idiotype-anti-idiotype complex. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jan;25(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond L. M., Reese M. J. Immunochemical characterization of human antibodies to lymphoblastoid interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Dec;86(3):514–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb02962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trown P. W., Kramer M. J., Dennin R. A., Jr, Connell E. V., Palleroni A. V., Quesada J., Gutterman J. U. Antibodies to human leucocyte interferons in cancer patients. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Treuner J., Flehmig B., Joester K. E., Niethammer D. Interferon-neutralizing antibodies in a patient treated with human fibroblast interferon. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):496–497. doi: 10.1038/289496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. T., Unanue E. R. The costimulatory function of antigen-presenting cells. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


