Abstract
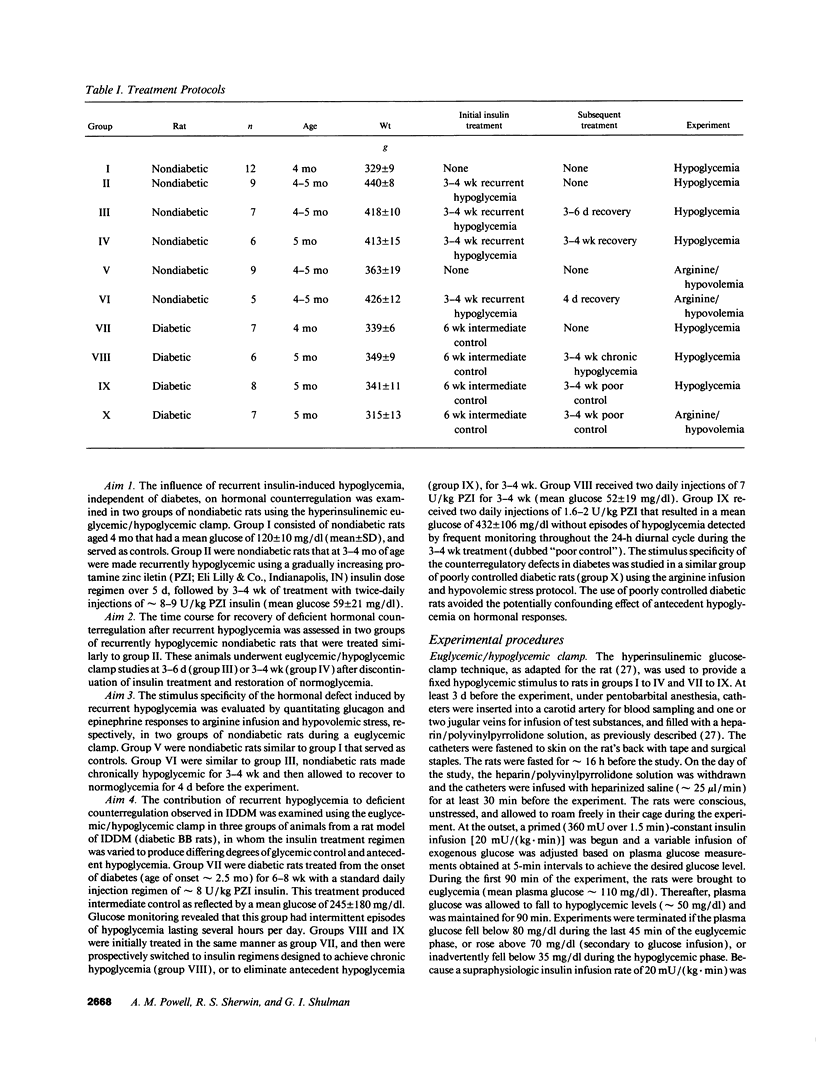
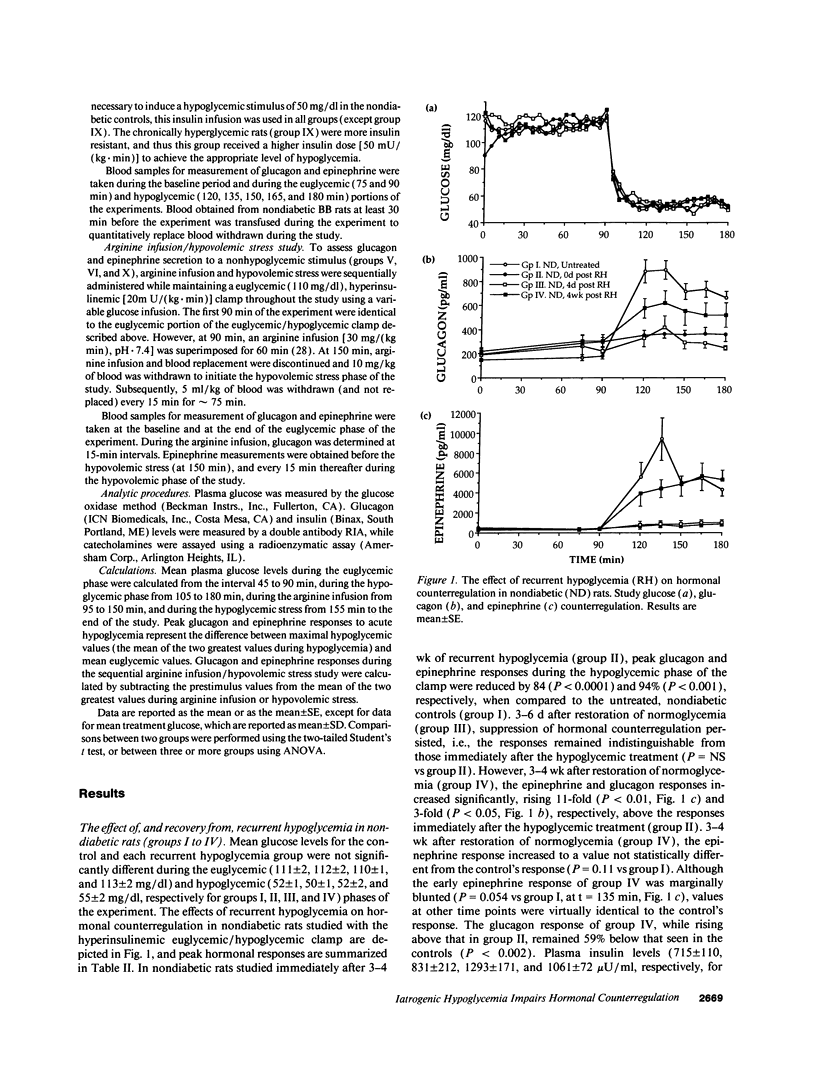
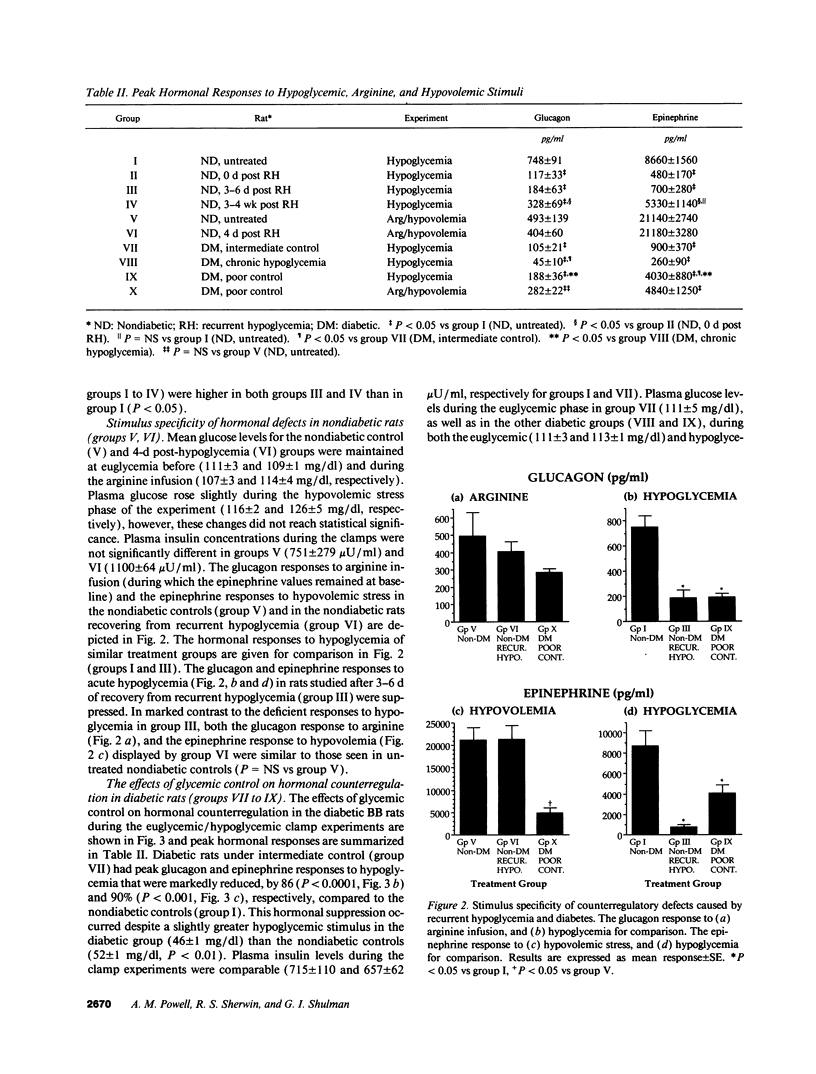
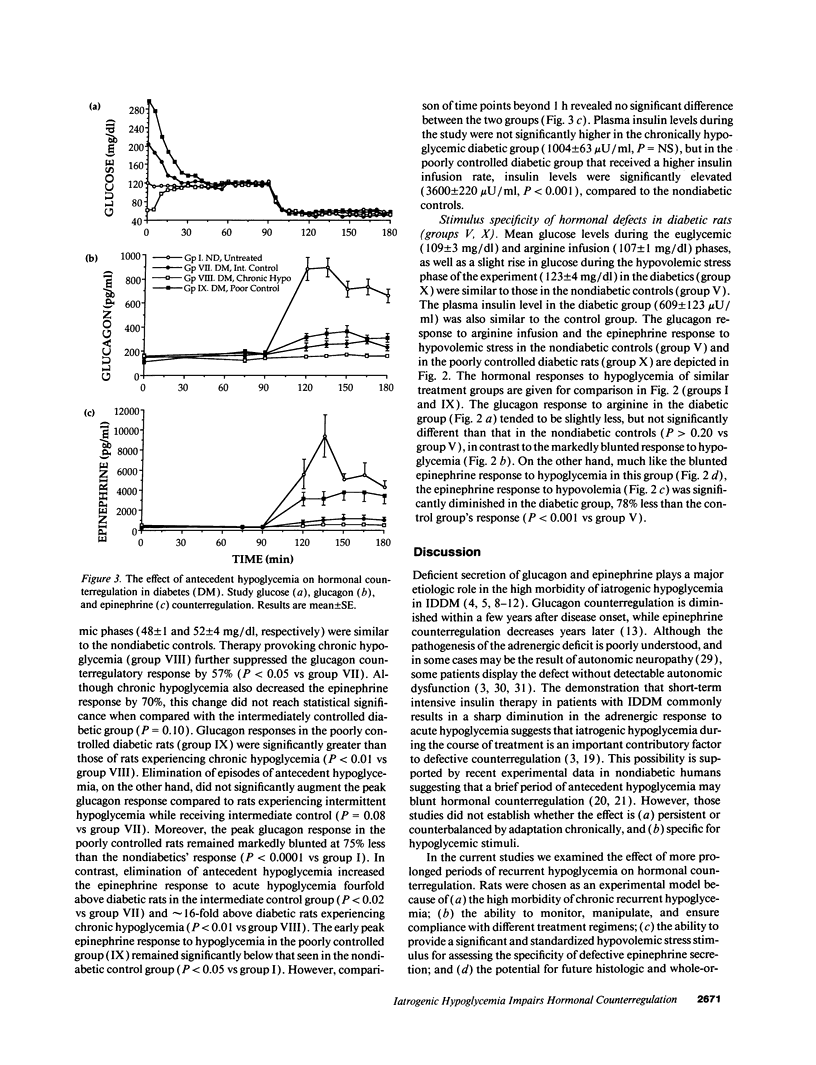
To evaluate the roles of iatrogenic hypoglycemia and diabetes per se in the pathogenesis of defective hormonal counterregulation against hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), nondiabetic, and spontaneously diabetic BB/Wor rats were studied using a euglycemic/hypoglycemic clamp. In nondiabetic rats, recurrent (4 wk) insulin-induced hypoglycemia (mean daily glucose, MDG, 59 mg/dl) dramatically reduced glucagon and epinephrine responses by 84 and 94%, respectively, to a standardized glucose fall from 110 to 50 mg/dl. These deficits persisted for > 4 d after restoring normoglycemia, and were specific for hypoglycemia, with normal glucagon and epinephrine responses to arginine and hypovolemia, respectively. After 4 wk of normoglycemia, hormonal counterregulation increased, with the epinephrine, but not the glucagon response reaching control values. In diabetic BB rats (MDG 245 mg/dl with intermittent hypoglycemia), glucagon and epinephrine counterregulation were reduced by 86 and 90%, respectively. Chronic iatrogenic hypoglycemia (MDG 52 mg/dl) further suppressed counterregulation. Prospective elimination of hypoglycemia (MDG 432 mg/dl) improved, but did not normalize hormonal counterregulation. In diabetic rats, the glucagon defect appeared to be specific for hypoglycemia, whereas deficient epinephrine secretion also occurred during hypovolemia. We concluded that both recurrent hypoglycemia and the diabetic state independently lead to defective hormonal counterregulation. These data suggest that in IDDM iatrogenic hypoglycemia magnifies preexisting counterregulatory defects, thereby increasing the risk of severe hypoglycemia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiel S. A., Sherwin R. S., Simonson D. C., Tamborlane W. V. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on glycemic thresholds for counterregulatory hormone release. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):901–907. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiel S. A., Tamborlane W. V., Saccà L., Sherwin R. S. Hypoglycemia and glucose counterregulation in normal and insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Feb;4(1):71–89. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiel S. A., Tamborlane W. V., Simonson D. C., Sherwin R. S. Defective glucose counterregulation after strict glycemic control of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 28;316(22):1376–1383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705283162205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiel S. Glucose counter-regulation in health and disease: current concepts in hypoglycaemia recognition and response. Q J Med. 1991 Sep;80(293):707–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., De Feo P., Perriello G., De Cosmo S., Compagnucci P., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Unger R. H. Mechanisms of glucagon secretion during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Role of the beta cell and arterial hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):917–922. doi: 10.1172/JCI111315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):134–141. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Important role of adrenergic mechanisms in acute glucose counterregulation following insulin-induced hypoglycemia in type I diabetes. Evidence for an effect mediated by beta-adrenoreceptors. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):641–647. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Binder C., Bolli G. B., Cherrington A. D., Gale E. A., Gerich J. E., Sherwin R. S. Hypoglycemia in IDDM. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1193–1199. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Iatrogenic hypoglycemia as a cause of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in IDDM. A vicious cycle. Diabetes. 1992 Mar;41(3):255–260. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.3.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Shah S. D. Roles of glucagon and epinephrine in hypoglycemic and nonhypoglycemic glucose counterregulation in humans. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 1):E198–E205. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.2.E198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. R., Shamoon H. Counterregulatory adaptation to recurrent hypoglycemia in normal humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Nov;73(5):995–1001. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-5-995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. N., Dobbins R., Tarumi C., Colburn C., Neal D., Cherrington A. D. Effects of differing insulin levels on response to equivalent hypoglycemia in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):E688–E695. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.4.E688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Bolli G., Perriello G., De Cosmo S., Compagnucci P., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Gerich J. E., Motolese M., Brunetti P. The adrenergic contribution to glucose counterregulation in type I diabetes mellitus. Dependency on A-cell function and mediation through beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Diabetes. 1983 Oct;32(10):887–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. P., Hallarman L., Starick-Zych K., Jones T. W., Connolly-Howard M., Tamborlane W. V., Sherwin R. S. Suppression of counterregulatory hormone response to hypoglycemia by insulin per se. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jun;72(6):1388–1390. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Bohannon N. V., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of acute insulin withdrawal and administration on plasma glucagon responses to intravenous arginine in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1976 Oct;25(10):955–960. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.10.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Mokan M., Veneman T., Korytkowski M., Mitrakou A. Hypoglycemia unawareness. Endocr Rev. 1991 Nov;12(4):356–371. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-4-356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller S. R., Cryer P. E. Reduced neuroendocrine and symptomatic responses to subsequent hypoglycemia after 1 episode of hypoglycemia in nondiabetic humans. Diabetes. 1991 Feb;40(2):223–226. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch B. R., Shamoon H. Defective epinephrine and growth hormone responses in type I diabetes are stimulus specific. Diabetes. 1987 Jan;36(1):20–26. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junod A., Lambert A. E., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: relationship of dose to metabolic response. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2129–2139. doi: 10.1172/JCI106180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamori R., Shichiri M., Kikuchi M., Yamasaki Y., Abe H. Perfect normalization of excessive glucagon responses to intravenous arginine in human diabetes mellitus with the artificial beta-cell. Diabetes. 1980 Sep;29(9):762–765. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.9.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Reza M., Smith N., Leatherdale B. A. Importance of insulin in subjective, cognitive, and hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in patients with IDDM. Diabetes. 1991 Aug;40(8):1057–1062. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.8.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuku S. F., Jaspan J. B., Emmanouel D. S., Katz A. I., Rubenstein A. H. Plasma glucagon, insulin and glucose responses to intravenous arginine infusion in the rat. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Mar;10(2):99–100. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Moberg E., Kollind M., Lins P. E., Adamson U. A high concentration of circulating insulin suppresses the glucagon response to hypoglycemia in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Nov;73(5):1123–1128. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-5-1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetopoulos J., Valiquette N., Madura E., Cvet D. The onset and progression of pancreatic insulitis in the overt, spontaneously diabetic, young adult BB rat studied by pancreatic biopsy. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):33–36. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Nakhooda A. F., Poussier P., Sima A. A. The diabetic syndrome of the 'BB' Wistar rat: possible relevance to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes in man. Diabetologia. 1982 Apr;22(4):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00281296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Wei C. N., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat (the "BB" rat). Studies prior to and during development of the overt syndrome. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00429781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Wheatley T., Malaisse-Lagae F., Orci L. Elevated portal and peripheral blood concentration of immunoreactive somatostatin in spontaneously diabetic (BBL) Wistar rats: suppression with insulin. Diabetes. 1980 Sep;29(9):757–761. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.9.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Bergenstal R., Pons G., Schneider M., Jaspan J., Rubenstein A. Relation of counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in type I diabetics. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1106–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp D. A., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Role of epinephrine-mediated beta-adrenergic mechanisms in hypoglycemic glucose counterregulation and posthypoglycemic hyperglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):315–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI110455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Smith D., Shulman G. I., Papachristou D., DeFronzo R. A. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1510–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI112981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. E., Owens D. R., Hayes T. M., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Unawareness of hypoglycaemia and inadequate hypoglycaemic counterregulation: no causal relation with diabetic autonomic neuropathy. BMJ. 1990 Oct 6;301(6755):783–787. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6755.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago J. V., White N. H., Skor D. A., Levandoski L. A., Bier D. M., Cryer P. E. Defective glucose counterregulation limits intensive therapy of diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 1):E215–E220. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.2.E215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson D. C., Tamborlane W. V., DeFronzo R. A., Sherwin R. S. Intensive insulin therapy reduces counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):184–190. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum G. S., Colle E., Wanamaker L., Gurd W., Goldman H., Seemayer T. A. Dynamic time-course studies of the spontaneously diabetic BB Wistar rat. II. Insulin-, glucagon-, and somatostatin-reactive cells in the pancreas. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):1880–1887. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-1880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Meticulous control of diabetes: benefits, risks, and precautions. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):479–483. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R., Bone A. J., Cooke A., Baird J. D. Distinct macrophage subpopulations in pancreas of prediabetic BB/E rats. Possible role for macrophages in pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1301–1304. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. H., Skor D. A., Cryer P. E., Levandoski L. A., Bier D. M., Santiago J. V. Identification of type I diabetic patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia during intensive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 3;308(9):485–491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303033080903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom B., Simonson D. C. Glycemic control and neuropsychologic function during hypoglycemia in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 15;112(12):904–912. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-12-904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



