Abstract
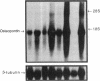
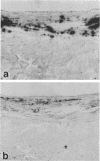
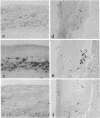
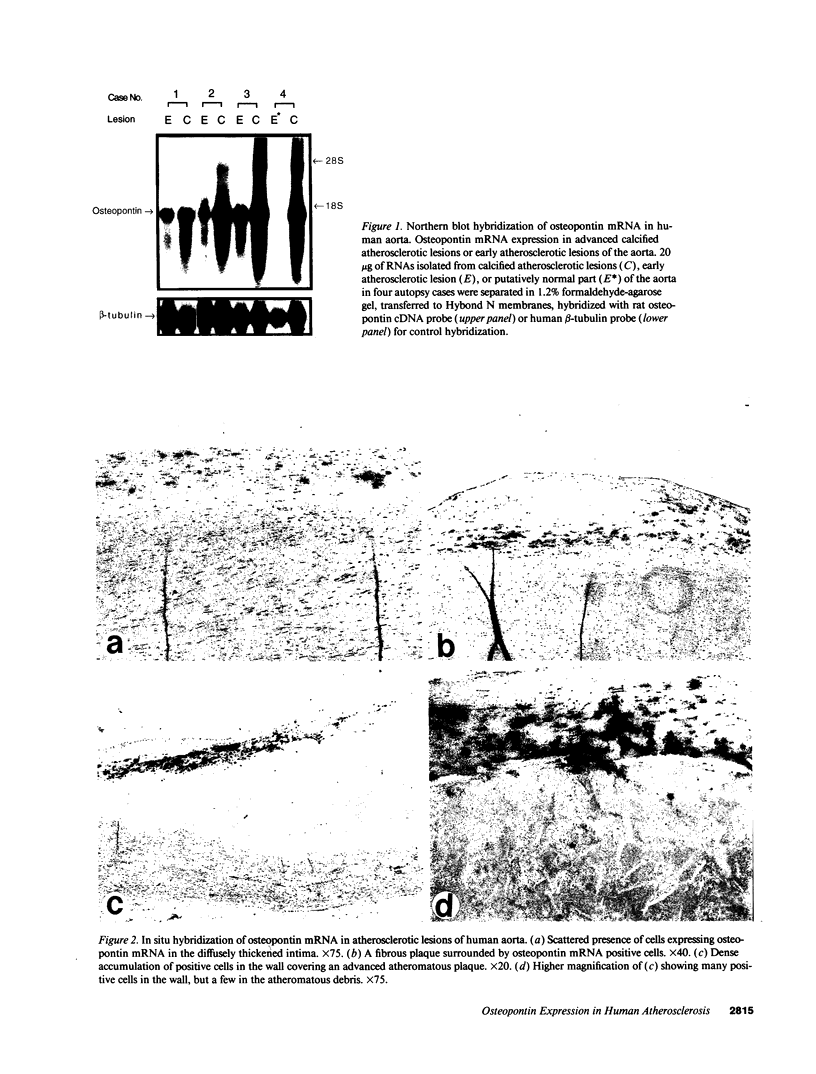
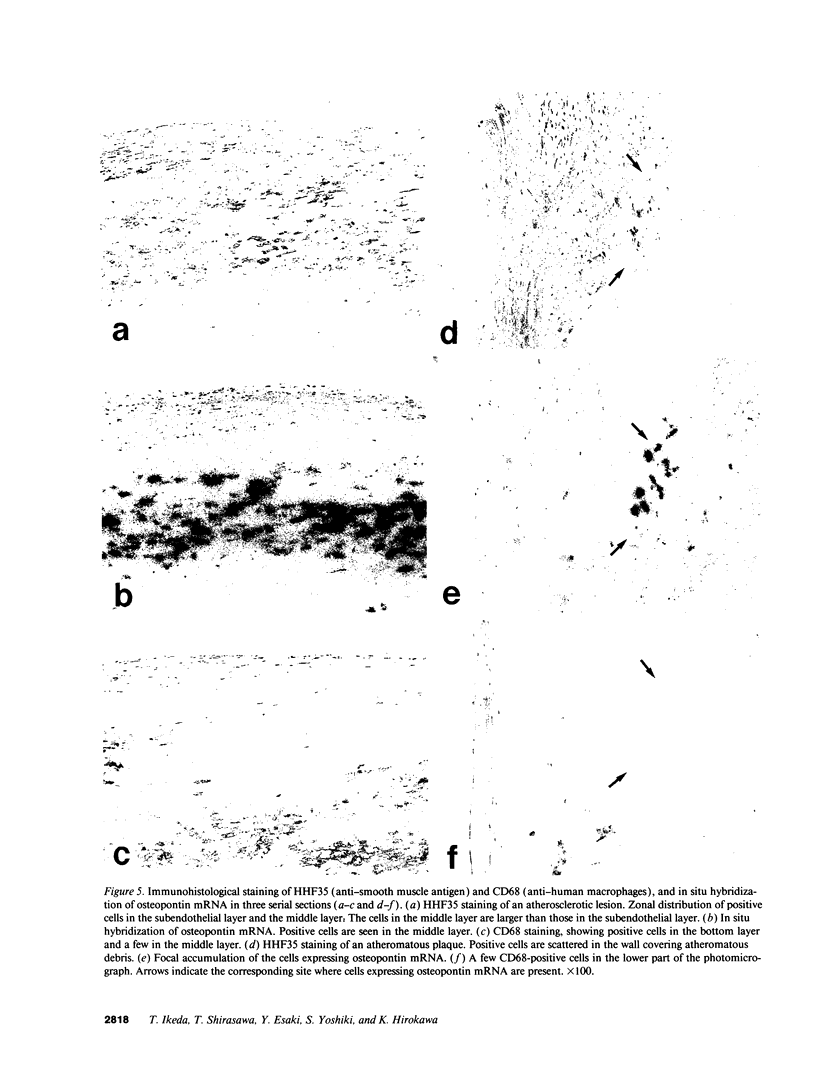
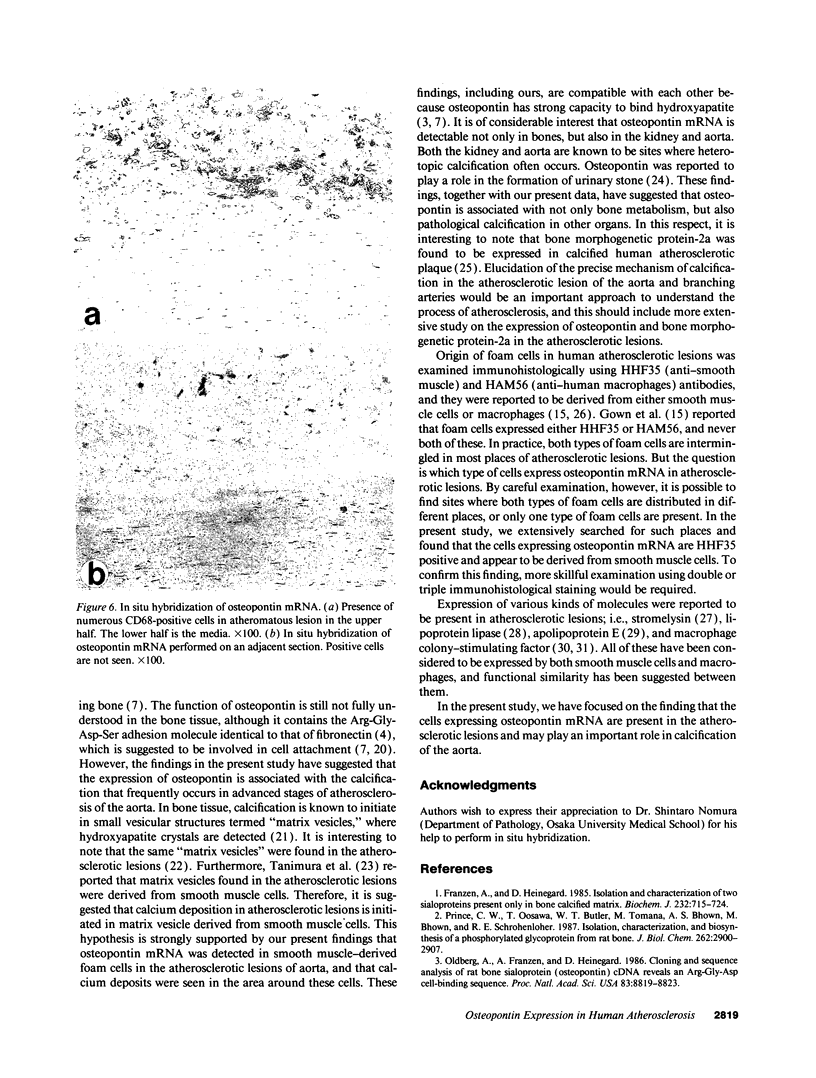
Osteopontin is a phosphorylated, sialic acid-rich, noncollagenous bone matrix protein containing the Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser amino acid sequence responsible for cell adhesion. The protein strongly binds to hydroxyapatite and play an important role in calcification. Expression of osteopontin mRNA was analyzed in human aortic atherosclerotic lesion by Northern blot hybridization, as well as by in situ hybridization. The expression of osteopontin mRNA was detected in 24 out of 25 samples of aorta obtained from 17 autopsy cases, but not in one normal aortic sample. The magnitude of expression was proportional to the stage of atherosclerosis. In situ hybridization revealed that the cells expressing osteopontin mRNA were detected in the wall surrounding atheroma and closely associated with calcification. They were morphologically identified as foam cells and immunohistologically positive with HHF35, appearing to be derived from smooth muscle cells. These findings have suggested that smooth muscle cell-derived foam cells express osteopontin mRNA and play an important role in calcification of the atherosclerotic lesions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boström K., Watson K. E., Horn S., Wortham C., Herman I. M., Demer L. L. Bone morphogenetic protein expression in human atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1800–1809. doi: 10.1172/JCI116391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Berse B., Van de Water L., Papadopoulos-Sergiou A., Perruzzi C. A., Manseau E. J., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Expression and distribution of osteopontin in human tissues: widespread association with luminal epithelial surfaces. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1169–1180. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T. The nature and significance of osteopontin. Connect Tissue Res. 1989;23(2-3):123–136. doi: 10.3109/03008208909002412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton S. K., Underwood R., Hayes L., Sherman M. L., Kufe D. W., Libby P. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene expression in vascular cells and in experimental and human atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):301–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig A. M., Smith J. H., Denhardt D. T. Osteopontin, a transformation-associated cell adhesion phosphoprotein, is induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in mouse epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9682–9689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. W., Termine J. D. Noncollagenous proteins influencing the local mechanisms of calcification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985 Nov;(200):362–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Heinegård D. Isolation and characterization of two sialoproteins present only in bone calcified matrix. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):715–724. doi: 10.1042/bj2320715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachelli C., Bae N., Lombardi D., Majesky M., Schwartz S. Molecular cloning and characterization of 2B7, a rat mRNA which distinguishes smooth muscle cell phenotypes in vitro and is identical to osteopontin (secreted phosphoprotein I, 2aR). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 14;177(2):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91870-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney A. M., Wakeley P. R., Davies M. J., Foster K., Hembry R., Murphy G., Humphries S. Localization of stromelysin gene expression in atherosclerotic plaques by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8154–8158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Nomura S., Yamaguchi A., Suda T., Yoshiki S. In situ hybridization of bone matrix proteins in undecalcified adult rat bone sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Aug;40(8):1079–1088. doi: 10.1177/40.8.1619274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuda S., Boyd H. C., Fligner C., Ross R., Gown A. M. Human atherosclerosis. III. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cell composition of lesions of young adults. Am J Pathol. 1992 Apr;140(4):907–914. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Bauer D. M., Barr P. J. The cDNA and derived amino acid sequence for human osteopontin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3306–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. M. Calcification of matrix vesicles in human aortic valve and aortic media. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohri K., Suzuki Y., Yoshida K., Yamamoto K., Amasaki N., Yamate T., Umekawa T., Iguchi M., Sinohara H., Kurita T. Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding urinary stone protein, which is identical to osteopontin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):859–864. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90669-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark M. P., Prince C. W., Oosawa T., Gay S., Bronckers A. L., Butler W. T. Immunohistochemical demonstration of a 44-KD phosphoprotein in developing rat bones. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Jul;35(7):707–715. doi: 10.1177/35.7.3295029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Wills A. J., Edwards D. R., Heath J. K., Hogan B. L. Developmental expression of 2ar (osteopontin) and SPARC (osteonectin) RNA as revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):441–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Franzén A., Heinegård D. Cloning and sequence analysis of rat bone sialoprotein (osteopontin) cDNA reveals an Arg-Gly-Asp cell-binding sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince C. W., Oosawa T., Butler W. T., Tomana M., Bhown A. S., Bhown M., Schrohenloher R. E. Isolation, characterization, and biosynthesis of a phosphorylated glycoprotein from rat bone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2900–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinholt F. P., Hultenby K., Oldberg A., Heinegård D. Osteopontin--a possible anchor of osteoclasts to bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4473–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Ylä-Herttuala S., Lipton B. A., Ord V. A., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA and protein in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbits and humans. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):291–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon R. N., Underwood R., Doyle M. V., Wang A., Libby P. Increased apolipoprotein E and c-fms gene expression without elevated interleukin 1 or 6 mRNA levels indicates selective activation of macrophage functions in advanced human atheroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. H., Denhardt D. T. Molecular cloning of a tumor promoter-inducible mRNA found in JB6 mouse epidermal cells: induction is stable at high, but not at low, cell densities. J Cell Biochem. 1987 May;34(1):13–22. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240340103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimura A., McGregor D. H., Anderson H. C. Matrix vesicles in atherosclerotic calcification. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Feb;172(2):173–177. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb M., Shinar D., Rodan G. A. Different pattern of alkaline phosphatase, osteopontin, and osteocalcin expression in developing rat bone visualized by in situ hybridization. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Aug;5(8):831–842. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Lipton B. A., Rosenfeld M. E., Goldberg I. J., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Macrophages and smooth muscle cells express lipoprotein lipase in human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10143–10147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K., Buenaga R., Rodan G. A. Tissue specificity and developmental expression of rat osteopontin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]