Abstract
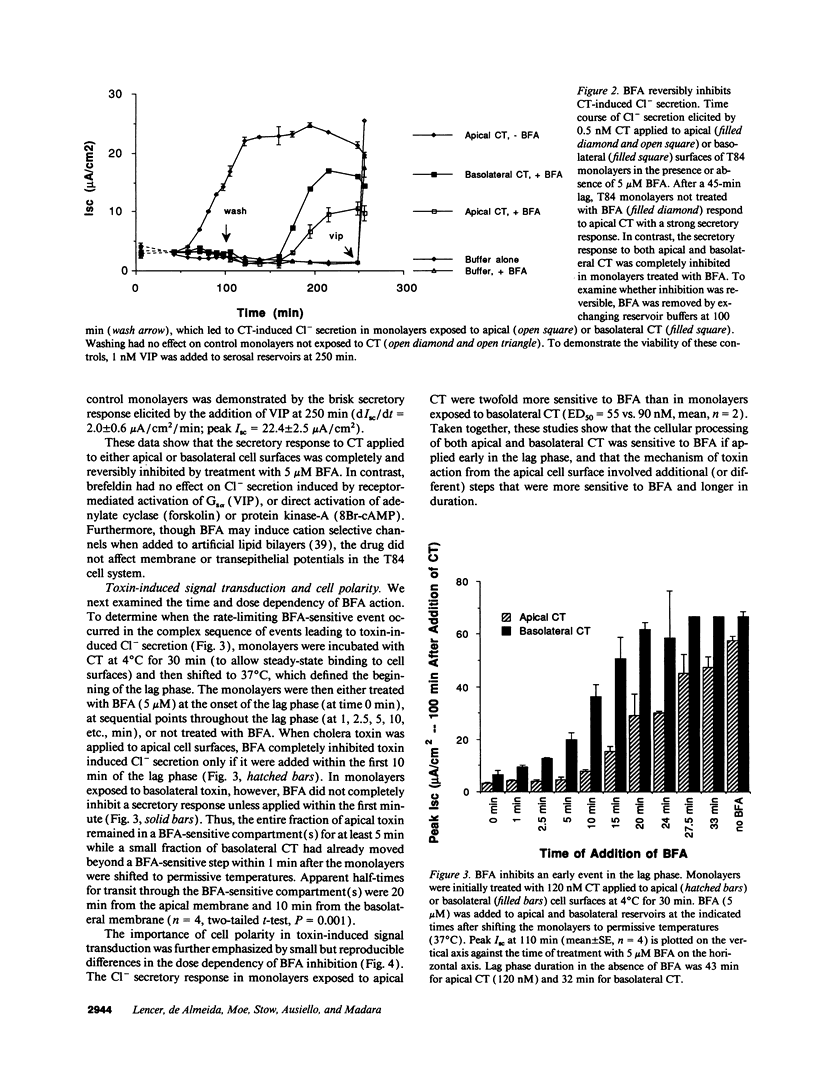
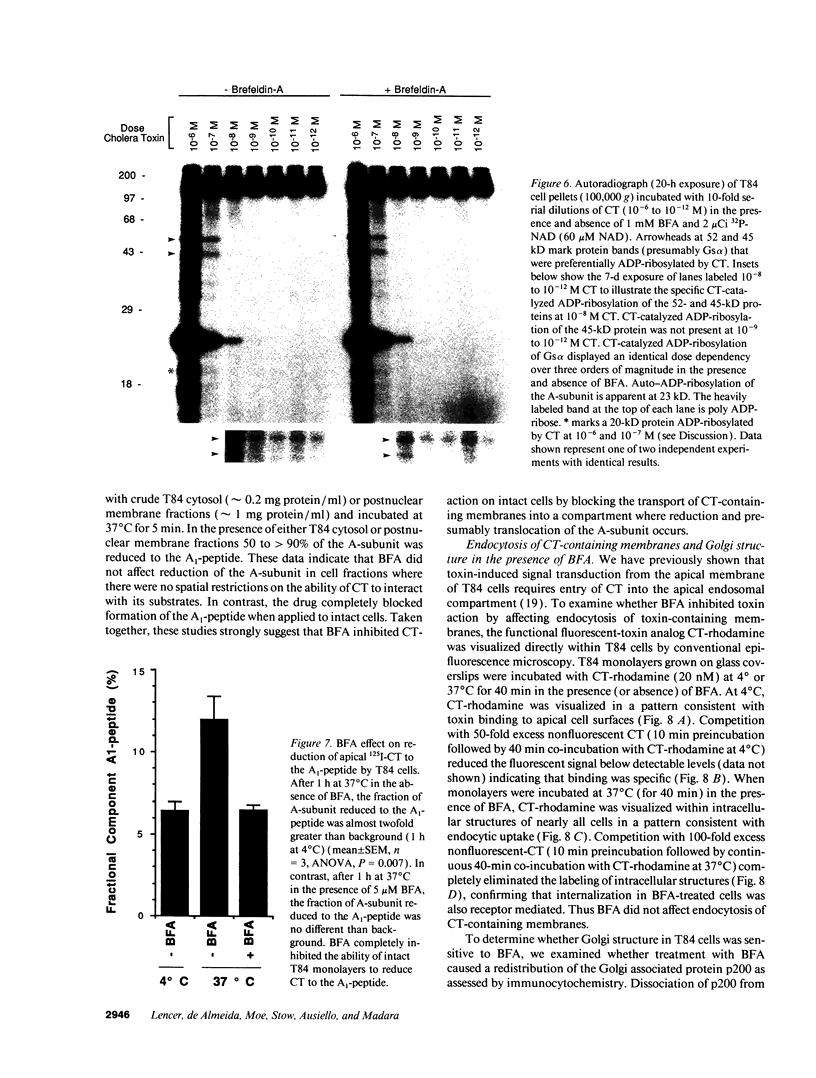
The effect of brefeldin-A (BFA), a reversible inhibitor of vesicular transport, on cholera toxin (CT)-induced Cl- secretion (Isc) was examined in the polarized human intestinal cell line, T84. Pretreatment of T84 monolayers with 5 microM BFA reversibly inhibited Isc in response to apical or basolateral addition of 120 nM CT (2.4 +/- 0.5 vs. 68 +/- 3 microA/cm2, n = 5). In contrast, BFA did not inhibit Isc responses to the cAMP agonist VIP (63 +/- 7 microA/cm2). BFA had no effect on cell surface binding and endocytosis of a functional fluorescent CT analog or on the dose dependency of CT induced 32P-NAD ribosylation of Gs alpha in vitro. In contrast, BFA completely inhibited (> 95%) the ability of T84 cells to reduce CT to the enzymatically active A1-peptide. BFA had to be added within the first 10 min of CT exposure to inhibit CT-elicited Isc. The early BFA-sensitive step occurred before a temperature-sensitive step essential for apical CT action. These studies show that sequential steps are required for a biological response to apical CT: (a) binding to cell surfaces and rapid endocytosis; (b) early, BFA-sensitive vesicular transport essential for reduction of the A1-peptide; and (c) subsequent temperature-sensitive translocation of a signal (the A1-peptide or possibly ADP-ribose-Gs alpha) to the basolateral domain.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Ullrich S. J., Appella E., Fuchs S. Inhibition by brefeldin A of presentation of exogenous protein antigens to MHC class II-restricted T cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):63–66. doi: 10.1038/346063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Kahn R. A., Schwaninger R. ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13053–13061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto J., Jodal M., Tuttle R., Lundgren O. On the role of intramural nerves in the pathogenesis of cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981 Apr;16(3):377–384. doi: 10.3109/00365528109181984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Madara J. L. Established intestinal cell lines as model systems for electrolyte transport studies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:354–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92082-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez P., Velasco G., Barros F., Lazo P. S. Intestinal brush border membranes contain regulatory subunits of adenylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Guanine nucleotides modulate the effects of brefeldin A in semipermeable cells: regulation of the association of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):579–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H. Internalization and degradation of cholera toxin by cultured cells: relationship to toxin action. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):860–865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin: studies on the lag period. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01875377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Yokota S., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18545–18552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):352–354. doi: 10.1038/360352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Whitney J. A., Mellman I. Selective inhibition of transcytosis by brefeldin A in MDCK cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):617–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Fouque F., Desbuquois B. Activation of rat liver adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin requires toxin internalization and processing in endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12858–12865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph K. C., Stieber A., Gonatas N. K. Endocytosis of cholera toxin in GERL-like structures of murine neuroblastoma cells pretreated with GM1 ganglioside. Cholera toxin internalization into Neuroblastoma GERL. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):543–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Randazzo P., Serafini T., Weiss O., Rulka C., Clark J., Amherdt M., Roller P., Orci L., Rothman J. E. The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is a critical determinant of ARF activities and is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13039–13046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaoutzani P., Parkos C. A., Delp-Archer C., Madara J. L. Isolation of plasma membrane fractions from the intestinal epithelial model T84. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1327–C1335. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Hagmann J., Fishman P. H., Chang P. P., Moss J. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin on intact cells. Generation of A1 peptide and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12148–12152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktistakis N. T., Linder M. E., Roth M. G. Action of brefeldin A blocked by activation of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G protein. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):344–346. doi: 10.1038/356344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktistakis N. T., Roth M. G., Bloom G. S. PtK1 cells contain a nondiffusible, dominant factor that makes the Golgi apparatus resistant to brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1009–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Sambuy Y., Mostov K., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Vectorial targeting of an endogenous apical membrane sialoglycoprotein and uvomorulin in MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1533–1539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lencer W. I., Chu S. H., Walker W. A. Differential binding kinetics of cholera toxin to intestinal microvillus membrane during development. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3126–3130. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3126-3130.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lencer W. I., Delp C., Neutra M. R., Madara J. L. Mechanism of cholera toxin action on a polarized human intestinal epithelial cell line: role of vesicular traffic. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1197–1209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard J. M., Kahn R. A., Stahl P. D. Evidence for ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) as a regulator of in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13047–13052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Glickman J., Donaldson J. G., Robbins J., Kreis T. E., Seamon K. B., Sheetz M. P., Klausner R. D. Forskolin inhibits and reverses the effects of brefeldin A on Golgi morphology by a cAMP-independent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):567–577. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom D., van Heyningen S. The activation of rabbit intestinal adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. H., Tang B. L., Wong S. H., Hong W. Selective inhibition of protein targeting to the apical domain of MDCK cells by brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):51–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. H., Wong S. H., Tang B. L., Tan P., Subramaniam V. N., Hong W. Inhibition by brefeldin A of protein secretion from the apical cell surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17729–17732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Roth J., Robert A., Orci L. Non-coated membrane invaginations are involved in binding and internalization of cholera and tetanus toxins. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):651–653. doi: 10.1038/296651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Ammann E., Biber J., Hopfer U. The surface membrane of the small intestinal epithelial cell. I. Localization of adenyl cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambiar M. P., Oda T., Chen C., Kuwazuru Y., Wu H. C. Involvement of the Golgi region in the intracellular trafficking of cholera toxin. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Feb;154(2):222–228. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narula N., McMorrow I., Plopper G., Doherty J., Matlin K. S., Burke B., Stow J. L. Identification of a 200-kD, brefeldin-sensitive protein on Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):27–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchtern J. G., Biddison W. E., Klausner R. D. Class II MHC molecules can use the endogenous pathway of antigen presentation. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):74–76. doi: 10.1038/343074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Tagaya M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D., Rothman J. E. Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non-clathrin-coated buds on Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1183–1195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi P. A., Curran P. K., Fishman P. H. Brefeldin A blocks the response of cultured cells to cholera toxin. Implications for intracellular trafficking in toxin action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12010–12016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Multiple targets for brefeldin A. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):449–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M. Toxin entry: how reversible is the secretory pathway? Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):183–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90230-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., LoSpalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Localization of cholera toxin in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):617–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Ochoa L. G. Role of prostaglandins and cAMP in the secretory effects of cholera toxin. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):857–859. doi: 10.1126/science.2549637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimplikar S. W., Simons K. Regulation of apical transport in epithelial cells by a Gs class of heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):456–458. doi: 10.1038/362456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Perturbation of the morphology of the trans-Golgi network following Brefeldin A treatment: redistribution of a TGN-specific integral membrane protein, TGN38. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):85–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Ullrich S., Kahn R. A., Wollheim C. B. Redistribution of ADP-ribosylation factor during stimulation of permeabilized cells with GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):639–644. doi: 10.1042/bj2750639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi H. O., Ludwig D. S., Mercer K. L., Schoolnik G. K., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of cholera toxin penetrating a lipid membrane. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1272–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.3344432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S., Kreis T. E. Recruitment of coat proteins onto Golgi membranes in intact and permeabilized cells: effects of brefeldin A and G protein activators. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90124-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma T. K., Pronk S. E., Kalk K. H., Wartna E. S., van Zanten B. A., Witholt B., Hol W. G. Crystal structure of a cholera toxin-related heat-labile enterotoxin from E. coli. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):371–377. doi: 10.1038/351371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel S., Blumenthal R., Fishman P. H., Handler J. S. Gangliosides do not move from apical to basolateral plasma membrane in cultured epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 5;821(2):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., van Kerkhof P., van Meer G., Rijnboutt S., Stoorvogel W. Differential effects of brefeldin A on transport of secretory and lysosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2341–2347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. C., Kahn R. A., Melançon P. Two distinct members of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTP-binding proteins regulate cell-free intra-Golgi transport. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90534-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Moss J., Vaughan M. Enhancement of choleragen ADP-ribosyltransferase activities by guanyl nucleotides and a 19-kDa membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5139–5142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Bramhall J. S. Photolabelling of cholera toxin subunits during membrane penetration. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):319–321. doi: 10.1038/289319a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. A., Park J. E., Brown W. J. Brefeldin A causes a microtubule-mediated fusion of the trans-Golgi network and early endosomes. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Chen C. C., Zhang M. S., Wu H. C. Disruption of the Golgi apparatus by brefeldin A inhibits the cytotoxicity of ricin, modeccin, and Pseudomonas toxin. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90056-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zizi M., Fisher R. S., Grillo F. G. Formation of cation channels in planar lipid bilayers by brefeldin A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18443–18445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Echten G., Iber H., Stotz H., Takatsuki A., Sandhoff K. Uncoupling of ganglioside biosynthesis by Brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






