Abstract
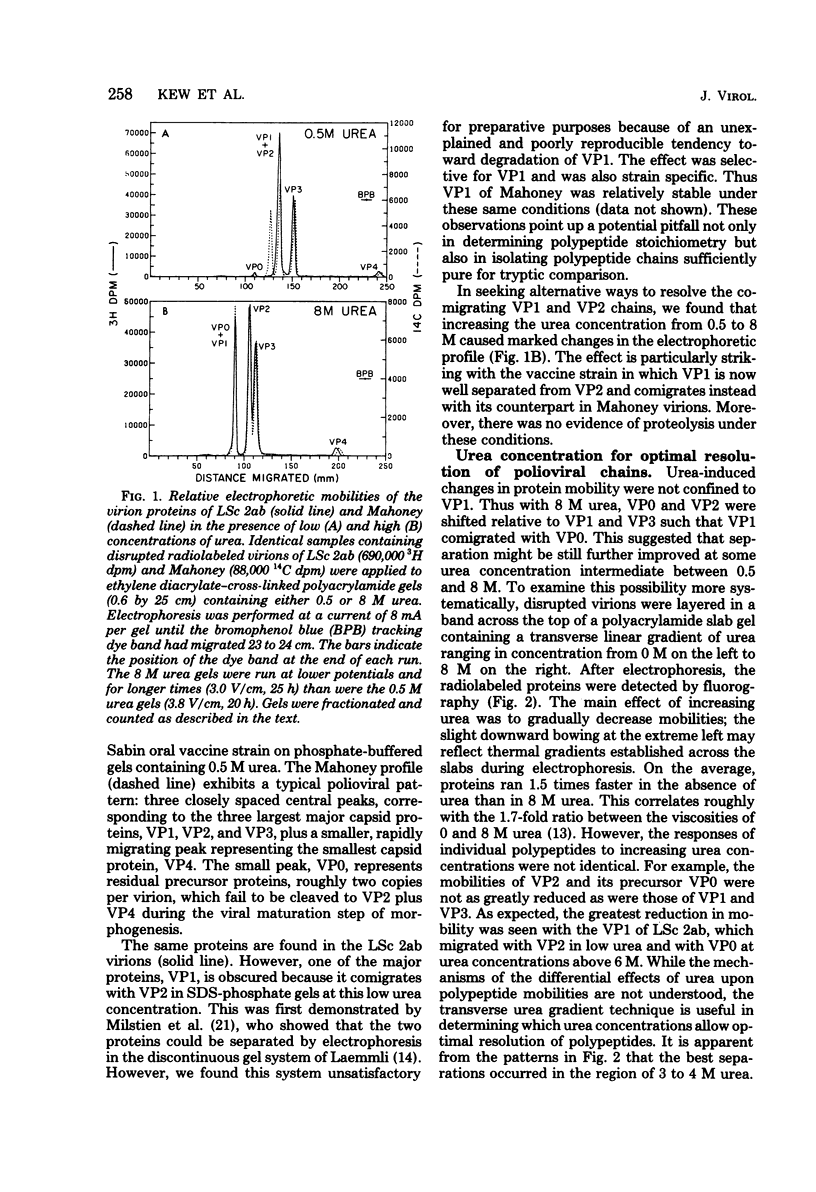
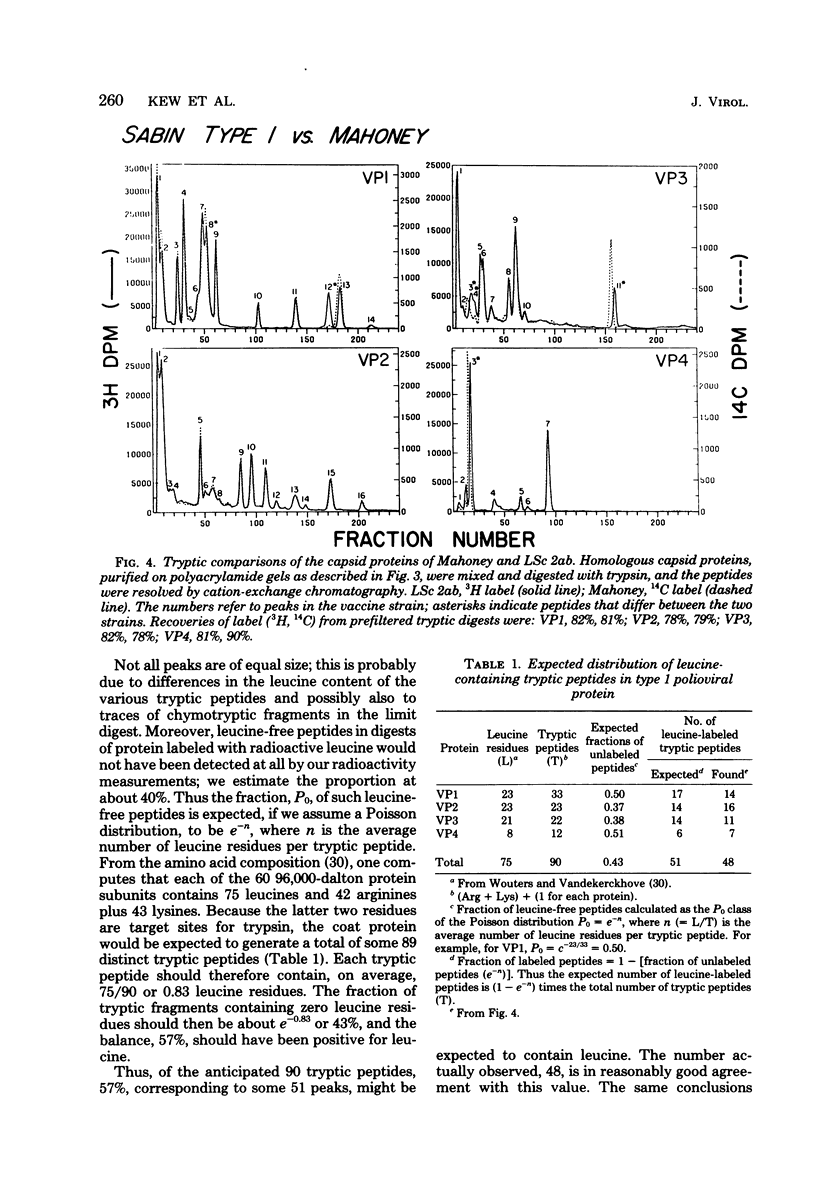
Little is yet known about the nature, or extent, of the changes involved in attenuation of neurovirulent poliovirus. The tryptic comparison reported here, of coat proteins from the Sabin type 1 polio vaccine and parental Mahoney virus, provides a useful approach and affords some insight into this question. The main obstacle, separation of the labile proteins VP1 and VP2 in an intact state from the vaccine strain, was overcome by incorporating 3.5 M urea into an otherwise standard preparative gel electrophoresis system. Tryptic maps revealed six altered leucine-containing peaks: two in VP1, none in VP2, three in VP3, and one in VP4. It is estimated, after correcting for leucine-free peptides, that the coat protein sequences may have undergone some 10 to 13 amino acid replacements, roughly 1.5% of the total, in the course of attenuation leading to the vaccine strain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Cooper P. D. Anomalous behavior of certain poliovirus polypeptides during SDS-gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jun;73(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beneke T. W., Habermehl K. O., Diefenthal W., Buchholz M. Iodination of poliovirus capsid proteins. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):387–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson S. Attempts to map the poliovirus genome by analysis of selected recombinants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(4):592–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDS C. E., HOLLAND J. J. ALTERATION OF THE SPECIES AND TISSUE SPECIFICITY OF POLIOVIRUS BY ENCLOSURE OF ITS RNA WITHIN THE PROTEIN CAPSID OF COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:492–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew P., Martin S. J. The iodination of bovine enterovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Immunogenic and cell attachment sites of FMDV: further evidence for their location in a single capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):149–158. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danno G. i. Isoelectric focusing of proteins separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90525-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. T. STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF AMINOETHYLATED HEMOGLOBINS BY AUTOMATIC PEPTIDE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1964;29:297–308. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1964.029.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Tanford C. Viscosity and density of aqueous solutions of urea and guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3228–3232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J., Lenoir G. Structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Aug;20(2):161–168. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Butterworth B. E. Investigation of the structure of polio- and human rhinovirions through the use of selective chemical reactivity. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Ziola B. R., Salmi A., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. V. Distribution of the capsid polypeptides with respect to the surface of the virus particle. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien J. B., Walker J. R., Eron L. J. Correlation of virus polypeptide structure with attenuation of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):811–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.811-815.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKANO J. H., GELFAND H. M. The use of a modified Wecker technique for the serodifferentiation of type 1 polioviruses related and unrelated to Sabin's vaccine strain. I. Standardization and evaluation of the test. Am J Hyg. 1962 May;75:363–376. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J. H., Hatch M. H., Thieme M. L., Nottay B. Parameters for differentiating vaccine-derived and wild poliovirus strains. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:178–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Bachrach H. L. Number and molecular weights of foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid proteins and the effects of maleylation. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):250–259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.250-259.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetz K., Habermehl K. O. Topographical studies on poliovirus capsid proteins by chemical modification and cross-linking with bifunctional reagents. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters M., Vandekerckhove J. Amino acid composition of the poliovirus capsid polypeptides isolated as fluorescamine conjugates. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):529–533. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Zweers A., Cohen L. H. Influence of single amino acid substitutions on electrophoretic mobility of sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wezel A. L., Hazendonk A. G. Intratypic serodifferentiation of poliomyelitis virus strains by strain-specific antisera. Intervirology. 1979;11(1):2–8. doi: 10.1159/000149005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



