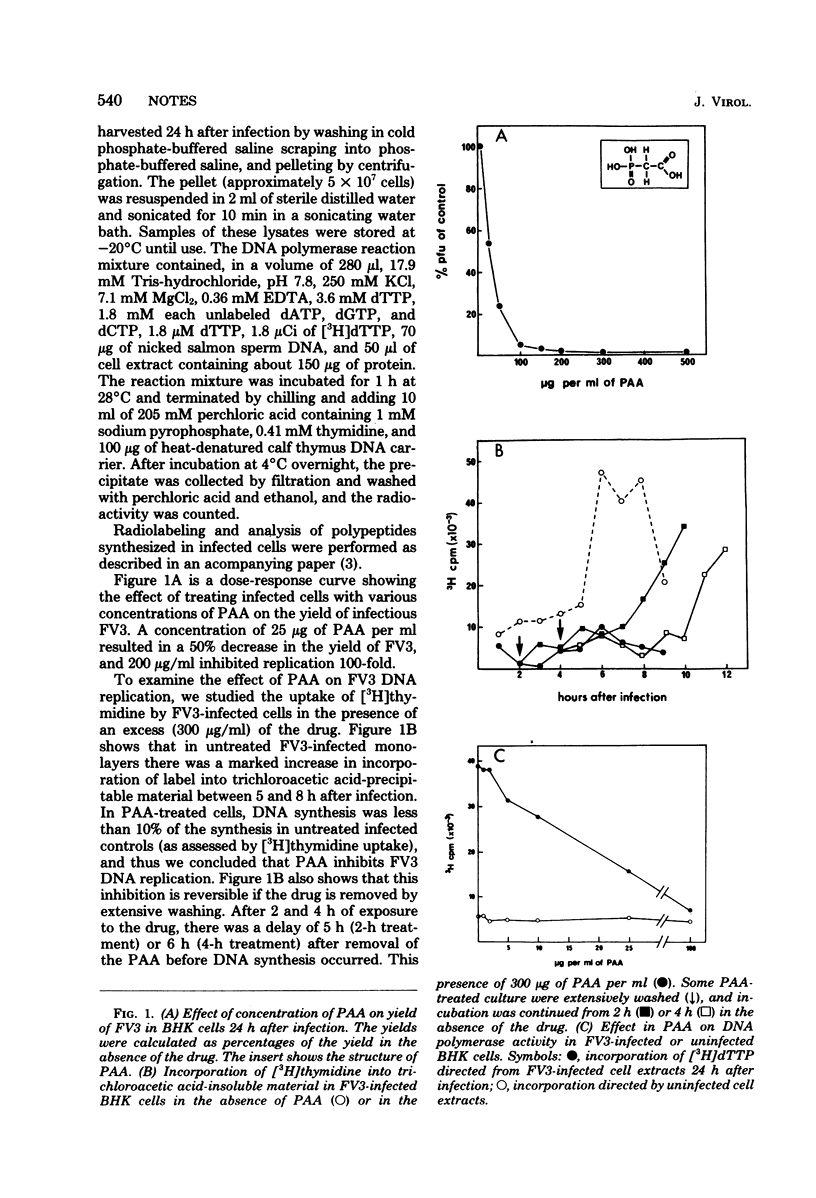
Abstract
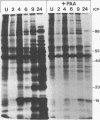
Phosphonoacetic acid at concentrations above 200 μg/ml inhibited the replication of frog virus 3 in BHK cells. The inhibition of viral DNA replication observed in these cells was reversible and correlated with the inhibition of the virus-induced DNA polymerase activity in an in vitro assay. The synthesis of frog virus 3-induced late or γ polypeptides was also inhibited by phosphonoacetic acid, although the early (α and β) polypeptides were unaffected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. M., Kelly D. C. Frog virus 3 replication: induction and intracellular distribution of polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):28–51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.28-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein D. D., Dawson C. R., O J. O. Phosphonoacetic acid in the treatment of experimental herpes simplex keratitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):285–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R., Murti G., Granoff A., Tirey R. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. VIII. The nucleus is a site of frog virus 3 DNA and RNA synthesis. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):32–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R., Willis D. B., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. VI. Frog virus 3 replication is dependent on the cell nucleus. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):802–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.802-805.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff A. Viruses of amphibia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;50:107–137. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46169-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess W. R. African swine fever virus. Virol Monogr. 1971;9:1–33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-3987-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Unity and diversity in the herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):15–37. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. IV. Specific inhibition of virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1560–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1560-1565.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. C., Robertson J. S. Icosahedral cytoplasmic deoxyriboviruses. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;20(Suppl):17–41. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-Supplement-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E. Phosphonoacetic acid-resistant herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera L. S. Effects of temperature on frog polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyribovirus multiplication: thermosensitivity of initiation, replication, and encapsidation of viral DNA. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):576–589. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90304-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera L. S., Granoff A. Induction and regulation of DNA nucleotidyltransferase activity in fish cells infected with frog virus 3. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuslan B. R., Armentrout R. W. The biochemistry of icosahedral cytoplasmic deoxyviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;(68):77–105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66044-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuslan B. R., Kuchera L. DNA polymerase activity in FV3-infected BHK cells. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. F., Varnell E. D., Kaufman H. E. Phosphonoacetic acid in the treatment of experimental ocular herpes simplex infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. A., Carrascosa A. L., Ortín J., Viñuela E. Inhibition of African swine fever (ASF virus replication by phosphonoacetic acid. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):253–258. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overby L. R., Robishaw E. E., Schleicher J. B., Rueter A., Shipkowitz N. L., Mao J. C. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by phosphonoacetic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):360–365. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipkowitz N. L., Bower R. R., Appell R. N., Nordeen C. W., Overby L. R., Roderick W. R., Schleicher J. B., Von Esch A. M. Suppression of herpes simplex virus infection by phosphonoacetic acid. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):264–267. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.264-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Klein G. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus DNA synthesis and late gene expression by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.151-155.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]