Abstract
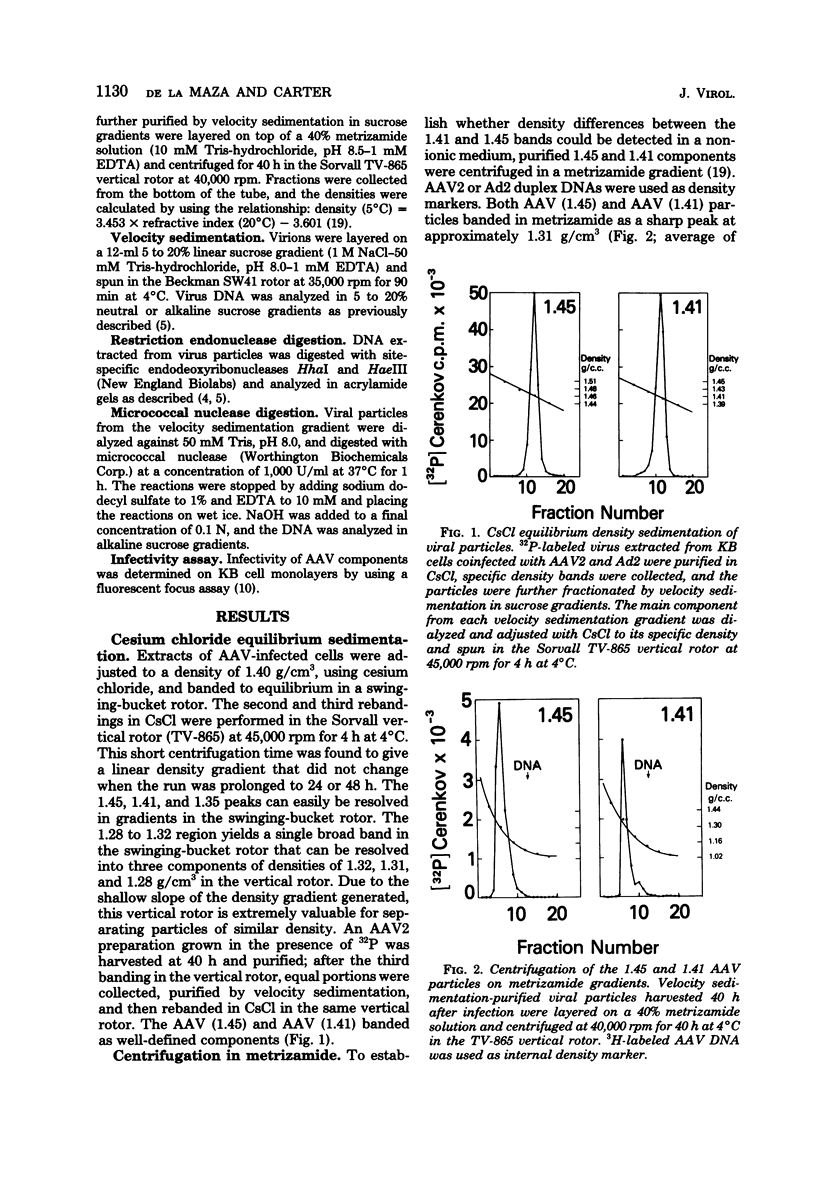
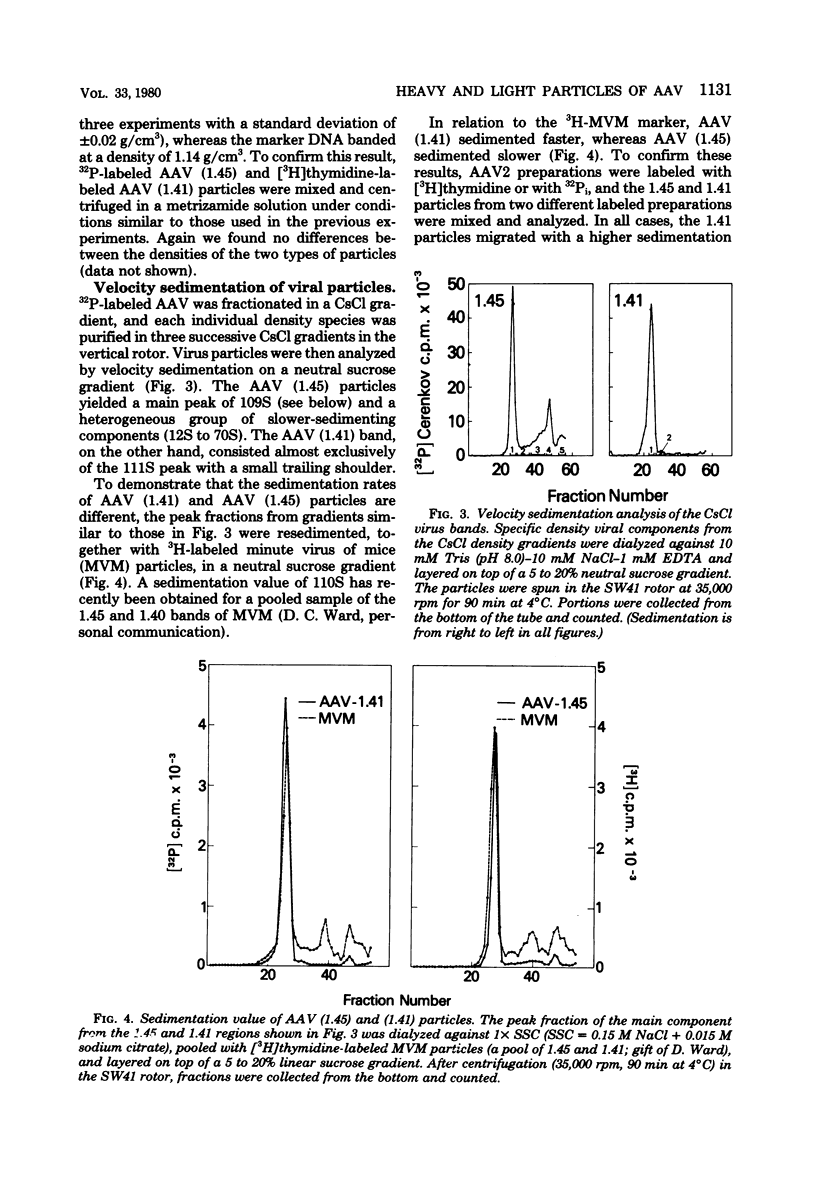
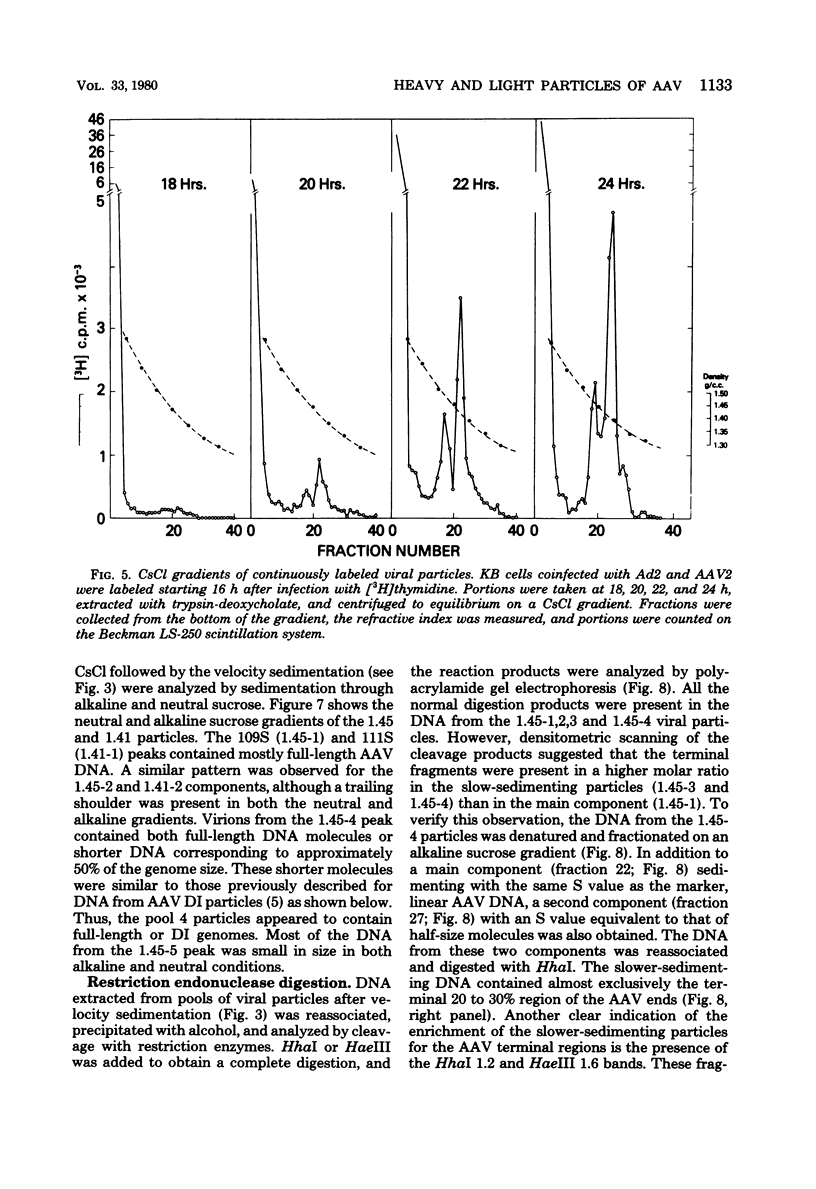
KB cells coinfected with adenovirus and adeno-associated virus (AAV) yielded two kinds of infectious AAV particles that banded in CsCl at densities of 1.45 and 1.41 g/cm2, respectively. The 1.45 band was found to be composed of a heterogeneous group of viral particles that could be subfractionated by velocity sedimentation. The main component from this band had a smaller S value (109) than the main component from the 1.41 band (111S), although both had the same DNA/protein ratio and the same density in metrizamide gradients. Continuous-label experiments showed that early after infection, both components (1.45 and 1.41) were generated in the same amounts, but this was followed by a relative increase in the proportion of the 1.41 component over the 1.45 particles. Pulse-chase analysis failed to demonstrate a precursor-product relationship between these two bands. The slower-sedimenting components from the 1.45 band were unstable in CsCl and were present in a greater proportion early after infection. These particles contained DNA that was enriched for the terminal sequences of the AAV genomes and was accessible to digestion with micrococcal nuclease.
Full text
PDF

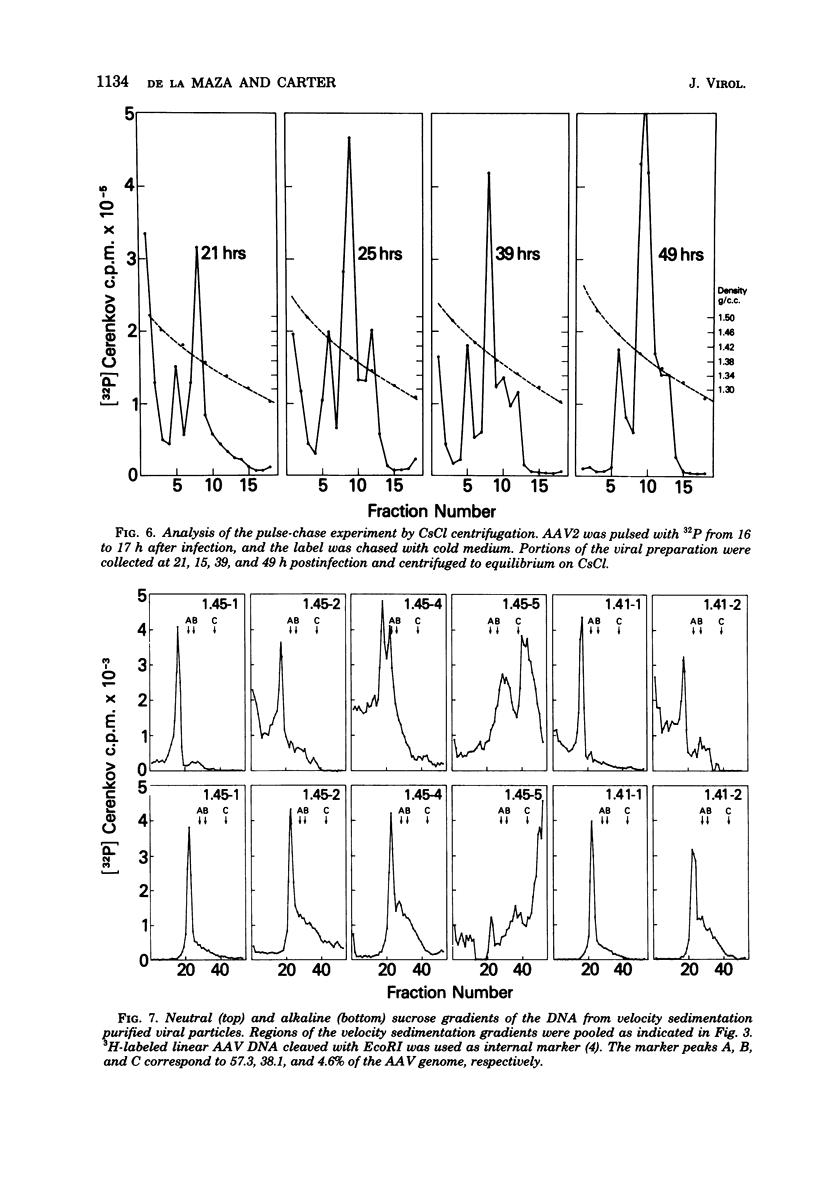



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter B. J., Laughlin C. A., de la Maza L. M., Myers M. Adeno-associated virus autointerference. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):449–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Hayashi M. The parovivirus MVM: particles with altered structural proteins. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):261–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Hayashi M. The parvovirus MVM: a comparison of heavy and light particle infectivity and their density conversion in vitro. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Blacklow N. R., Rowe W. P. Studies of small DNA viruses found in various adenovirus preparations: physical, biological, and immunological characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1467–1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Ozer H. L., Hoggan M. D. Structural proteins of adenovirus-associated virus type 3. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):860–863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.860-863.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsvik J. R., Hopkins M. S., Ellem K. A. Subfractionation of CsCl-purified H-1 parvovirus on metrizamide gradients. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):646–651. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Myers M. W., Risin D. L., Carter B. J. Defective-interfering particles of the human parvovirus adeno-associated virus. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Hoggan M. D., Shatkin A. J. Nucleic acid from an adeno-associated virus: chemical and physical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):86–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Koczot F. Adenovirus-associated virus multiplication. VI. Base compostion of the deoxyribonucleic acid strand species and strand-specific in vivo transcription. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):771–777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.771-777.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Koczot F. Adenovirus-associated virus multiplication. VII. Helper requirement for viral deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.1-8.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Sequence homology between the structural polypeptides of minute virus of mice. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torikai K., Ito M., Jordan L. E., Mayor H. D. Properties of light particles produced during growth of Type 4 adeno-associated satellite virus. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):363–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.363-369.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Carter B. J. Adeno-associated virus DNA structure. Restriction endonuclease maps and arrangement of terminal sequences. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):409–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]