Abstract
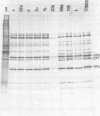
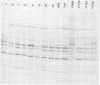
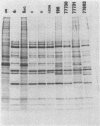
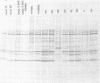
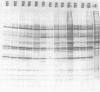
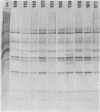
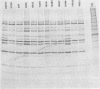
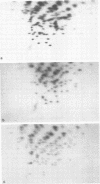
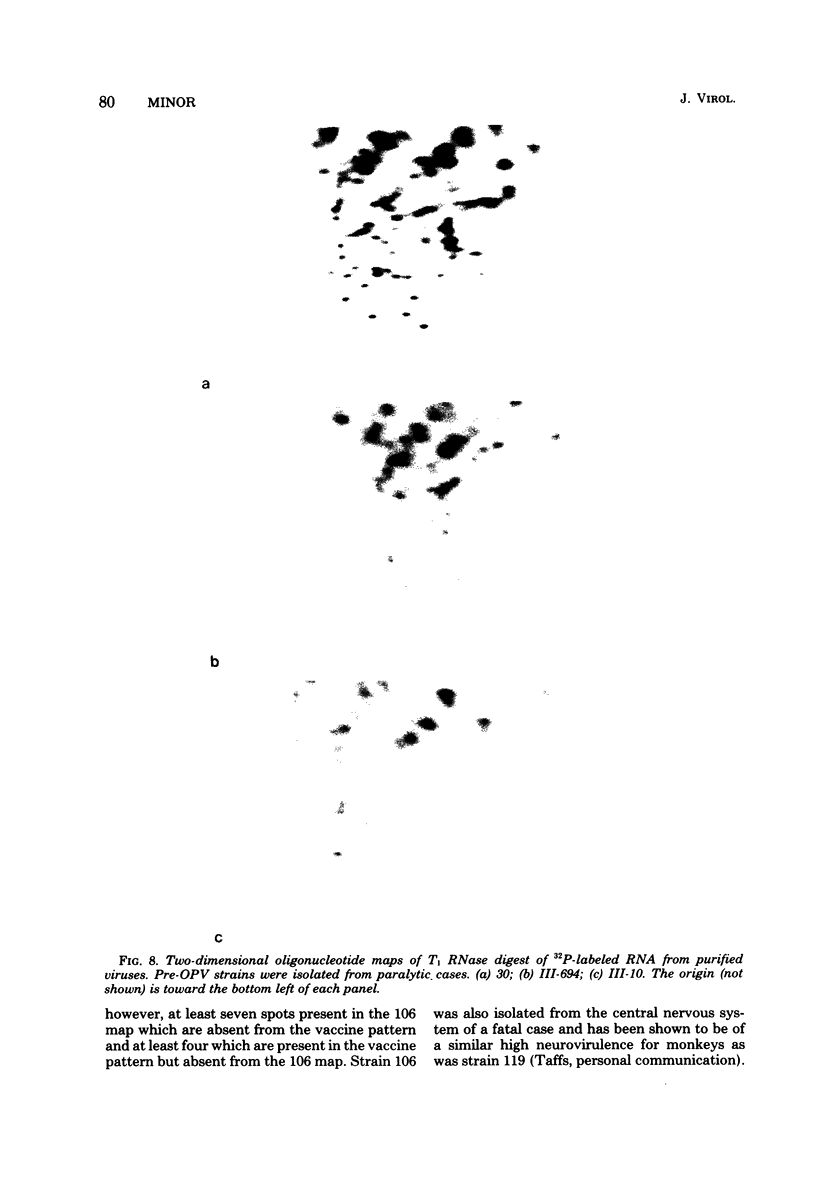
A study of the biochemistry of type 3 poliovirus strains which involves the examination of the virus-coded polypeptides in infected cells and the preparation of oligonucleotide maps is reported. The polypeptide patterns were shown to be a relatively stable property of virus strains and distinguished Sabin vaccine strains from wild strains of poliovirus type 3. This approach may be of value in deciding the origin (vaccine or nonvaccine) of field isolates of poliovirus. Oligonucleotide maps were found to be sensitive indicators of differences among strains and appear to form a basis for determining genetic relationships among strains. The nucleotide maps of two viruses isolated from human cases of paralytic poliomyelitis temporally associated with the administration of attenuated vaccine suggested a vaccine origin for the strain. In one case the nucleotide map was indistinguishable from that of the vaccine strain.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R., Tershak D. R. Temperature-sensitive defect of type 2 poliovirus. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulger L. R., Marsden S. A., Magrath D. I., Taffs L. F., Schild G. C. Comparative monkey neurovirulence of Sabin type III poliovirus vaccines. J Biol Stand. 1979 Apr;7(2):97–111. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P., Bishop D. H., Kang C. Y., Coffin J., Schnitzlein W. M., Reichmann M. E., Shope R. E. Oligonucleotide fingerprints of RNA species obtained from rhabdoviruses belonging to the vesicular stomatitis virus subgroup. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.152-166.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingham K. E., Pollock T. M., Roebuck M. O. Paralytic poliomyelitis in England and Wales 1976-7. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):976–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M., Reynier M., Bucchini D., Girard M. Thermosensitive block of the Sabin strain of poliovirus type I. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1143–1151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1143-1151.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkle D. B., Tershak D. R. Degradation of poliovirus polypeptides in vivo. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 16;238(85):206–208. doi: 10.1038/newbio238206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jense H., Knauert F., Ehrenfeld E. Two initiation sites for translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: comparison of LSc and Mahoney strains. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.387-394.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Kitamura N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. IV. Nucleotide sequence complexities of poliovirus type 1, type 2 and two type 1 defective interfering particles RNAs, and fingerprint of the poliovirus type 3 genome. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):311–322. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. "Fingerprinting" high molecular weight RNA by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: application to poliovirus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jul;3(7):1647–1658. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.7.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien J. B., Walker J. R., Eron L. J. Correlation of virus polypeptide structure with attenuation of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):811–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.811-815.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Desselberger U., Palese P. Recent human influenza A (H1N1) viruses are closely related genetically to strains isolated in 1950. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):334–339. doi: 10.1038/274334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J. H., Gelfand H. M., Cole J. T. Antigenic segregation of type 3 poliovirus isolates related and unrelated to Sabin's vaccine strain with the use of modified Wecker and McBride techniques. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jan;83(1):130–145. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obijeski J. F., Palmer E. L., Gafford L. G., Randall C. C. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of fowlpox and vaccinia virus proteins. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):512–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90454-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Guttman N., Baltimore D., Lodishi H. F. Complete translation of poliovirus RNA in a eukaryotic cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]