Abstract
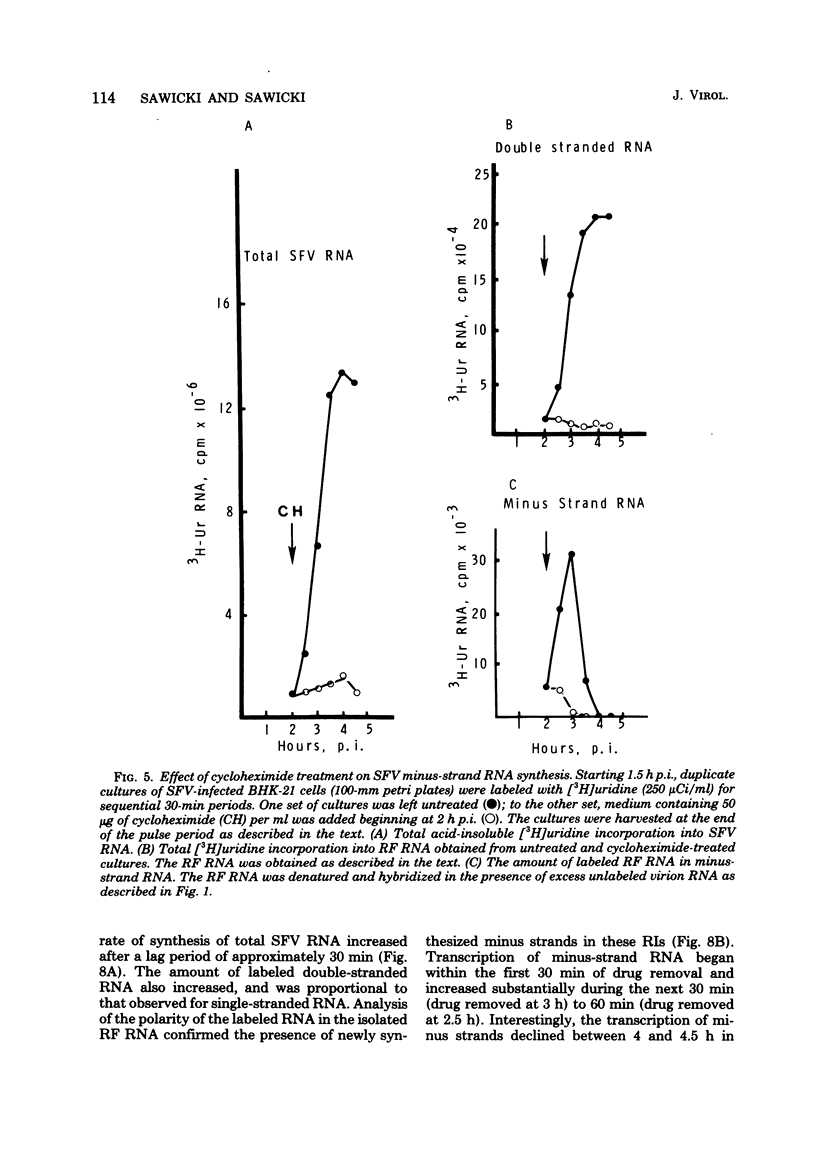
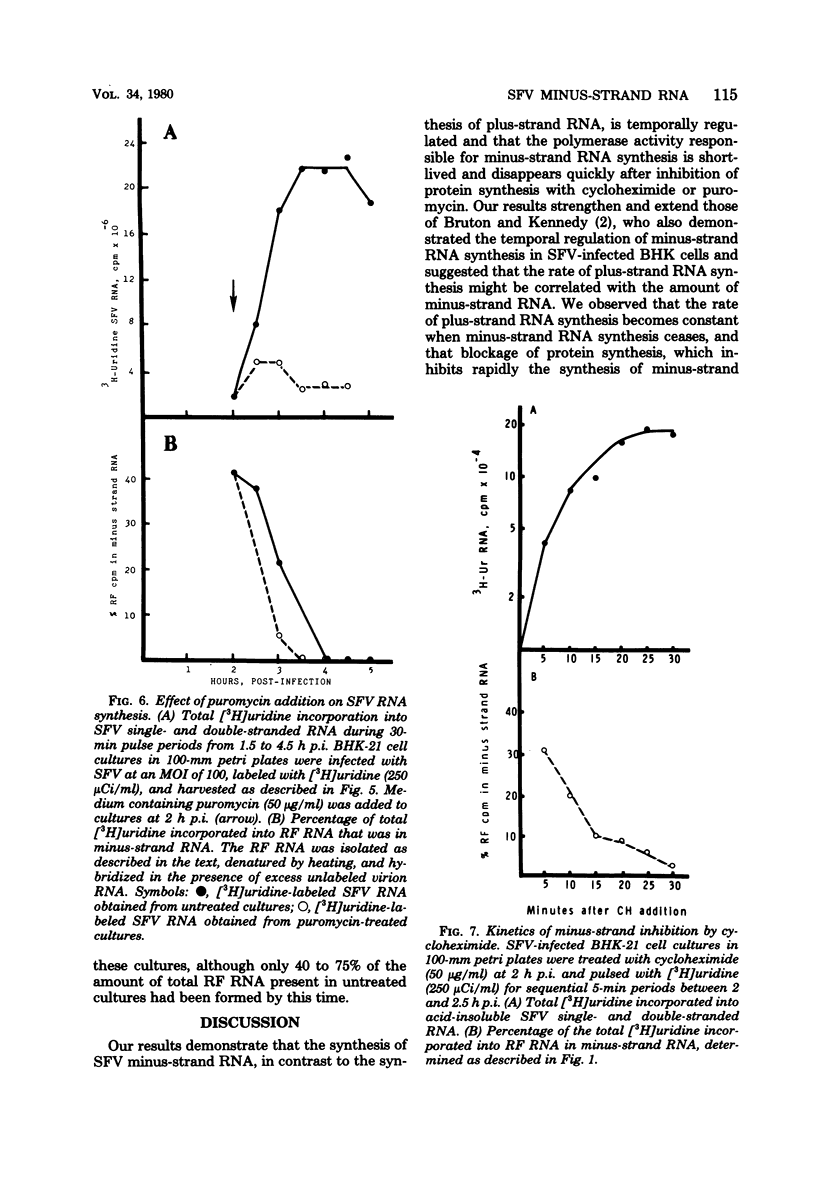
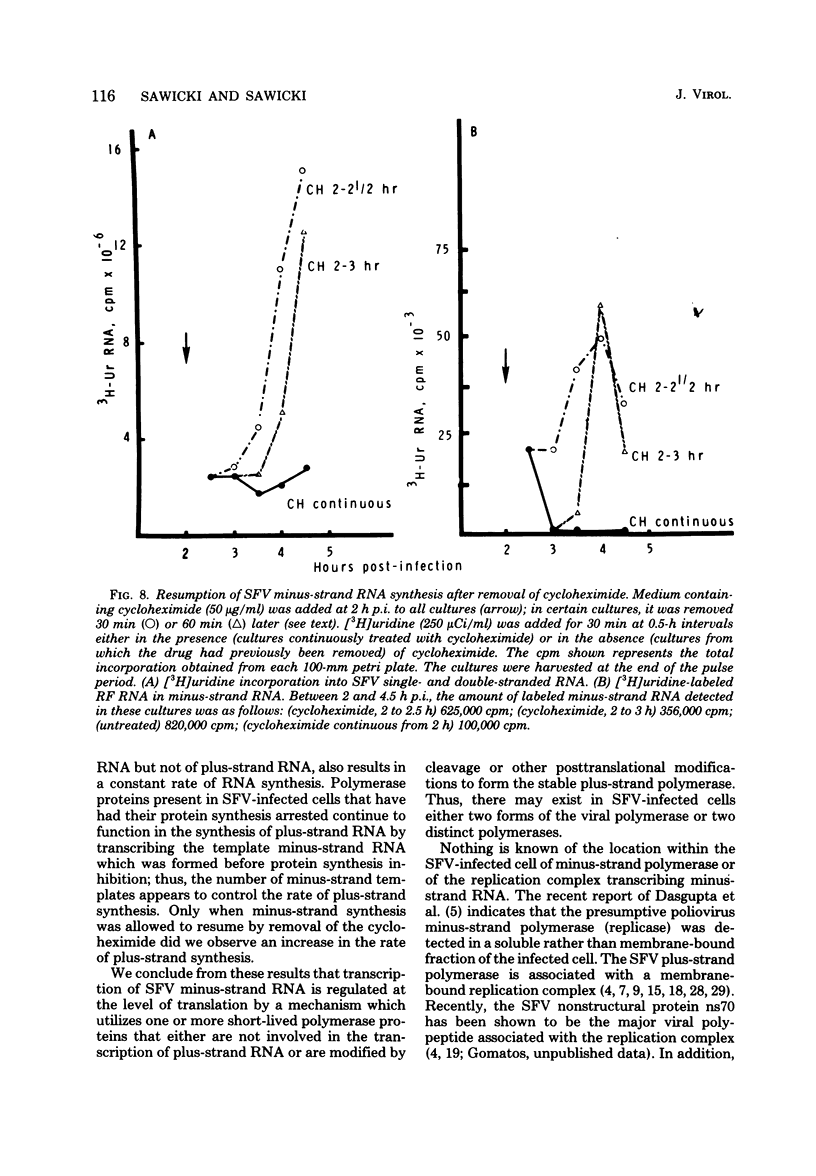
Semliki Forest virus (SFV)-infected BHK-21, Vero, and HeLa cells incorporated [3H]uridine into 42S and 26S plus-strand RNA and into viral minus-strand RNA (complementary to the 42S virion RNA) early in the infectious cycle. Between 3 and 4 h postinfection, the synthesis of minus-strand RNA ceased in these cultures, although the synthesis of plus-strand RNA continued at a maximal rate. At the time of cessation of minus-strand RNA synthesis, two changes in the pattern of viral protein synthesis were detected: a decrease in the translation of nonstructural proteins and an increase in the translation of the viral structural proteins. Addition of cycloheximide and puromycin to cultures of SFV-infected BHK cells actively synthesizing both viral plus- and minus-strand RNA resulted within 15 to 30 min in the selective shutoff of minus-strand RNA synthesis. Removal of the cycloheximide-containing medium led to the resumption of minus-strand synthesis and to an increased rate of viral RNA synthesis. We conclude that the minus-strand polymerase regulates the rate of SFV plus-strand RNA synthesis by determining the number of minus-strand templates and that the synthesis of the minus-strand templates is regulated at the level of translation by a mechanism which utilizes one or more short-lived polymerase proteins.
Full text
PDF

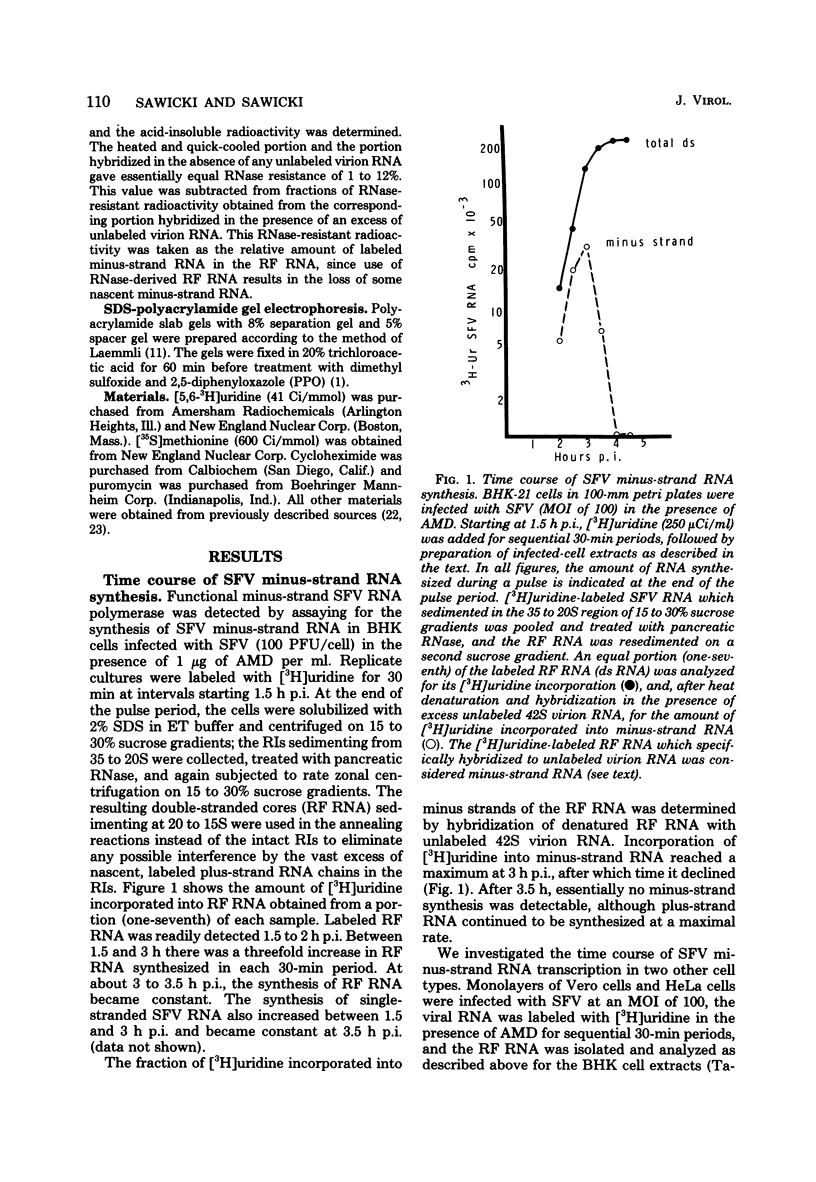
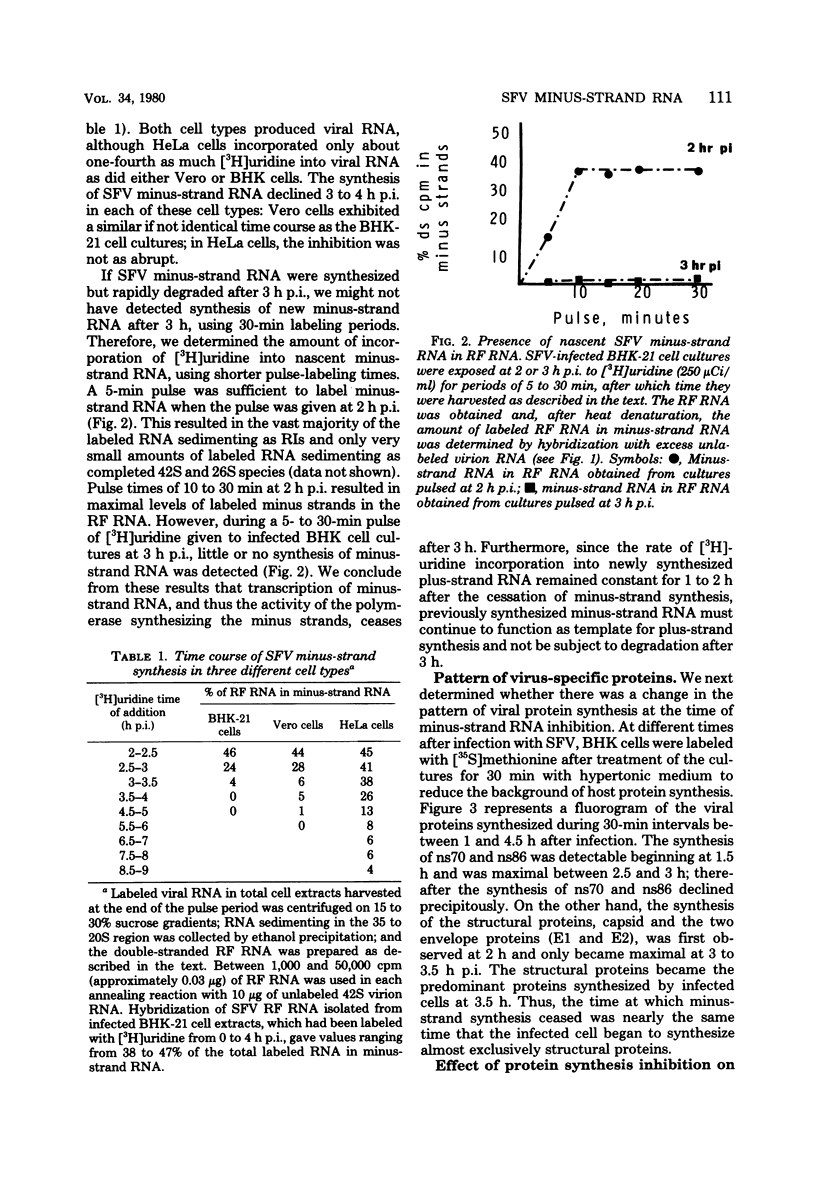
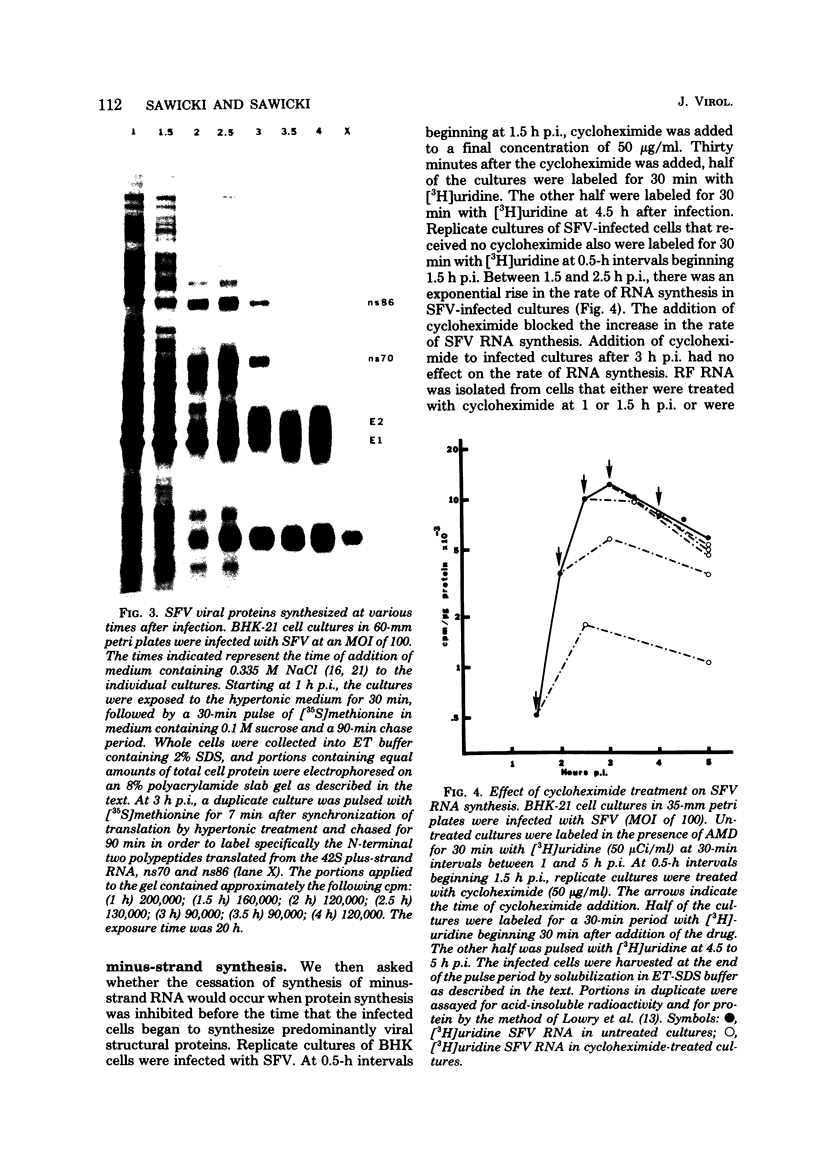



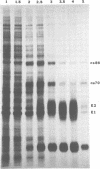
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Semliki Forest virus intracellular RNA: properties of the multi-stranded RNA species and kinetics of positive and negative strand synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jul;28(1):111–127. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. RNA polymerase components in Semliki Forest virus-infected cells: synthesis from large precursors. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):413–430. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P., Kennedy S. I. Purification and polypeptide composition of Semliki Forest virus RNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):395–411. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Grimley P. M. Inhibition of arbovirus assembly by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):292–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.292-299.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K. Membrane-associated replication complex in arbovirus infection. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):504–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.504-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Structure and replication of alpha-viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:15–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Friedman R. M. Analysis of arbovirus ribonucleic acid forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):504–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.504-514.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. A., Burke D. C. The replication of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):45–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M. Studies on the RNA polymrase of some temperature-sensitive mutants of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90352-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Oppermann H., Koch G. Selective blockage of initiation of host protein synthesis in RNA-virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki M., Käriäinen L. Solubilized RNA replication complex from Semliki Forest virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Gomatos P. J. Replication of semliki forest virus: polyadenylate in plus-strand RNA and polyuridylate in minus-strand RNA. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):446–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.446-464.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Kaariainen L., Lambek C., Gomatos P. J. Mechanism for control of synthesis of Semliki Forest virus 26S and 42s RNA. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.19-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Godman G. C. On the differential cytotoxicity of actinomycin D. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):746–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Pfefferkorn E. R. Inhibition of interjacent ribonucleic acid (26S) synthesis in cells infected by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):117–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.117-122.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Sreevalsan T. Sindbis virus replicative intermediates: purification and characterization. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):428–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. II. Multiple forms of double-stranded RNA isolated from infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):615–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Yin F. H. Sindbis virus-induced viral ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):599–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.599-604.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. Studies on the synthesis of viral RNA-polymerase-template complexes in BHK 21 cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Levine M. RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus and a small plaque mutant: effects of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):253–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.253-264.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]