Abstract
A microwave-assisted, sequential, one-pot protocol has been developed for the synthesis of a variety of benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides. This protocol utilizes a copper-catalyzed N-arylation of α-bromo-benzenesulfonamides with a number of amines to generate the corresponding 2-aminobenzenesulfonamides, which undergo cyclization to the desired sultams using carbonyl diimidazole (CDI). A range of conditions was evaluated for the key C–N bond formation step with tolerance toward functionalized amines.
1. Introduction
The development of protocols for the synthesis of skeletally diverse heterocyclic scaffolds is a critical step in the drug discovery process. The growing demand for libraries of small molecules as potential small molecule therapeutic agents for high-throughput screening presents challenging opportunities in this field. One-pot strategies are highly efficient pathways to rapidly synthesize complex heterocyclic molecules from simple substrates.1 When coupled with transition metal-catalyzed processes, one-pot processes enable the generation of complex heterocyclic scaffolds from simple building blocks. In this regard, α-haloarylsulfonamides represent an attractive building block for the production of benzofused sultams.2,3
Sultams and their sulfonamide precursors possess a number of advantageous chemical properties making them ideal building blocks for the titled process, the most prominent of these include: (i) click coupling between starting α-halobenzenesulfonyl chlorides and amines under mild conditions, (ii) the α-halo group can be utilized in transition metal-catalyzed cross coupling (iii) the α-halo group enhances the acidity of the aryl sulfonamide N–H enabling Mitsunobu and conventional alkylation reactions to occur under mild conditions, and (iv) the commercial availability of a variety of substituted α-halo benzenesulfonyl chlorides. Taken collectively, these attributes have guided our efforts to develop a microwave-assisted, sequential one-pot protocol for the synthesis of benzothiazdiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides based on a pivotal copper-catalyzed N-arylation strategy.
Traditionally, sultams have been synthesized using a number of classical cyclization protocols such as Friedel–Crafts, [3+2] cycloadditions, Diels–Alder reactions, and recently the application of oxa- and aza-Michael reactions.4 Notably, there have been a number of transition metal-catalyzed protocols reported for the generation of diverse sultams.3,5
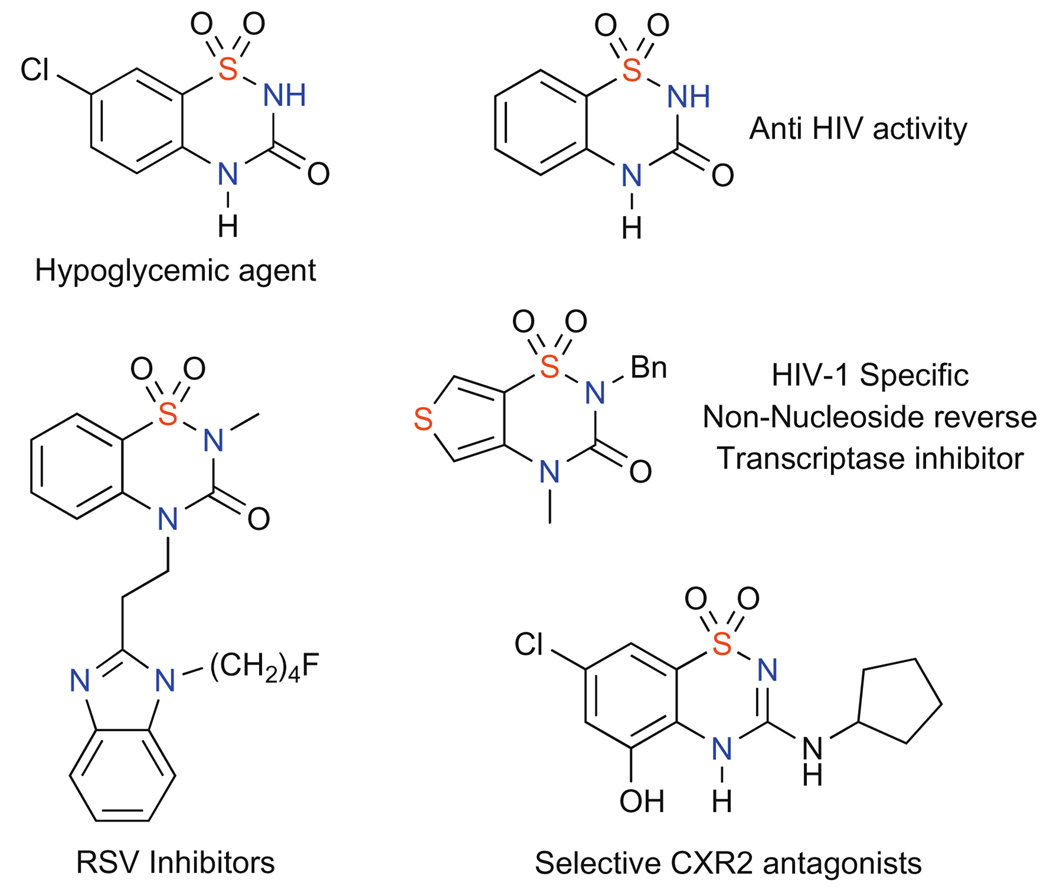
In addition to their inherent chemical properties, sultams have emerged as important targets for drug discovery due to their potent biological activities. In particular, benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides and their derivatives have shown promising activity, including hypoglycemic,6 anti-HIV,7 RSV inhibitory activity,8 as well asand serving as selective antagonists of CXR2 (Fig. 1).9
Figure 1.
Biologically active benzofuzed sultams.
2. Results and discussion
Since the observation of copper-catalyzed coupling of a arylbromide with an acetanilide by Goldberg in 1907,10 copper-catalyzed N-arylation represents an effective reaction for the formation of C–N and C–O bonds.11 Early reports classically required harsh reaction conditions and stoichiometric quantities of copper. Seminal work by Buchwald, Hartwig and Ley reported notable advances in both ligands and reduced reaction temperatures for copper-catalyzed couplings.12
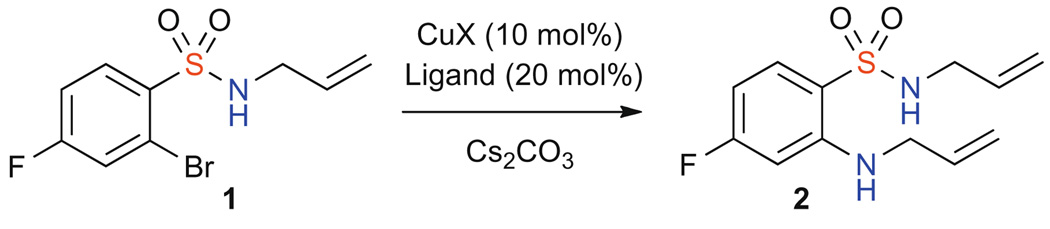
Traditionally, benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides have been synthesized in a number of linear protocols.6–9,13 Envisioning a copper-catalyzed approach to benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides, a variety of conditions were evaluated to probe and subsequently optimize the N-arylation of allyl amine with N-allyl-2-bromo-4-fluorobenzenesulfonamide 1 to yield N-allyl-2-(allylamino)-4-fluorobenzenesulfonamide 2 (Scheme 1, Table 1).14 An array of copper sources (Table 1, entries 1–3) and ligands (Table 1, entries 4–7) were initially evaluated followed by a survey of reaction solvent. Under conventional heating, the desired sulfonamide 2, could be isolated in 92% yield after 6 h.
Scheme 1.
Table 1.
Screening conditions for reaction optimization
| Entrya,d | [Cu] cat. | Ligand | Solvent | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CuI | l-Proline | DMSO | 65 |
| 2 | CuBr | l-Proline | DMSO | 55 |
| 3 | Cu2O | l-Proline | DMSO | 10 |
| 4 | CuI | (CH2OH)2 | DMSO | 78 |
| 5 | CuI | 1,10-Phenanthroline | DMSO | 94 |
| 6 | CuI | DBU | DMSO | 50 |
| 7 | CuI | (CH2NHMe)2 | DMSO | 72 |
| 8 | CuI | 1,10-Phenanthroline | DMF | 92 |
| 9 | CuI | 1,10-Phenanthroline | Dioxane | 84 |
| 10 | CuI | 1,10-Phenanthroline | DMF | 96b |
| 11 | CuI | 1,10-Phenanthroline | DMF | 94c |
Reaction conditions: 1 (0.17 mmol), allylamine (0.2 mmol), CuX (0.017 mmol), ligand (0.034 mmol), Cs2CO3 (0.34 mmol) in solvent (0.5 M) at 100 °C for 6 h.
Microwave irradiation for 22 min at 140 °C.
Microwave irradiation for 11 min at 150 °C.
Other bases were also investigated (DBU, K2CO3, Et3N) but Cs2CO3 was preferred.
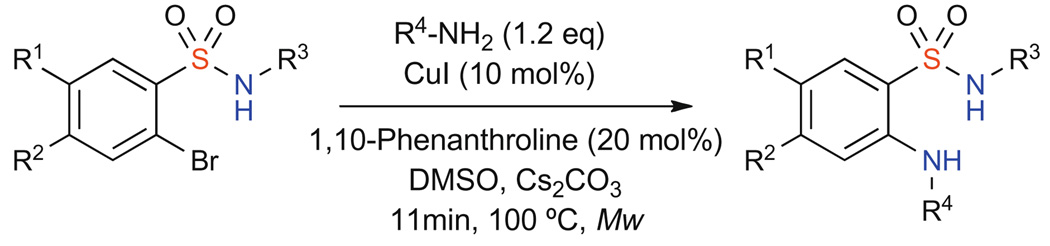
Further optimization was achieved using microwave irradiation, which reduced reaction times to 11 min at 150 °C with comparable yields (Table 1, entry 8 vs 11).15 With these results in hand, a number of 2-aminobenzenesulfonamide derivatives were synthesized to demonstrate the versatility of the protocol with a variety of amines, amides, and sulfonamide starting materials (Scheme 2, Table 2).
Scheme 2.
Table 2.
Catalytic N-arylation of α-bromobenzene sulfonamides16
| Entrya | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4–NH2 | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | Bn | 4-MeOBnNH2 | 90 |
| 2 | H | H | Bn | 4-ClBnNH2 | 89 |
| 3 | H | H | Bn | Octylamine | 94 |
| 4 | H | H | Bn | Phenethylamine | 91 |
| 5 | H | H | Bn | Allylamine | 96 |
| 6 | H | H | 4-MeOBn | Cyclopentylamine | 90 |
| 7 | H | H | Cp | 4-MeOBnNH2 | 96 |
| 8 | H | F | Allyl | Allyl NH2 | 94 |
| 9 | H | F | n-Butyl | BnNH2 | 92 |
| 10 | CF3 | H | Allyl | n-Butyl amine | 95 |
| 11 | CF3 | H | (CH2)2Bn | Propargyl amine | 69 |
| 12 | H | F | Allyl | EtC(O)NH2 | 80 |
Reaction conditions: sulfonamide (0.17 mmol), amine (0.2 mmol), CuI (0.017 mmol), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.034 mmol), Cs2CO3 (0.34 mmol) in dry DMSO (0.5 M) in microwave for 11 min at 150 °C.
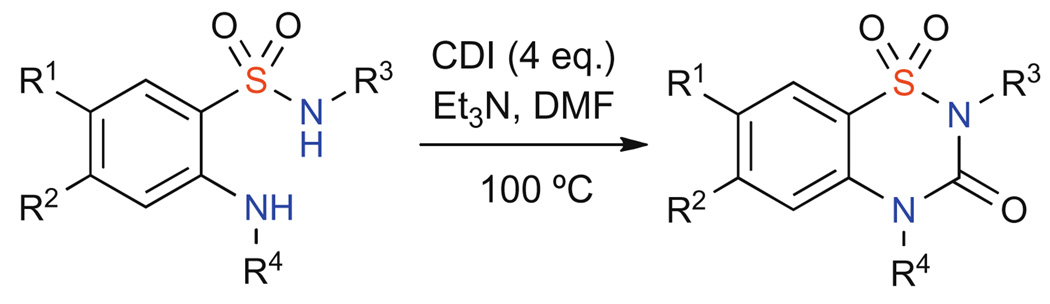
With an array of 2-aminobenzenesulonfamides in hand, cyclization to the corresponding benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides with carbonyl diimidazole (CDI) was achieved in excellent yields under thermal conditions (Scheme 3, Table 3).13b,17
Scheme 3.
Table 3.
| Entrya | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4–NH2 | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | Bn | 4-MeOBnNH2 | 96 |
| 2 | H | H | Bn | Octylamine | 96 |
| 3 | H | F | Allyl | Allylamine | 98 |
| 4 | H | H | Bn | Phenethylamine | 94 |
| 5 | CF3 | H | Allyl | n-Butylamine | 97 |
| 6 | H | H | 4-MeOBn | Cyclopentylamine | 92 |
| 7 | H | H | Cp | 4-MeOBnNH2 | 93 |
| 8 | H | F | n-Butyl | BnNH2 | 97 |
Reaction conditions: sulfonamide (0.17 mmol), CDI (0.69 mmol), Et3N (0.34 mmol) in dry DMF (0.2 M) at 100 °C for 6 h.
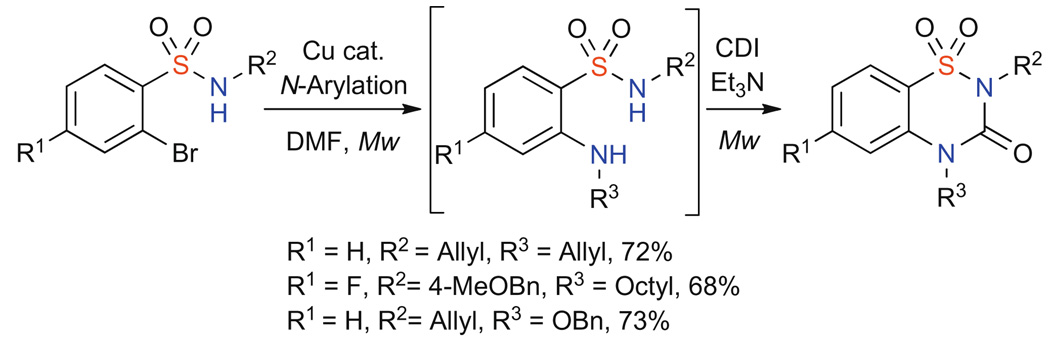
Finally with both protocols in hand, a sequential, two-step, one-pot approach was achieved whereby microwave irradiation afforded the desired benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides in good yield (Scheme 4).18 To achieve this, the CDI cyclization was conducted under microwave irradiation following the initial copper-catalyzed step in the same microwave vial. This required a change of solvent to DMF which was the optimum compatible solvent for both the N-arylation and CDI cyclization steps while maintaining good yields.
Scheme 4.
In conclusion, we have developed a microwave-assisted, copper-catalyzed, sequential, one-pot synthesis of benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides. A variety of derivatives of benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides can be rapidly accessed by combining a copper-mediated N-arylation followed by cyclization with CDI. Further efforts toward employment of this method in library production will be published in due course.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary data associated with this article Letter can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.09.090.
Acknowledgments
This publication was made possible by the Pilot-Scale Libraries Program (P41 GM076302), the National Institutes of General Medical Sciences (KU Chemical Methodologies and Library Development Center of Excellence P50 GM069663) and by Grant Number P20 RR015563 from the National Center for Research Resources, a component of the National Institutes of Health, and the State of Kansas. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of the NCRR or NIH.
References and notes
- 1.(a) Fustero S, Jiméez D, Sánchez-Roselló M, del Pozo C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:6700–6701. doi: 10.1021/ja0709829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Bi H-P, Liu X-Y, Gou F-R, Guo L-N, Duan X-H, Shu X-Z, Liang Y-M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007;46:7068–7071. doi: 10.1002/anie.200702238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zeng Y, Reddy DS, Hirt E, Aubé J. Org. Lett. 2004;6:4993–4995. doi: 10.1021/ol047809r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Kirschbaum S, Waldmann H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997;38:2829–2832. [Google Scholar]
- 2.For the use of a-halo arylsulfonamides in synthesis of sultams see: Grigg R, York M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41:7255–7258. Evans P, McCabe T, Morgan BS, Reau S. Org. Lett. 2005;7:44–46. doi: 10.1021/ol0480123. Vasudevan A, Tseng P-S, Djuric SW. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006;47:8591–8593. Paquette LA, Dura R, Fosnaugh N, Stephanian MJ. Org. Chem. 2006;71:8445–8483. doi: 10.1021/jo061404y. For radical cyclization: Bressy C, Menant C, Piva O. Synlett. 2005:577–582. For alkyne 6-endo cyclizations: Barange DK, Nishad TC, Swamy K, Bandameedi V, Kumar D, Bukkapattanam RS, Vyas K, Pal MJ. Org. Chem. 2007;72:8547–8550. doi: 10.1021/jo701470h.
- 3.(a) Zhou A, Hanson PR. Org. Lett. 2008;10:2951–2954. doi: 10.1021/ol8009072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Jeon KO, Rayabarapu D, Rolfe A, Volp K, Omar I, Hanson PR. Tetrahedron. 2009:4992–5000. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2009.03.080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Zhou A, Rayabarapu KD, Hanson PR. Org. Lett. 2009:531–534. doi: 10.1021/ol802467f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rolfe A, Young K, Hanson PR. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008:5254–5262. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.200800651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Rolfe A, Young K, Volp KA, Schoenen F, Neuenswander B, Lushington GH, Hanson PR. J. Comb. Chem. 2009;11:732–738. doi: 10.1021/cc900025e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Rayabarapu DK, Zhou A, Jeon KO, Samarakoon T, Rolfe A, Siddiqui H, Hanson PR. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:3180–3188. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2008.11.053. and references cited therein. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) McReynolds MD, Dougherty JM, Hanson PR. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:2239–2258. doi: 10.1021/cr020109k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Jiménez-Hopkins M, Hanson PR. Org. Lett. 2008;10:2951–2954. doi: 10.1021/ol8009072. and references cited therein. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wales JK, Krees SV, Grant AM, Vikroa JK, Wolff F, Pharm WJ. Exp. Ther. 1968;164:421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Buckheit WR, Fliaka-Boltz V, Decker DW, Roberson LJ, Pyle CA, White LE, Bowden BJ, McMahon JB, Boyd MR, Bader JP, Nickell DG, Barth H, Antonucci TK. Antiviral Res. 1994;25:43–56. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(94)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Arranz EM, Diaz JA, Ingate ST, Witvrouw M, Pannecouque C, Balzarini J, Clercq ED, Vega S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999;7:2811–2822. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(99)00221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Combrink KD, Gulgeze HB, Thuring JW, Yu K-L, Civiello RL, Zhang Y, Pearce BC, Yin Z, Langley DR, Kadow KF, Cianci CW, Li Z, Clarke J, Genovesi EV, Medina I, Lamb L, Yang Z, Zadjura L, Krystal M, Meanwell NA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007;17:4784–4790. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.06.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang Y, Busch-Petersen J, Wang F, Ma L, Fu W, Kerns JK, Jin J, Palovich MR, Shen J-K, Burman M, Foley JJ, Schmidt DB, Hunsberger GE, Sarau HM, Widdowson KL. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007;17:3864–3867. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Golberg I. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1907;40:4541. [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) George TG, Endeshaw MM, Morgan RE, Mahasenan KV, Delfin DA, Mukherjee MS, Yakovich AJ, Fotie J, Li C, Werbovetz KA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007;15:6071–6079. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.06.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Zhu L, Li G, Luo L, Guo P, Lan J, You J. J. Org. Chem. 2009;74:2200–2202. doi: 10.1021/jo802669b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Feng E, Huang H, Zhou Y, Ye D, Jiang H, Liu H. J. Org. Chem. 2009;74:2846–2849. doi: 10.1021/jo802818s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Stieter ER, Bhayana B, Buchwald SL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;31:78–88. doi: 10.1021/ja0781893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Klapars A, Abtilla JC, Huang X, Buchwald SL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:7727. doi: 10.1021/ja016226z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hartwig JF. Synlett. 2006:1283. [Google Scholar]; (c) Ley SV, Thomas AW. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003;42:5400. doi: 10.1002/anie.200300594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Boverie S, Antoine M-H, Somers F, Becker B, Sebille S, Ouedraogo R, Counerotte S, Pirotte B, Lebrun P, Tullio P. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:3492–3503. doi: 10.1021/jm0311339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Khazi IA, Jung Y-S. Lett. Org. Chem. 2007;4:423–428. [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Lai G, Gum RJ, Daly M, Fry EH, Hutchins C, Abad-Zapatero C, von Geldern TW. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:1807–1810. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Freeman HS, Butler JR, Freedman LD. J. Org. Chem. 1978;43:4975–4978. [Google Scholar]; (c) Bacon RGR, Rennison SG. J. Chem. Soc. 1969:312. [Google Scholar]; (d) Wu Y-J, He H, L’Heureux A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004;44:4217–4218. [Google Scholar]; (e) Kim JK, Lee Y, Lee J, Do Y, Chang S. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:9454–9457. doi: 10.1021/jo802014g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.While final yields obtained with DMSO, using DMF gave results within 5% experimental error. However it was found that under microwave conditions at 150 °C, a small amount of by-product was formed from the addition of dimethylamine into the 4-F position of the benzene ring in a SNAr mechanism. It is proposed that a small amount of dimethylamine is produced from the decomposition of DMF under these conditions and hence DMSO is a better solvent for such substrates.
- 16.General procedure for the N-arylation of α-bromobenzenesulfonamides: Into a microwave reaction vial was added sulfonamide (0.17 mmol, 1 equiv), CuI (0.017 mmol. 0.1 equiv), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.034 mmol, 0.2 equiv), Cs2CO3 (0.34 mmol, 2 equiv), dry DMSO or DMF (0.5 M), and amine (0.2 mmol, 1.2 equiv). The reaction was heated in the microwave (Biotage initiator, www.biotage.com) at 150 °C for 11 min. After such time, the crude reaction was purified by flash chromatography [hexane/EtOAc, 8:2] to afford the desired product as a solid. Table 2, entry 8. FTIR (neat): 3400, 1579, 1301, 1149, 547 cm−1; mp 178–181 °C: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.73 (dd, J = 8.5, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.42 (ddd, J = 13.5, 9.7, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 6.19 (s, 1H), 5.98–5.83 (m, 1H), 5.67 (qt, J = 15.0, 7.5 Hz, 1H), 5.25 (dd, J = 19.5, 13.8 Hz, 2H), 5.12 (dd, J = 25.7, 13.7 Hz, 2H), 4.67 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 3.88–3.74 (m, 2H), 3.52 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 167.8, 165.8, 147.9 (d, JC–F = 13.1 Hz), 133.2, 132.7, 117.8, 116.9, 103.5, 103.3, 99.6, 99.4, 46.1; HRMS calcd for C12H16FN2O2S (M+H)+ 271.0917; found 271.0923.
- 17.General procedure for the synthesis of benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides via CDI cyclization: To a round-bottomed flask was added sulfonamide (0.17 mmol, 1 equiv), dry DMF (0.2 M), Et3N (0.34 mmol, 2 equiv) and CDI (0.69 mmol, 4 equiv). The reaction mixture was heated at 100 °C for 6 h, cooled to rt and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude oil was diluted in CH2Cl2, washed with 1 M HCl (aq, 5 mL), water (5 mL), and dried (MgSO4). Subsequent filtration and concentration yielded a crude oil which was purified by flash chromatography [hexane/EtOAc, 7:3] to afford the desired product as clear oil. (Table 3, entry 3). FTIR (neat): 3400, 1575, 1310, 1149 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92–7.83 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.94 (m, 2H), 6.04–5.88 (m, 2H), 5.39–5.30 (m, 2H), 5.29–5.19 (m, 2H), 4.69–4.59 (m, 2H), 4.52–4.46 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.7, 164.6, 150.2, 138.8 (dd, JC–F = 10.8 Hz), 131.6, 130.7, 125.3, 119.2, 118.0, 111.1, 104.7, 104.4, 48.5, 44.8; HRMS calcd for C13H13FN2O2S (M+H)+ 297.0709; found 297.0712.
- 18.General one-pot procedure for the synthesis of benzothiadiazin-3-one-1,1-dioxides: Into a microwave reaction vial (0.5–2.0 ml) was added sulfonamide (0.17 mmol, 1 equiv), CuI (0.017 mmol. 0.1 equiv), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.034 mmol, 0.2 equiv), Cs2CO3 (0.34 mmol, 2 equiv), dry solvent (0.5 M), and amine (0.2 mmol, 1.2 equiv). The reaction was heated in the microwave (Biotage initiator, www.biotage.com) at 150 °C for 11 min. After such time Et3N (0.34 mmol, 2 equiv) and CDI (0.69 mmol, 4 equiv) was added directly to the microwave vial. The reaction mixture was heated at 150 °C for 11 min, cooled to rt and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude oil was diluted in CH2Cl2, washed with 1 M HCl (aq, 5 mL), water (5 mL) and dried (MgSO4). Subsequent filtration and concentration yielded a crude oil, which was purified by flash chromatography [hexane/EtOAc, 7:3] to afford the desired product.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data associated with this article Letter can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.09.090.