Abstract
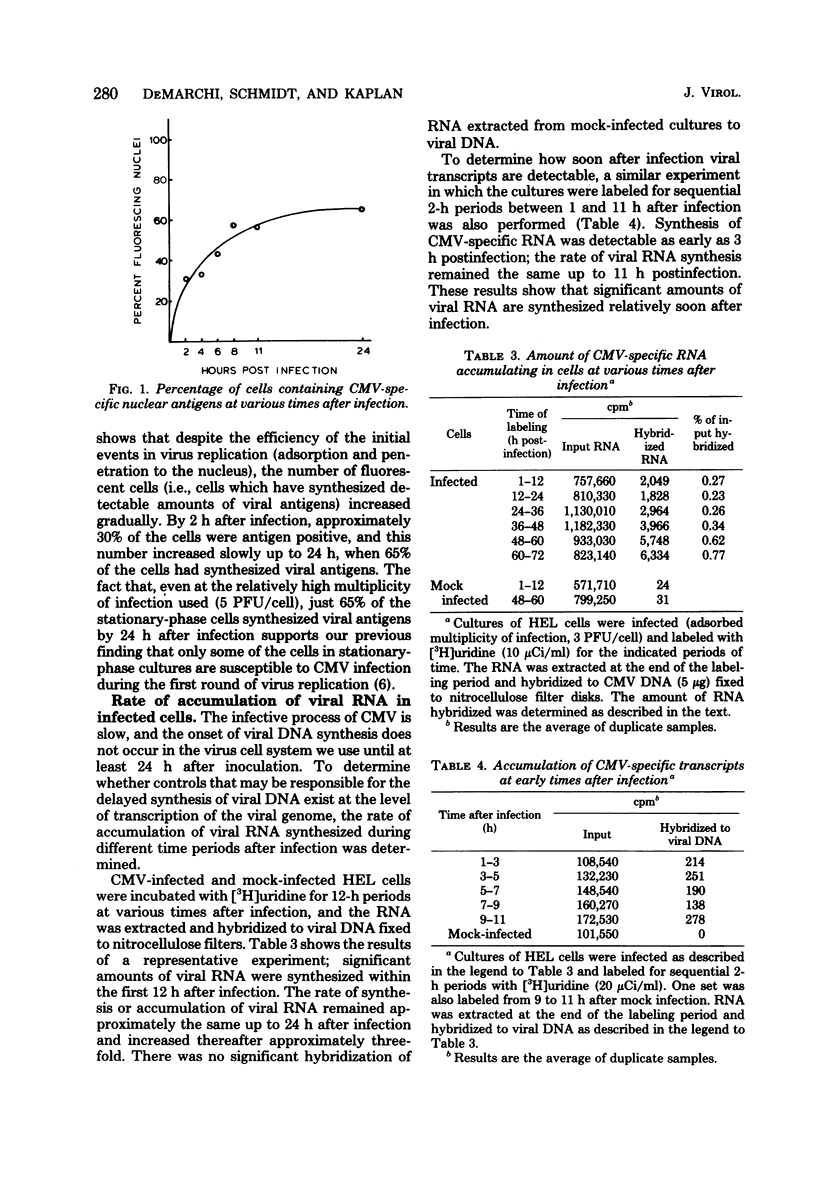
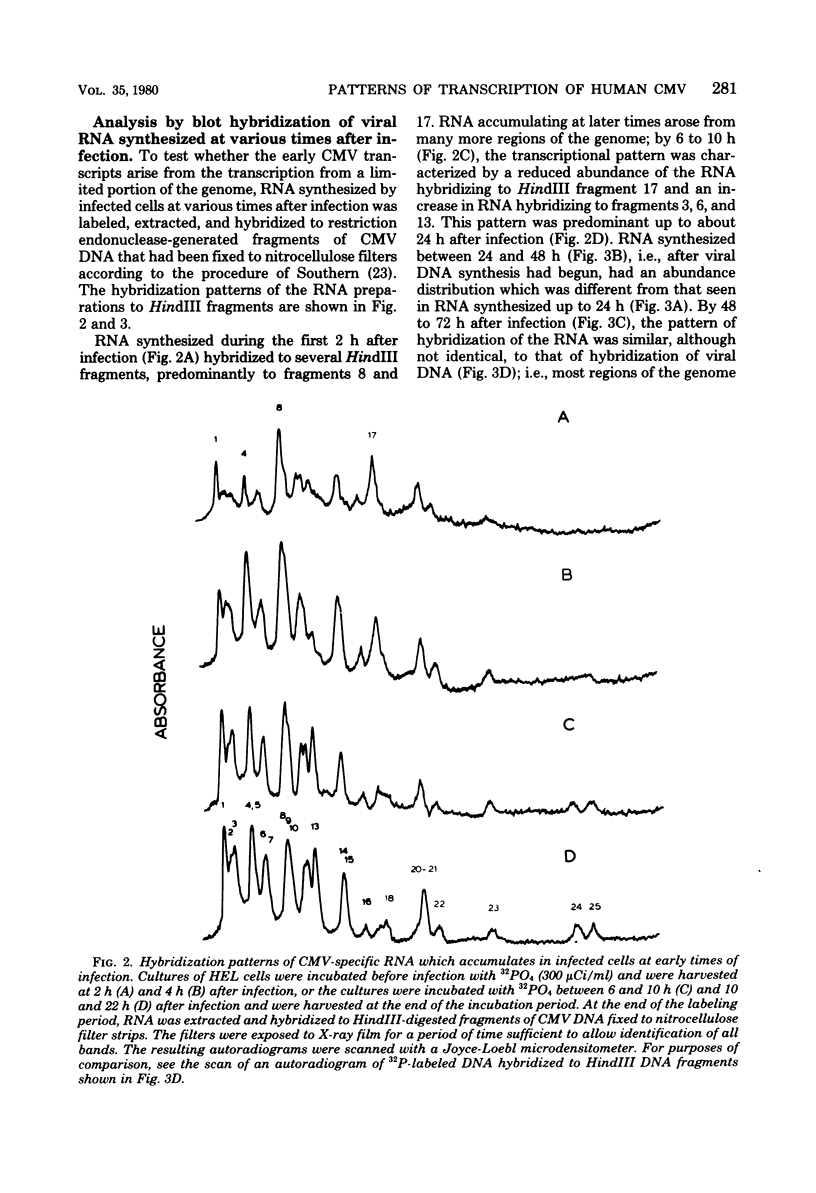
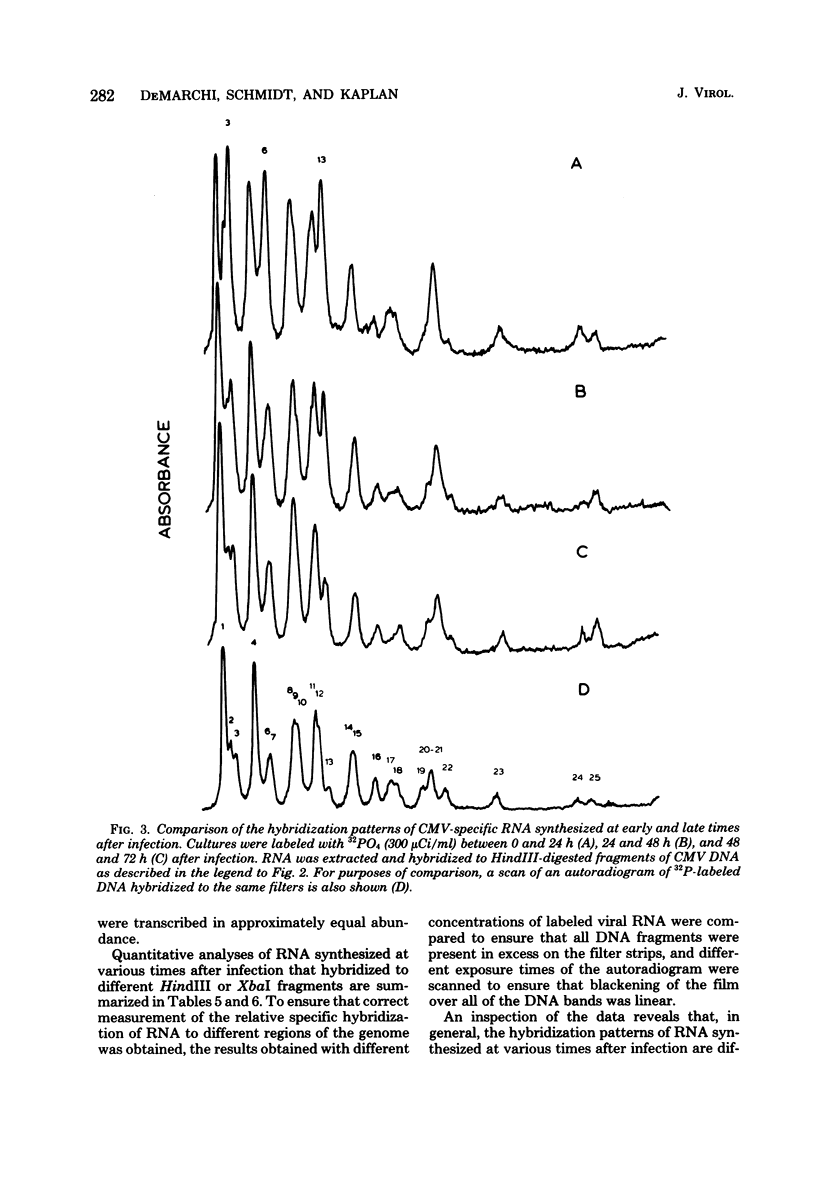
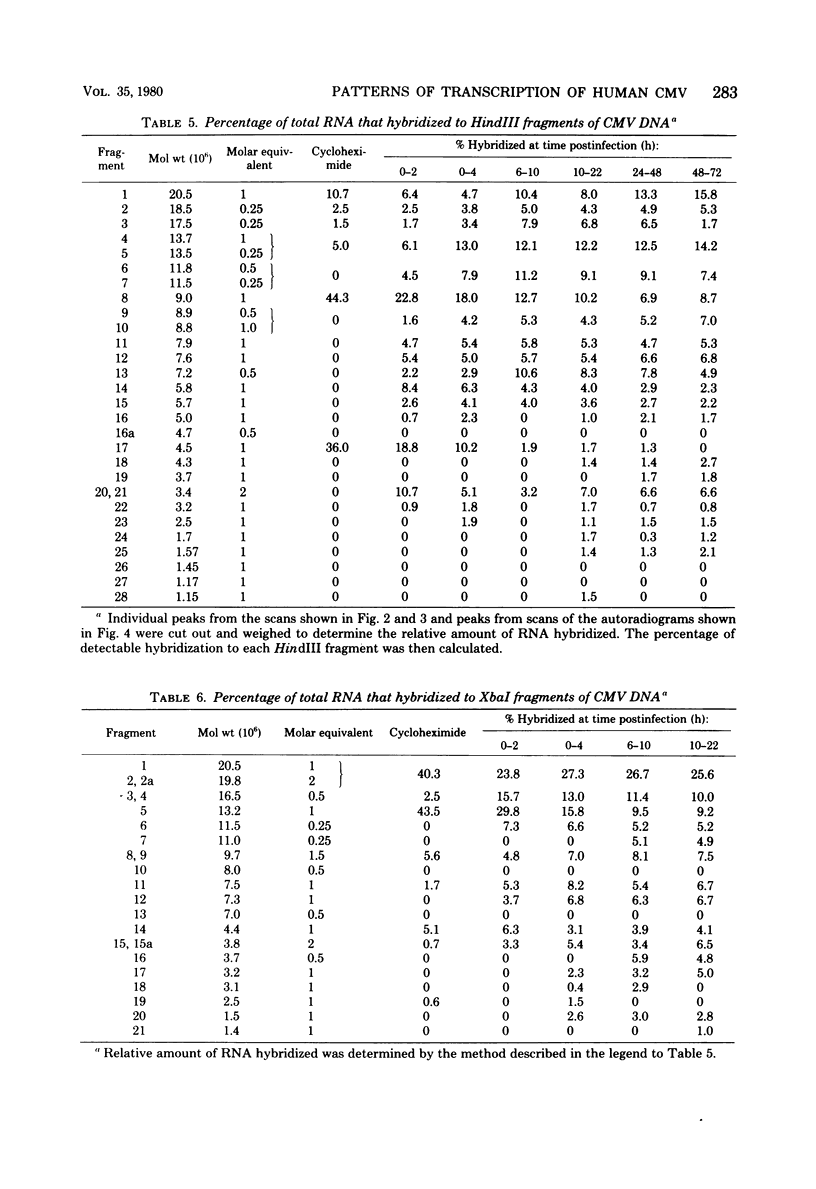
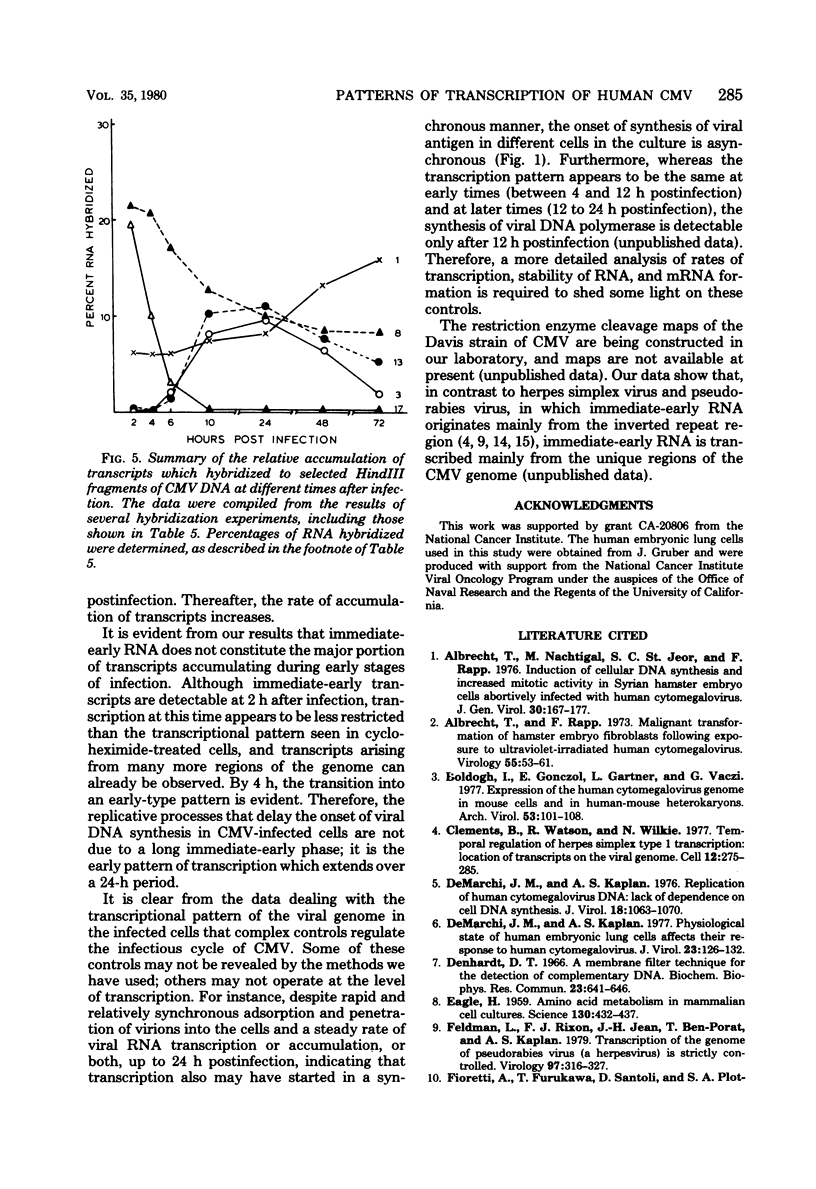
The rate of accumulation of cytomegalovirus transcripts in permissively infected human embryonic lung (HEL) cells was analyzed at various times after infection by hybridization of infected cell RNA to undigested or restriction endonuclease-digested cytomegalovirus DNA fixed to nitrocellulose filters. Differences in patterns of transcript accumulation were determined by measuring the abundance levels of RNA which hybridized to different HindIII-, XbaI-, or EcoRI-generated fragments of cytomegalovirus DNA. The results showed that a small but significant amount of cytomegalovirus RNA was detectable within the first 3 h after infection and that the rate of accumulation of these transcripts was static during the first 24 h, but increased thereafter. In general, the viral transcripts accumulating in infected cells could be divided into three classes. Immediate-early RNA (synthesized in the absence of protein synthesis in infected cells) hybridizes predominantly to a very restricted part of the genome and can be identified during the first 2 to 4 h postinfection. Early RNA (synthesized up to about 24 h after infection) originates from most regions of the genome but is characterized by the presence of transcripts which hybridize in great abundance to certain fragments. Late RNA (synthesized after 24 h, i.e., after the onset of viral DNA synthesis) hybridizes in approximately equal abundance to most regions of the viral genome. These results showed that a block in the transition from immediate-early to early RNA did not account for the extended period of time that elapses between the time of infection and the initiation of viral DNA synthesis. Interestingly, despite rapid adsorption and penetration and a static level of accumulation of transcripts in the cultures during the first 24 h, the number of cells that synthesized detectable amounts of viral antigens increased steadily during this time.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Nachtigal M., St Jeor S. C., Rapp F. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis and increased mitotic activity in syrian hamster embryo cells abortively infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):167–177. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., Gönczöl E., Gärtner L., Váczi G. Expression of the human cytomegalovirus genome in mouse cells and in human-mouse heterokaryons. Arch Virol. 1977;53(1-2):101–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01314851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Physiological state of human embryonic lung cells affects their response to human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.126-132.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus DNA: lack of dependence on cell DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1063-1070.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L., Rixon F. J., Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Transcription of the genome of pseudorabies virus (A herpesvirus) is strictly controlled. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Tanaka S., Plotkin S. A. Stimulation of macromolecular synethesis in guinea pig cells by human CMV. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):211–214. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Guerra A., Henle G. False negative and prozone reactions in tests for antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):751–754. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Chen S. T., Pagano J. S. Human cytomegalovirus. I. Purification and characterization of viral DNA. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1473–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1473-1481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeor S. C., Albrecht T. B., Funk F. D., Rapp F. Stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):353–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.353-362.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. E., Kaplan A. S. Synthesis of proteins in cells infected with herpesvirus. VII. Lack of migration of structural viral proteins to the nucleus of arginine-deprived cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson-Fiske S., Arnoult J., Febvre H. Growth of cytomegalovirus at supra-optimal temperatures. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):437–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson-Fiske S., Horodniceanu F., Guillon J. C. Immediate early antigens in human cytomegalovirus infected cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):615–617. doi: 10.1038/270615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakusanova T., Ben-Porat T., Himeno M., Kaplan A. S. Early functions of the genome of herpesvirus. I. Characterization of the RNA synthesized in cycloheximide-treated, infected cells. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):877–889. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Geder L., Murasko D., Lausch R., Ladda R., Huang E. S., Webber M. M. Long-term persistence of cytomegalovirus genome in cultured human cells of prostatic origin. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):982–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.982-990.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., de Harven E. Herpes simplex virus and human cytomegalovirus replication in WI-38 cells. II. An ultrastructural study of viral penetration. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):945–956. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.945-956.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Jeor S., Rapp F. Cytomegalovirus: conversion of nonpermissive cells to a permissive state for virus replication. Science. 1973 Sep 14;181(4104):1060–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4104.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Furukawa T., Plotkin S. A. Human cytomegalovirus stimulates host cell RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):297–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.297-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Otsuka M., Ihara S., Maeda F., Watanabe Y. Induction of pre-early nuclear antigen(s) in HEL cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(4):263–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]