Abstract
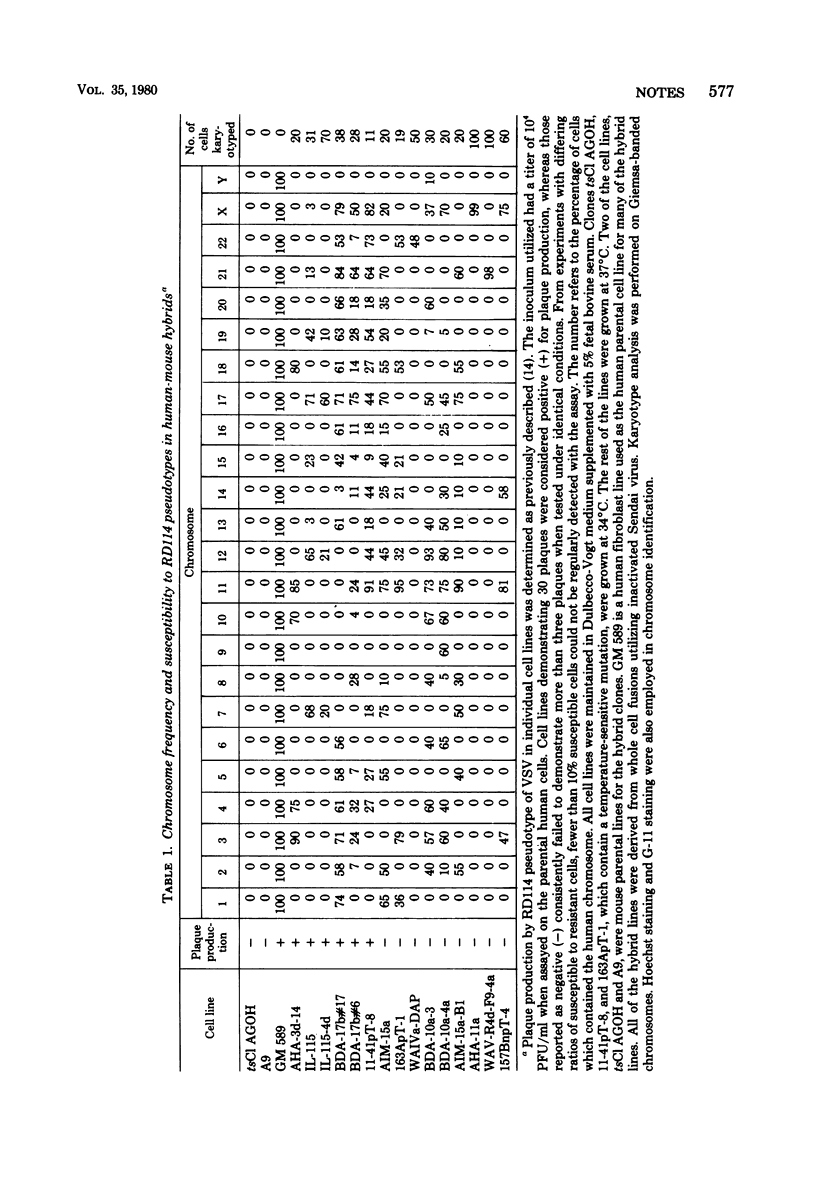
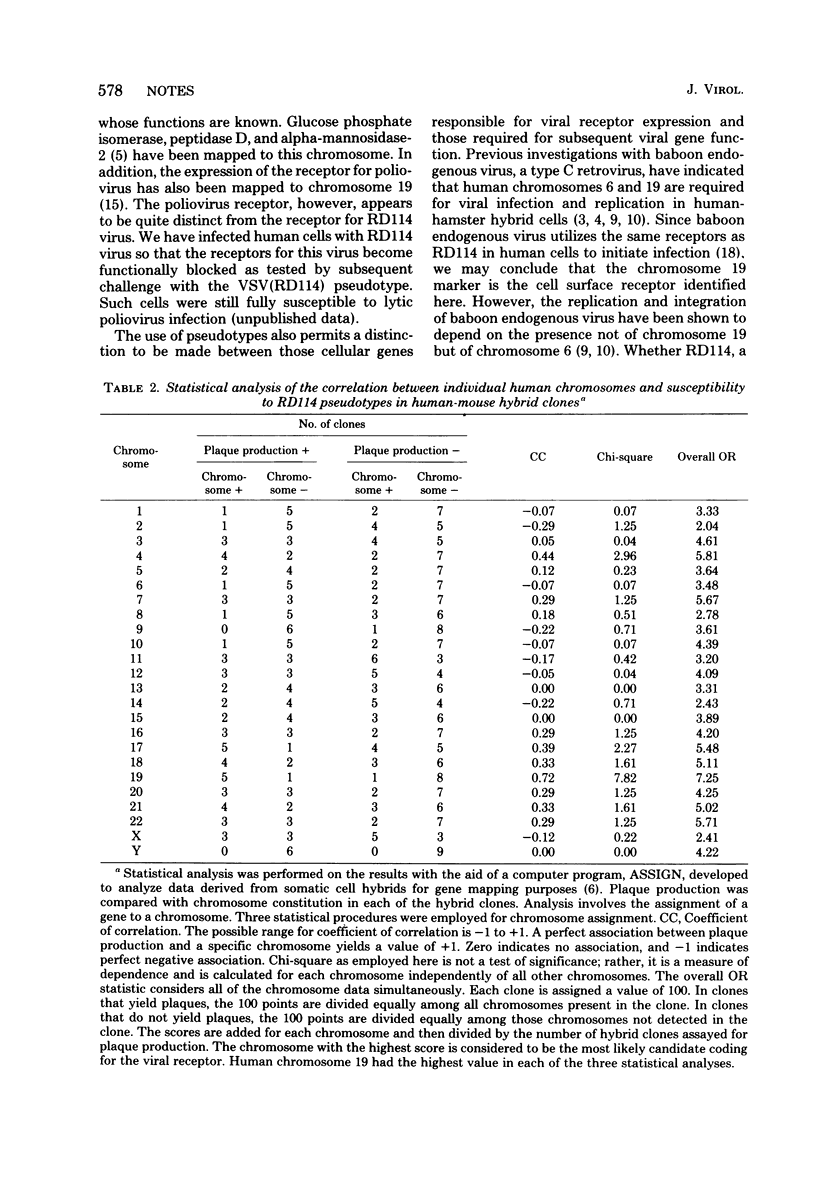
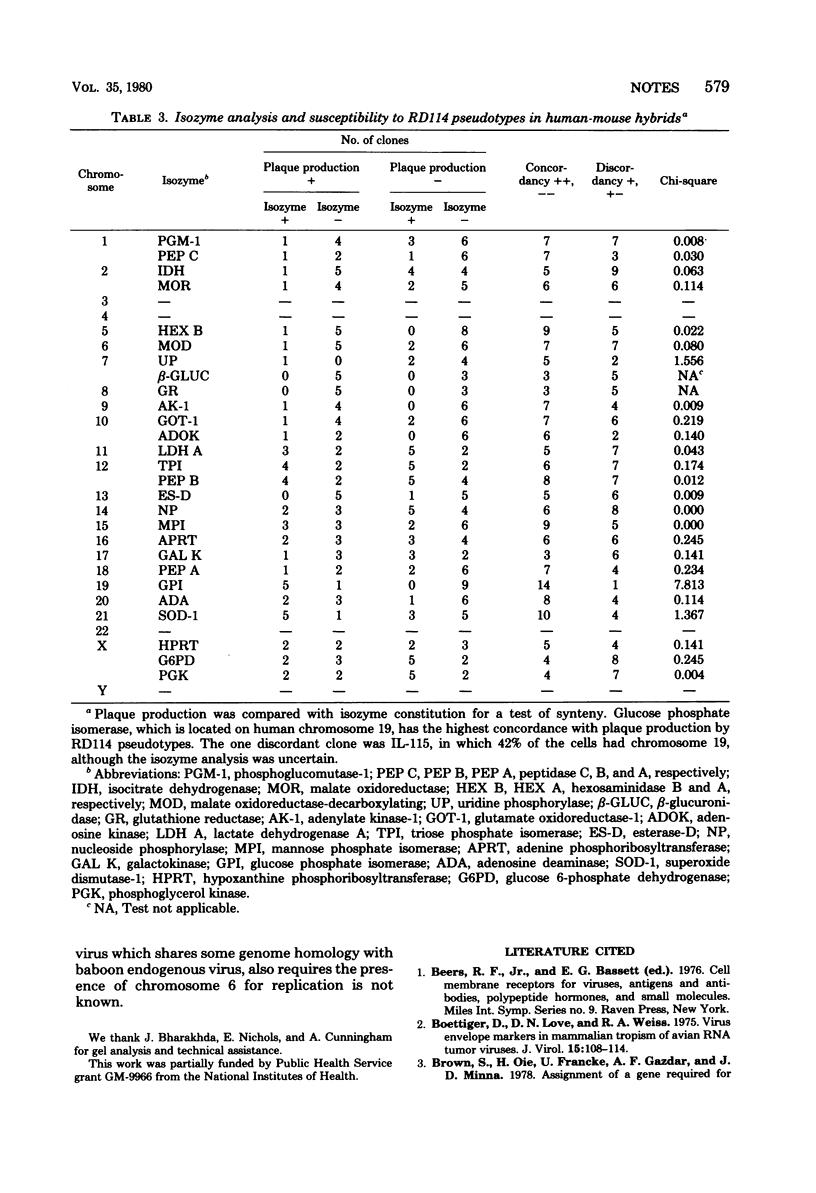
Vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotypes bearing envelope glycoproteins of the endogenous feline type C retrovirus, RD114, were used to assay the expression of receptors specific to RD114 on the surfaces of mouse-human hybrid cells carrying different human chromosomes. These studies show that the gene encoding the RD114 receptor is located on human chromosome 19.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boettiger D., Love D. N., Weiss R. A. Virus envelope markers in mammalian tropism of avian RNA tumor viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.108-114.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Francke U. Requirement of human chromosomes 19, 6 and possibly 3 for infection of hamster x human hybrid cells with baboon M7 type C virus. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Oie H., Francke U., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Assignment of a gene required for infection with endogenous baboon virus to human chromosome 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):239–242. doi: 10.1159/000130945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion M. J., Brown J. A., Shows T. B. Studies on the alpha-mannosidase (MANB), peptidase D (PEPD), and glucose phosphate isomerase (GPI) syntenic group on chromosome 19 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):186–189. doi: 10.1159/000130932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowmeadow M. P., Ruddle F. H. Computer-assisted statistical procedures for somatic cell gene assignment. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):694–697. doi: 10.1159/000131055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Stone H. A., Reamer R. H., Okazaki W. Two loci controlling genetic cellular resistance to avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):898–904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.898-904.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Oie H., Lalley P., Moss W. W., Minna J. D. Identification of mouse chromosomes required for murine leukemia virus replication. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):949–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemons R. S., Nash W. G., O'Brien S. J., Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J. A gene (Bevi) on human chromosome 6 is an integration site for baboon type C DNA provirus in human cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemons R. S., O'Brien S. J., Sherr C. J. A new genetic locus, Bevi, on human chromosome 6 which controls the replication of baboon type C virus in human cells. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic viruses: murine leukemia viruses associated with NIH Swiss, NZB, and other mouse strains. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Todaro G. J. Endogenous type C virus from a cat cell clone with properties distinct from previously described feline type C virus. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):142–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90473-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T. H., Rapp U. R. Genes controlling receptors for ecotropic and xenotropic type C virus in Mus cervicolor and Mus musculus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.501-506.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Nicolson M., Gardner M. B., Rasheed S., Rongey R. W., Hardy W. D., Jr, Gilden R. V. RD-114 virus compared with feline and murine type-C viruses released from RD cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 21;242(116):75–78. doi: 10.1038/newbio242075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Pani P. K., Weiss R. A. A dominant epistatic gene which inhibits cellular susceptibility to RSV(RAV-O). J Gen Virol. 1971 Dec;13(3):455–462. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Conta B. S., Leinwand L., Kozak C., Ruddle F., Besmer P., Baltimore D. Assignment of the receptor for ecotropic murine leukemia virus to mouse chromosome 5. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):451–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Weiss R. A., Zavada J. Pseudotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus with the envelope properties of mammalian and primate retroviruses. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):449–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.449-454.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallagher R. E., Gillespie D. H., Gallo R. C. Infective transmission and characterisation of a C-type virus released by cultured human myeloid leukaemia cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):551–555. doi: 10.1038/256551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada J. Viral pseudotypes and phenotypic mixing. Arch Virol. 1976;50(1-2):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01317996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



