Abstract
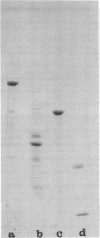
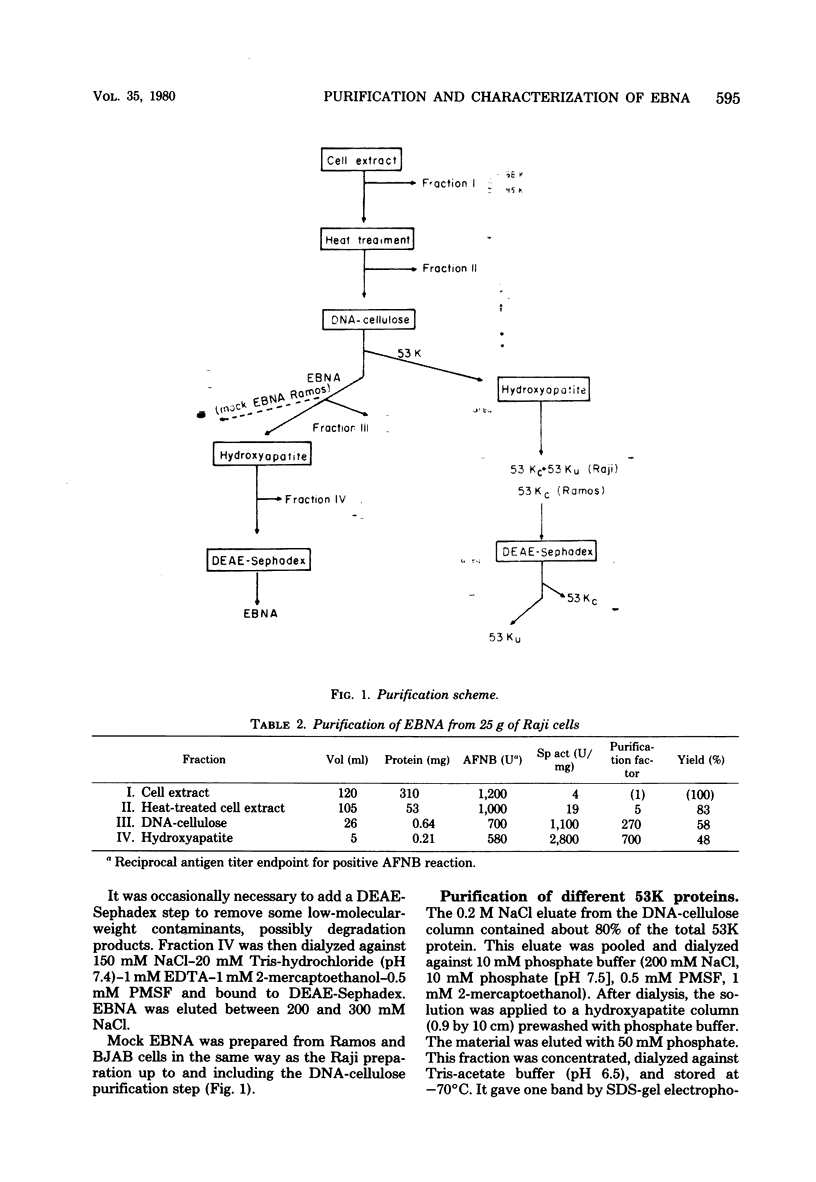
The Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) was purified 700-fold to apparent homogeneity from Raji and Namalwa cell extracts by a three-step procedure involving heat treatment, DNA-cellulose chromatography, and hydroxyapatite chromatography. Acid-fixed nuclear binding and complement fixation were used to monitor antigenic specificity. Purified EBNA was also capable of specifically inhibiting the regular anticomplement immunofluorescence reaction for EBNA against Raji target cells. The purified antigen had a molecular weight of 170,000 to 200,000. By sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, it yielded a single 48,000-dalton (48K) monomer. An EBNA-associated protein was also purified from the same cell extract. It had a molecular weight of about 200,000 and yielded a single 53K protein band by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The same protein was also found in Epstein-Barr virus negative B-cell lymphoma lines. The two types of protein were characterized by amino acid composition and peptide mapping. The results showed that the 53K and 48K protein components have no long regions in common; this excludes that the smaller product arises by breakdown of the larger product. Residue distributions were different, but an excess of hydrophilic residues was found in both proteins, suggesting a certain overall similarity in properties. 53K components from different cell lines appeared to differ somewhat. Epstein-Barr virus-positive lines carry two 53K components, one of which may be a slightly modified 53K product. Immunocomplexing assay showed that the 48K, but not the 53K, protein carries EBNA specificity. In mixtures, the 53K protein is co-precipitated with the 48K protein. The data suggest that EBNA may form a complex with the 53K proten within the cell.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. A., Pothier L., Hellerstein E. E., Boileau G. Malignant immunoblastoma: immunoglobulin synthesis and the progression to leukemia in heterotransplanted acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphatic leukemia, lymphoma, and infectious mononucleosis. Cancer. 1973 Jun;31(6):1397–1407. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197306)31:6<1397::aid-cncr2820310615>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron D., Strominger J. L. Partial purification and properties of the Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2875–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Jay G., Appella E., Dubois G. C., Law L. W., Old L. J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2420–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. L., Levy R., Kim H., Henle W., Henle G., Kaplan H. S. Biology of the human malignant lymphomas. IV. Functional characterization of ten diffuse histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. Cancer. 1978 Nov;42(5):2379–2391. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197811)42:5<2379::aid-cncr2820420539>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G., Barr Y. M., Zajac B., Henle G., Henle W. Morphological and virological investigations on cultured Burkitt tumor lymphoblasts (strain Raji). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Oct;37(4):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Nicolas R. H., Johns E. W. An improved large scale fractionation of high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):280–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L. Relationship between the sensitivity of EBV-carrying lymphoblastoid lines to superinfection and the inducibility of the resident viral genome. Int J Cancer. 1973 Mar 15;11(2):327–337. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Vonka V. Relationship between Epstein-Barr virus-determined complement-fixing antigen and nuclear antigen detected by anticomplement fluorescence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Dec;53(6):1645–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Zeuthen J., Terasaki P., Billing R., Honig R., Jondal M., Westman A., Clements G. Inducibility of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle and surface marker properties of EBV-negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):639–652. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G., Berthelon M. C., Favre M. C., de-Thé G. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus antigens. I. Biochemical analysis of the complement-fixing soluble antigen and relationship with Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):672–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.672-674.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Jörnvall H., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of the phosphorylated DNA-binding protein from adenovirus-type-2-infected cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. The SV40 A gene product is required for the production of a 54,000 MW cellular tumor antigen. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Purification of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.604-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Siegert W., Klein G. Solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen and its characterization as a DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.1-8.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Nishi S., Hirai H., Osato T. Studies on Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens. II. Biochemical properties of soluble antigen in Raji Burkitt lymphoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):364–370. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Luka J., Falk L., Klein G. Detection of a nuclear, EBNA-type antigen in apparently EBNA-negative Herpesvirus papio (HVP)-transformed lymphoid lines by the acid-fixed nuclear binding technique. Int J Cancer. 1977 Dec 15;20(6):941–946. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Identification of a purified complement-fixing antigen as the Epstein-Barr-virus determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) by its binding to metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills C., Jörnvall H. The two major isozymes of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beek W. P., Nilsson K., Klein G., Emmelot P. Cell surface glycoprotein changes in Epstein-Barr virus-positive and -negative human hematopoietic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1979 Apr 15;23(4):464–473. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]