Abstract
Friend murine leukemia virus (G-MuLV) is a helper-independent, type C retrovirus isolated from stocks of Friend virus complex (spleen focus-forming virus plus MuLV). In cell culture, F-MuLV has an ecotropic and NB-tropic host range and causes XC cells to fuse. When injected into newborn NIH Swiss mice, F-MuLV produces hepatosplenomegaly, severe anemia, and numerous circulating hematopoietic precursors in the peripheral blood with normal thymus and lymph nodes after 3 to 6 weeks. Recently, we molecularly cloned an 8.5-kilobase pair (kbp) form of F-MuLV DNA from which we could recover the pathogenic F-MuLV virus by DNA transfection of NIH 3T3 cells. From this molecularly cloned F-MuLV DNA, we have now subcloned in pBR322 a 4.1-kbp HindIII fragment which contains in continuity 3.0 kbp from the 3' terminus (env and c region), 0.6 kbp of the terminal repeat sequences, and 0.5 kbp from the 5'terminus of the viral RNA (genome). NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were transfected with this DNA fragment an then infected with the wild mouse amphotropic retrovirus (cl 1504-A). In cell culture, 1504-A is a helper-independent type C virus which has an N-tropic host range and does not cause fusion of XC cells. When injected into newborn NIH Swiss mice, 1504-A does not produce splenomegaly or thymic enlargement in mice held for up to 8 months. The transfection with the F-MuLV fragment and the infection with 1504-A consistently yielded virus preparations that were XC positive. From such virus stocks we were able to isolate both helper-independent and replication-defective XC-positive viruses. The helper-independent virus was shown to be a recombinant virus since it contains a gp70 molecule derived at least in part from F-MuLV and a specific gag precursor derived from 1504-A as determined by radioactive immune precipitation assays. When injected into newborn Swiss mice, the recombinant helper-independent virus caused hepatosplenomegaly in approximately 50% of the mice in 6 to 8 weeks. The histology of the diseased splenic tissue was indistinguishable from that seen in the disease caused by the whole F-MuLV. The replication-defective virus could be pseudotyped with new 1504-A virus, and this viral complex also caused the F-MuLV disease picture when the complex was injected into newborn Swiss mice. We conclude that the genetic information responsible for the pathogenicity of F-MuLV is contained within the 4.1-kbp DNA fragment, which includes env gene sequences, the terminal repeat sequences, and the c region sequences of the F-MuLV genome.
Full text
PDF


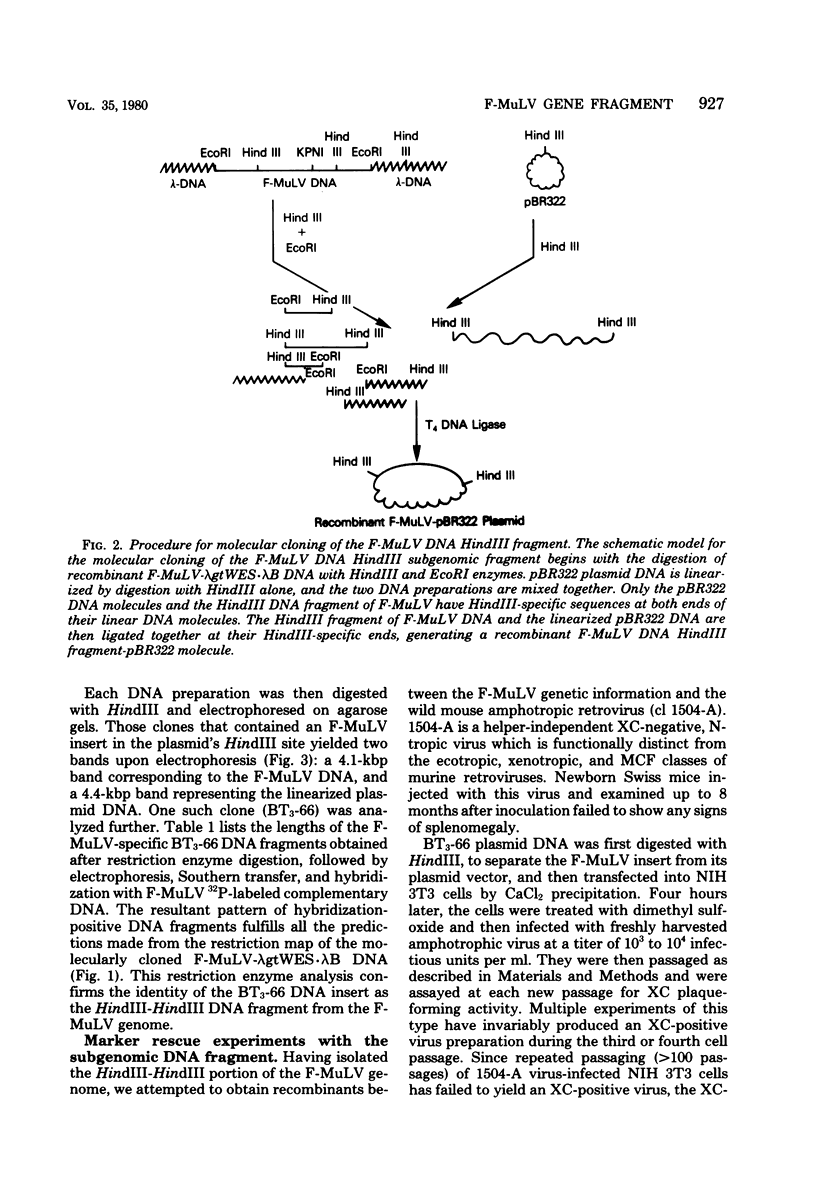


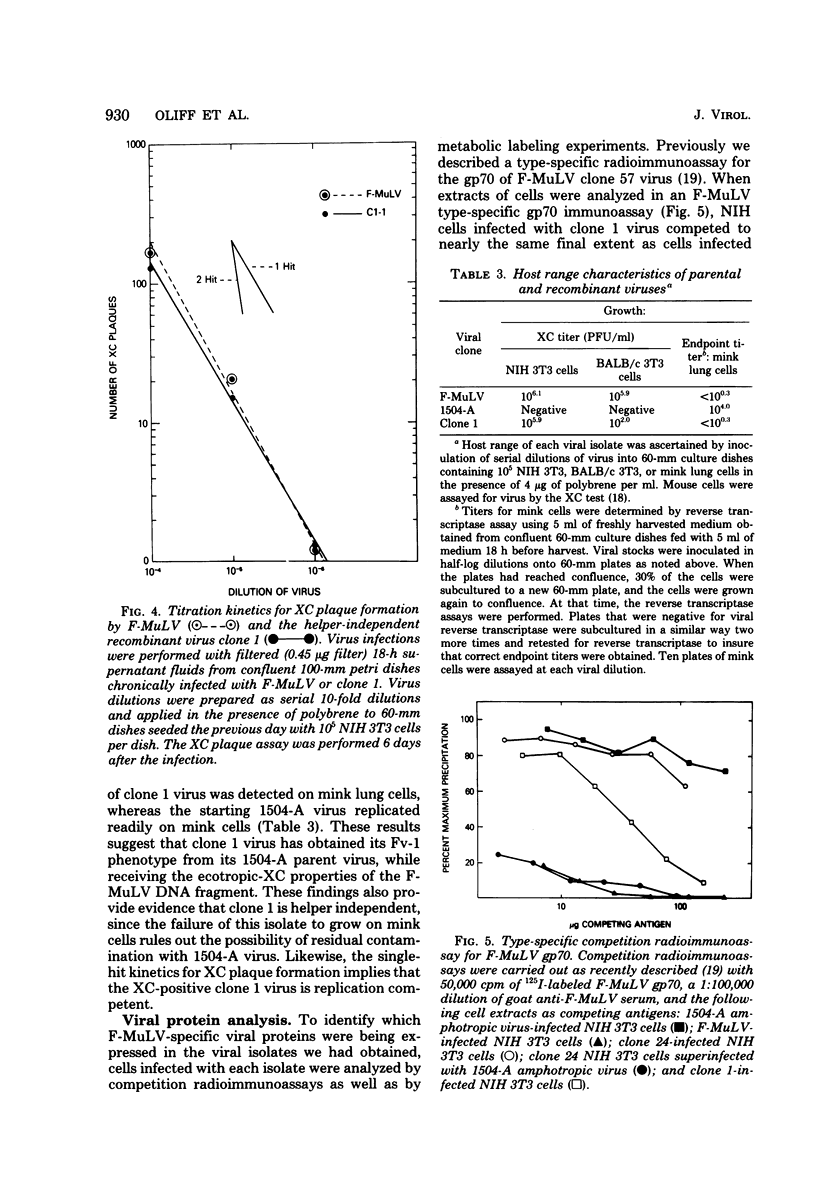
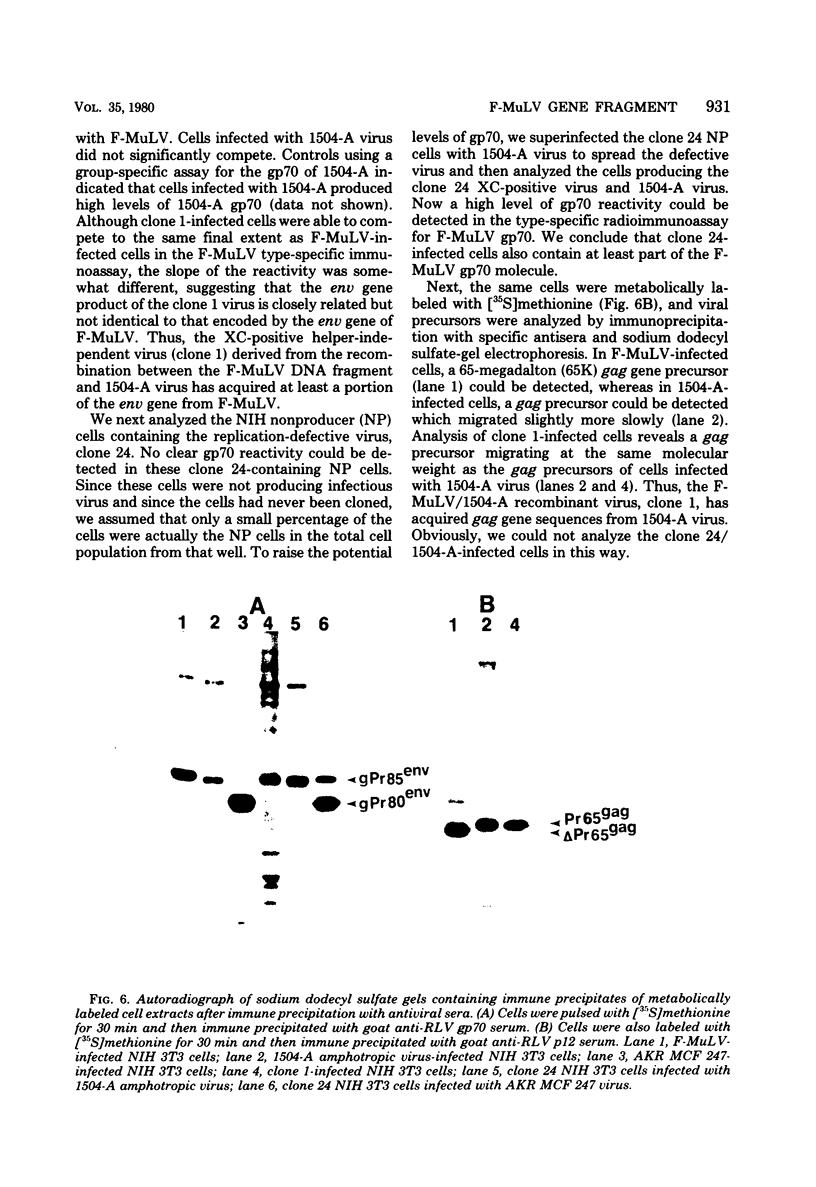




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. gag Gene of mammalian type-C RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):554–559. doi: 10.1038/262554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Verma I. M., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M., Davidson N. Heteroduplex analysis of the sequence relations between the RNAs of mink cell focus-inducing and murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.352-360.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H., Fadly A. M. Induction of neoplasms by subgroup E recombinants of exogenous and endogenous avian retroviruses (Rous-associated virus type 60). J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):915–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.915-919.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S. Size and genetic content of viral RNAs in avian oncovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):47–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.47-63.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R. H., Billeter M. A., Weissmann C. Mapping of biological functions on RNA of avian tumor viruses: location of regions required for transformation and determination of host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent transformation by unintegrated Harvey sarcoma virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.291-298.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Das S., Macdonnell D., McMillin-Helsel C. Organization of shared and unshared sequences in the genomes of chicken endogenous and sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A. L., Gerwin B. I., Bassin R. H., Schwarm L., Schidlovsky G. A replication-defective variant of Moloney murine leukemia virus. I. Biological characterization. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):146–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.146-156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Linemeyer D., Feild J., Troxler D., Scolnick E. M. Characterization of a protein found in cells infected with the spleen focus-forming virus that shares immunological cross-reactivity with the gp70 found in mink cell focus-inducing virus particles. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):787–798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.787-798.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Linemeyer D., Field J., Troxler D., Scolnick E. Type-specific radioimmunoassays for the gp70s of mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses: expression of a cross-reacting antigen in cells infected with the Friend strain of the spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):654–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E., Rands E., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity in five RNA viruses: divalent cation requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1789–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A. Editorial: Spleen focus-forming virus in Friend and Rauscher leukemia virus preparations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Feb;54(2):289–297. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Lowy D., Howk R., Young H., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus is a recombinant between ecotropic murine type C virus and the env gene region of xenotropic type C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4671–4675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Scolnick E. M. Rapid leukemia induced by cloned friend strain of replicating murine type-C virus. Association with induction of xenotropic-related RNA sequences contained in spleen focus-forming virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







