Abstract
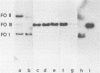
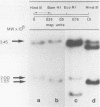
Bovine papilloma virus (BPV) appears to be the etiological agent of common equine connective tissue tumors. We investigated the physical state of the viral DNA within such tumors and found no indication for integration into the host genome. The BPV genomes were present as free circular episomes. Two equine sarcoids were shown to contain multiple copies of free circular BPV type 1 (BPV-1) DNA. When the tumors were digested with several single-cut restriction enzymes, there were only form III BPV-1 DNA sequences could be revealed. One of the sarcoids contained, apart from wild-type BPV-1 DNA, a class of smaller BPV-1 circular DNA molecules bearing a deletion of approximately 9% of the BPV-1 genome. This deletion is located in the physical map between the relative units 0 and 0.32.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK P. H., HARTLEY J. W., ROWE W. P., HUEBNER R. J. TRANSFORMATION OF BOVINE TISSUE CULTURE CELLS BY BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1963 Sep 7;199:1016–1018. doi: 10.1038/1991016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOIRON M., THOMAS M., CHENAILLE P. A BIOLOGICAL PROPERTY OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID EXTRACTED FROM BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1965 May;26:150–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Recent progress in Epstein-Barr virus research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:421–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett W. F., Murphy J., O'Neil B. W., Laird H. M. Virus-induced papillomas of the alimentary tract of cattle. Int J Cancer. 1978 Sep 15;22(3):323–328. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Olson C. Demonstration of two distinct classes of bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):372–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Olson C., Meinke W. Bovine papilloma virus: presence of virus-specific DNA sequences in naturally occurring equine tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):524–528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D. Physical maps of bovine papillomavirus type 1 and type 2 genomes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):684–687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.684-687.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Theilen G. H., Olson C. Hybridization of bovine papilloma virus type 1 and type 2 DNA to DNA from virus-induced hamster tumors and naturally occurring equine tumors. Intervirology. 1979;11(4):227–233. doi: 10.1159/000149038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meischke H. R. Experimental transmission of bovine papilloma virus (BPV) extracted from morphologically distinct teat and cutaneous lesions and the effects of inoculation of BPV transformed fetal bovine cells. Vet Rec. 1979 Apr 21;104(16):360–366. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.16.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON C., Jr, COOK R. H. Cutaneous sarcoma-like lesions of the horse caused by the agent of bovine papilloma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jun;77(2):281–284. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H., Linz U., Gissmann L., Huchthausen B., Hoffmann D., Zur Hausen H. Partial characterization of a new type of bovine papilloma viruses. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Krieg P., Pernfuss M., Sauer E., Eisinger V., Sauer G. Growth dynamics of a latent primate papovavirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):865–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.865-875.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS M., BOIRON M., TANZER J., LEVY J. P., BERNARD J. IN VITRO TRANSFORMATION OF MICE CELLS BY BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1964 May 16;202:709–710. doi: 10.1038/202709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Linke H., Miyamura T., Fareed G. C. Persistent BK papovavirus infection of transformed human fetal brain cells. I. Episomal viral DNA in cloned lines deficient in T-antigen expression. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1177–1185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1177-1185.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. L. Transmission of equine sarcoid. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Feb;30(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]