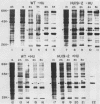
Abstract
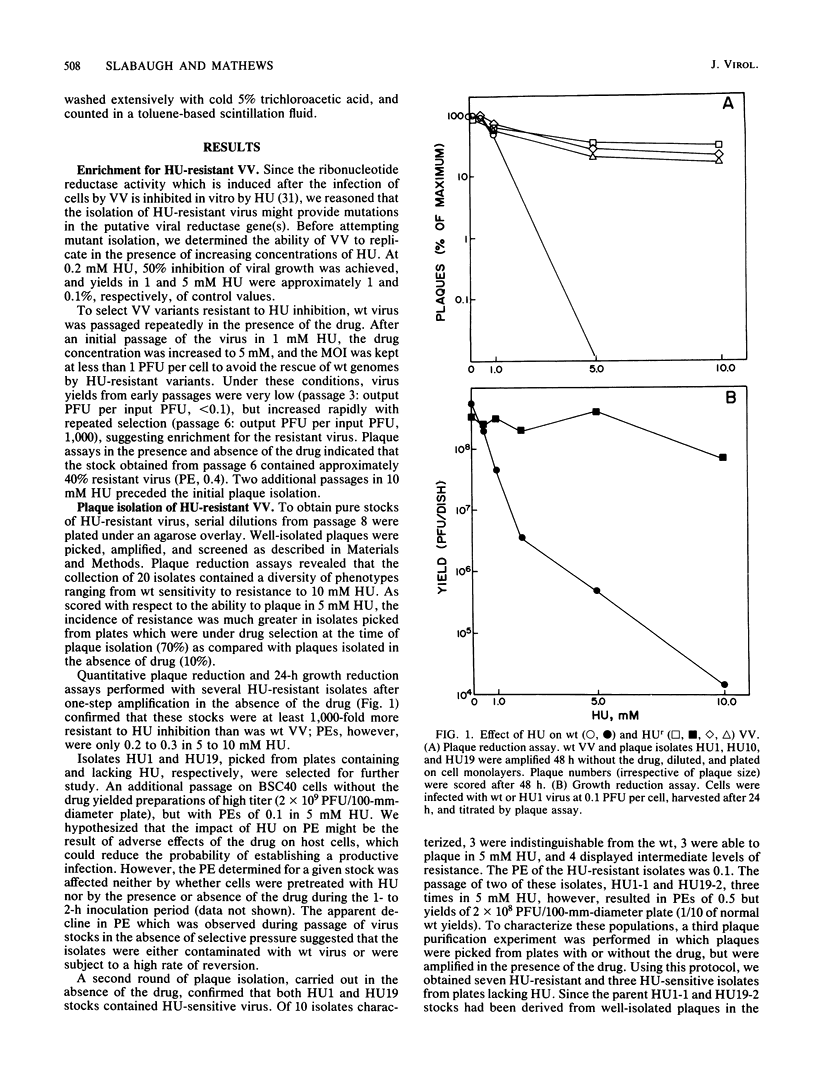
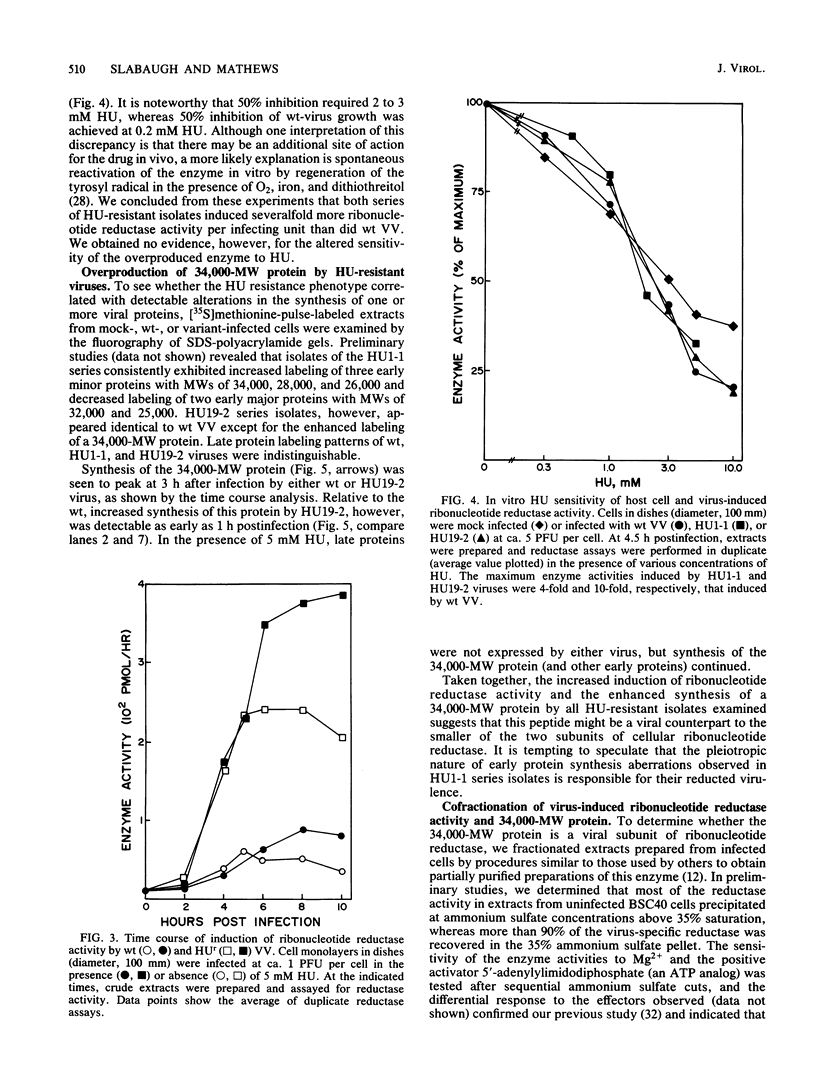
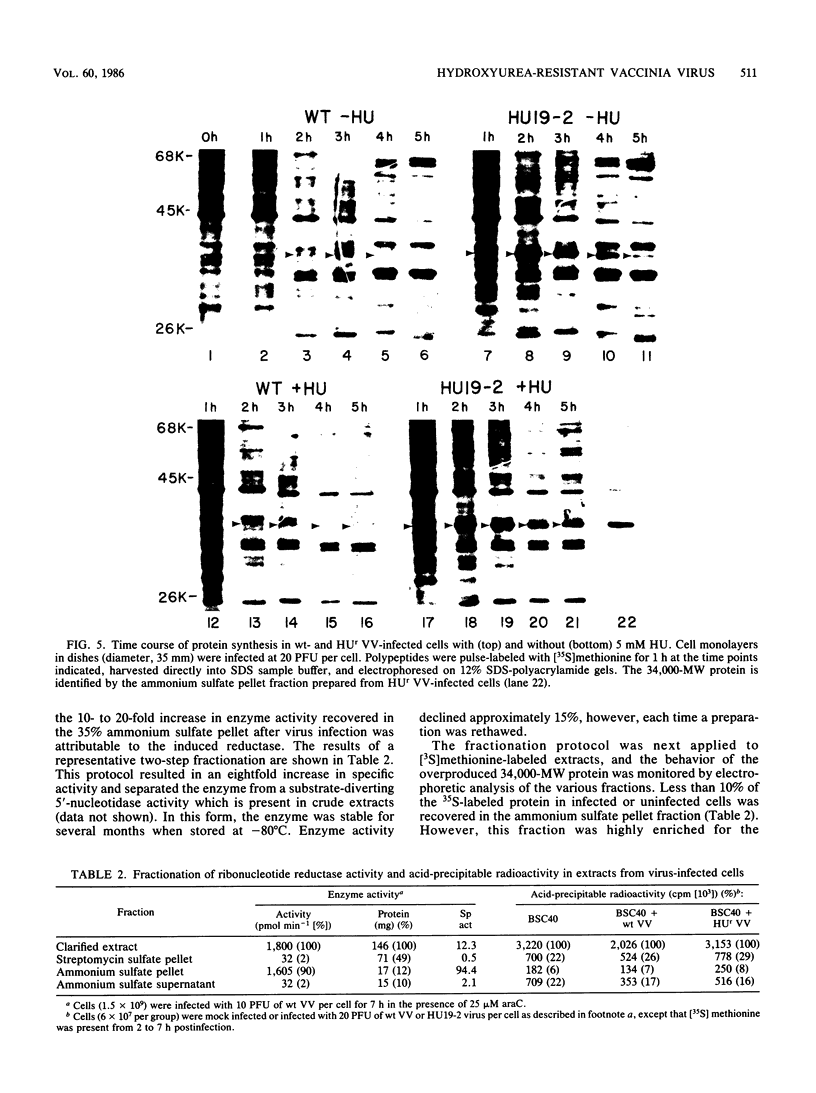
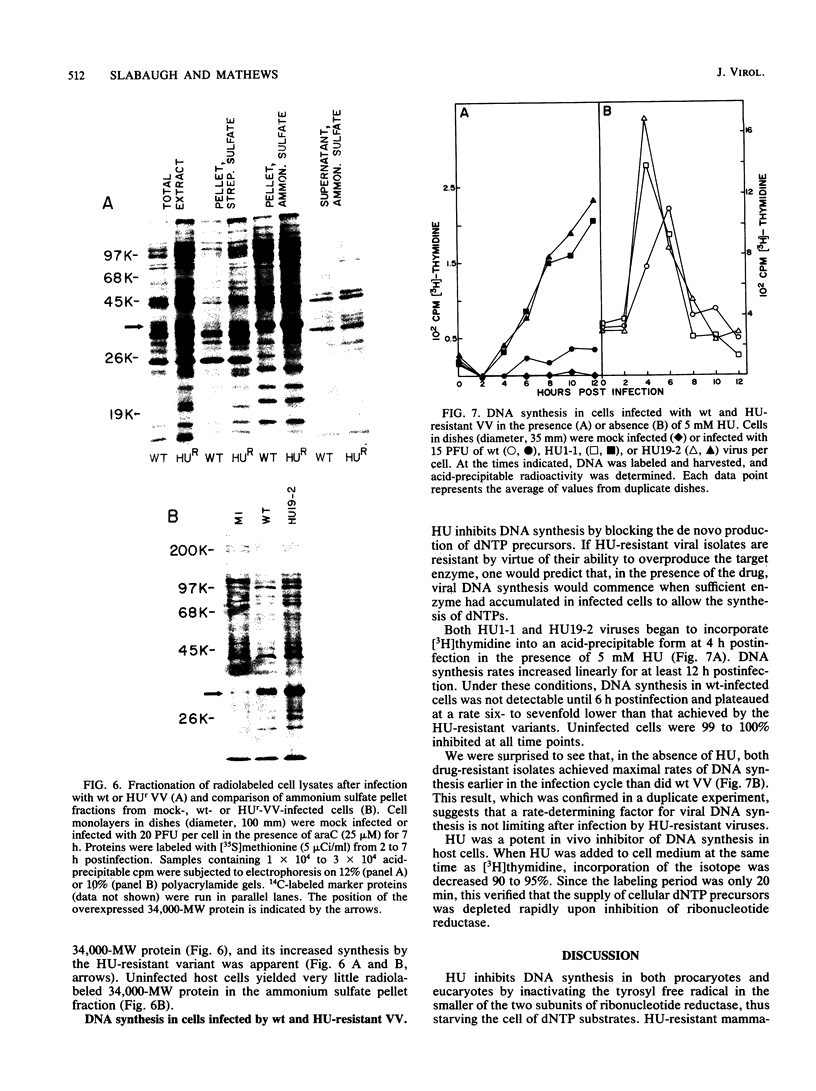
Repeated passages of vaccinia virus in increasing concentrations of hydroxyurea followed by plaque purification resulted in the isolation of variants capable of growth in 5 mM hydroxyurea, a drug concentration which inhibited the reproduction of wild-type vaccinia virus 1,000-fold. Analyses of viral protein synthesis by using [35S]methionine pulse-labeling at intervals throughout the infection cycle revealed that all isolates overproduced a 34,000-molecular-weight (MW) early polypeptide. Measurement of ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase (EC 1.17.4.1) activity after infection indicated that 4- to 10-fold more activity was induced by hydroxyurea-resistant viruses than by the wild-type virus. A two-step partial purification which yielded greater than 90% of the induced ribonucleotide reductase activity in the fraction obtained by 35% saturation with ammonium sulfate resulted in a substantial enrichment for the 34,000-MW protein from extracts of wild-type and hydroxyurea-resistant-virus-infected, but not mock-infected, cells. In the presence of the drug, the isolates incorporated [3H]thymidine into DNA earlier and at a rate substantially greater than that of the wild type, although the onset of DNA synthesis was delayed in both cases. In the absence of the drug, the attainment of a maximum viral DNA synthesis rate was accelerated after infection by drug-resistant isolates. The drug resistance trait was markedly unstable in all isolates. In the absence of selective pressure, plaque-purified isolates readily segregated progeny that displayed a wide range of resistance phenotypes. The results of this study indicate that vaccinia virus encodes a subunit of ribonucleotide reductase which is a 34,000-MW early protein whose overproduction confers hydroxyurea resistance on reproducing viruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchetti S., Evelegh M. J., Muirhead B., Sartori C. S., Huszar D. Immunological characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 polypeptide(s) involved in viral ribonucleotide reductase activity. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):591–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.591-593.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W. R., Ressner E. C., Kates J., Patzke J. V. A DNA nicking-closing enzyme encapsidated in vaccinia virus: partial purification and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1841–1845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Tanaka S., Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. Intracellular localization of human DNA polymerase alpha with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8391–8396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Tlsty T. D., Schimke R. T. Enhancement of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by treatment of mouse 3T6 cells with hydroxyurea. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1097–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Levinson B. B., Fabry M., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloned mouse ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 cDNA reveals amino acid sequence homology with Escherichia coli and herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7015–7022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus has a virus-specified constituent. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):513–521. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford H. L., Freese M., Passamani E., Morris H. P. Ribonucleotide reductase and cell proliferation. I. Variations of ribonucleotide reductase activity with tumor growth rate in a series of rat hepatomas. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5228–5233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström Y., Eriksson S., Jildevik I., Skog S., Thelander L., Tribukait B. Cell cycle-dependent expression of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Differential regulation of the two subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9114–9116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström Y., Rozell B., Hansson H. A., Stemme S., Thelander L. Localization of ribonucleotide reductase in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Gräslund A., Skog S., Thelander L., Tribukait B. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. The S phase-correlated increase in subunit M2 is regulated by de novo protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11695–11700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Martin D. W., Jr Ribonucleotide reductase in cultured mouse lymphoma cells. Cell cycle-dependent variation in the activity of subunit protein M2. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9436–9440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Stockwell P., Ginsburg M., Barrell B. Homology between two EBV early genes and HSV ribonucleotide reductase and 38K genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5087–5099. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Control of expression of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.456-464.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Guarino L. A., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication. I. Requirement for the host-cell nucleus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):705–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.705-715.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K., BECKER Y. THE REPLICATION AND COATING OF VACCINIA DNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:452–474. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. V., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene by marker rescue and cell-free translation of selected RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.72-77.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeds J. M., Slabaugh M. B., Mathews C. K. DNA precursor pools and ribonucleotide reductase activity: distribution between the nucleus and cytoplasm of mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3443–3450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Srinivasan P. R. Chromosome-mediated gene transfer of hydroxyurea resistance and amplification of ribonucleotide reductase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. DNA sequence homology between two co-linear loci on the HSV genome which have different transforming abilities. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1953–1961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Cooper N. Genetic evidence for vaccinia virus-encoded DNA polymerase: isolation of phosphonoacetate-resistant enzyme from the cytoplasm of cells infected with mutant virus. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):673–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.673-678.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H., Follett E. A. Vaccinia virus replication in enucleate BSC-1 cells: particle production and synthesis of viral DNA and proteins. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.488-493.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddar S. K., Bauer W. R. Type I topoisomerase activity after infection of enucleated, synchronized mouse L cells by vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.433-437.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Kates J. Viral-specific polypeptides associated with newly replicated vaccinia DNA. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):128–139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90184-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M., Kates J., Kirkpatrick J. B. Replication of vaccinia virus DNA in enucleated L-cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P., Ehrenberg A. Ribonucleotide reductase--a radical enzyme. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):514–519. doi: 10.1126/science.6306767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg B. M., Eklund H., Fuchs J. A., Carlson J., Standart N. M., Ruderman J. V., Bray S. J., Hunt T. Identification of the stable free radical tyrosine residue in ribonucleotide reductase. A sequence comparison. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 8;183(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80962-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Johnson T. L., Mathews C. K. Vaccinia virus induces ribonucleotide reductase in primate cells. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Mathews C. K. Vaccinia virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase can be distinguished from host cell activity. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.501-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloski M. J., Esteban M., Holowczak J. A. DNA-binding proteins in the cytoplasm of vaccinia virus-infected mouse L-cells. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):263–273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.263-273.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar P., Condit R. C. Selection for temperature-sensitive mutations in specific vaccinia virus genes: isolation and characterization of a virus mutant which encodes a phosphonoacetic acid-resistant, temperature-sensitive DNA polymerase. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):444–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traktman P., Sridhar P., Condit R. C., Roberts B. E. Transcriptional mapping of the DNA polymerase gene of vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.125-131.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal E. C., Hruby D. E. Mapping the genomic location of the gene encoding alpha-amanitin resistance in vaccinia virus mutants. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):65–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.65-70.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal E. C., Roseman N. A., Hruby D. E. Isolation of vaccinia virus mutants capable of replicating independently of the host cell nucleus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.359-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. A. Altered forms of mammalian nucleoside diphosphate reductase from mutant cell lines. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;22(1):81–102. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]