Abstract
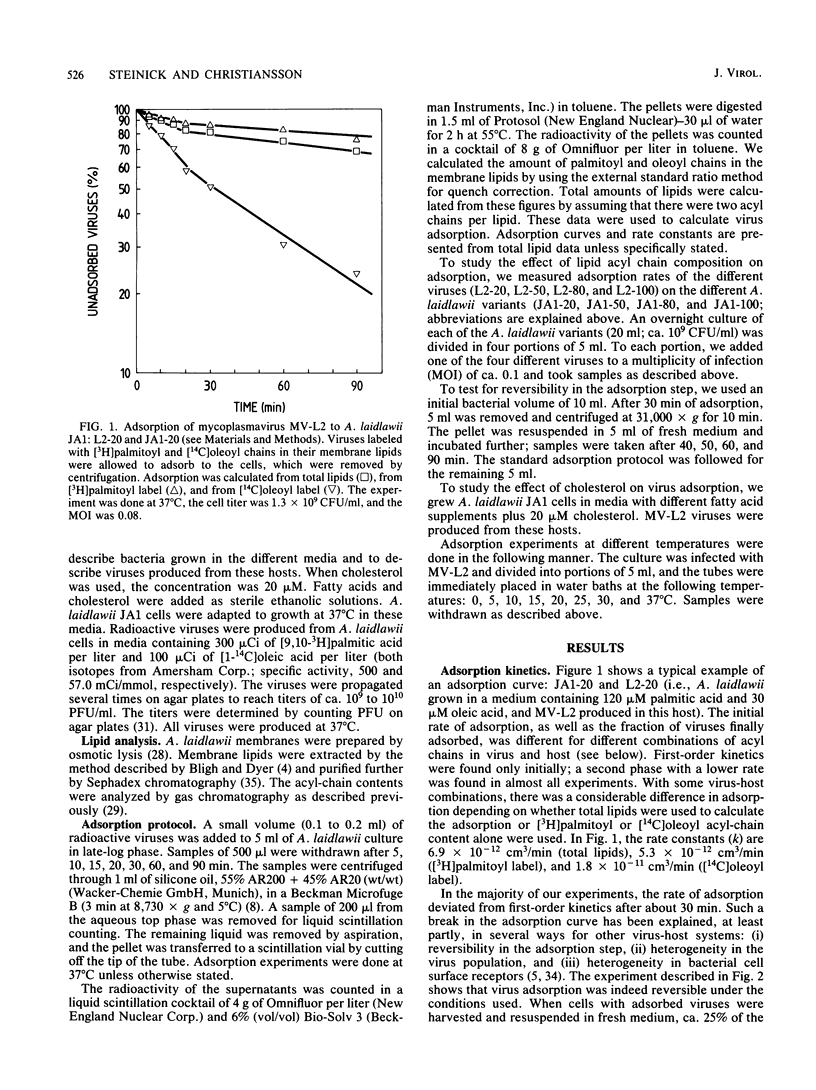
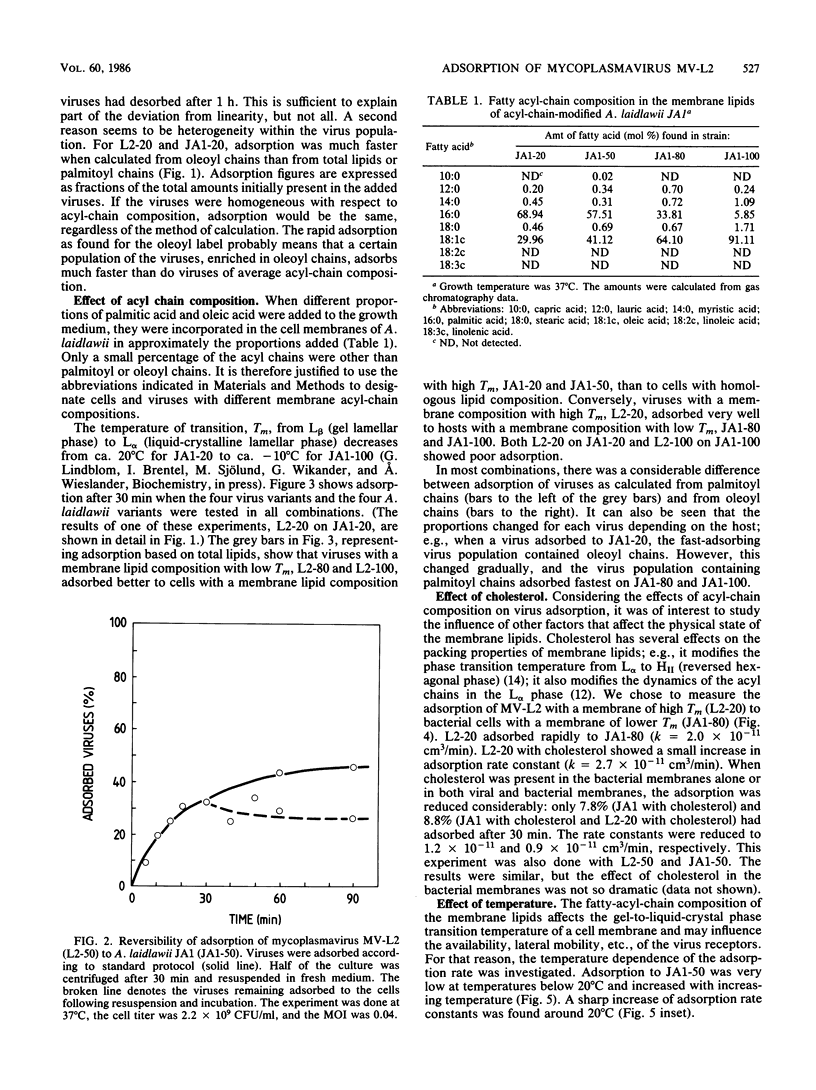
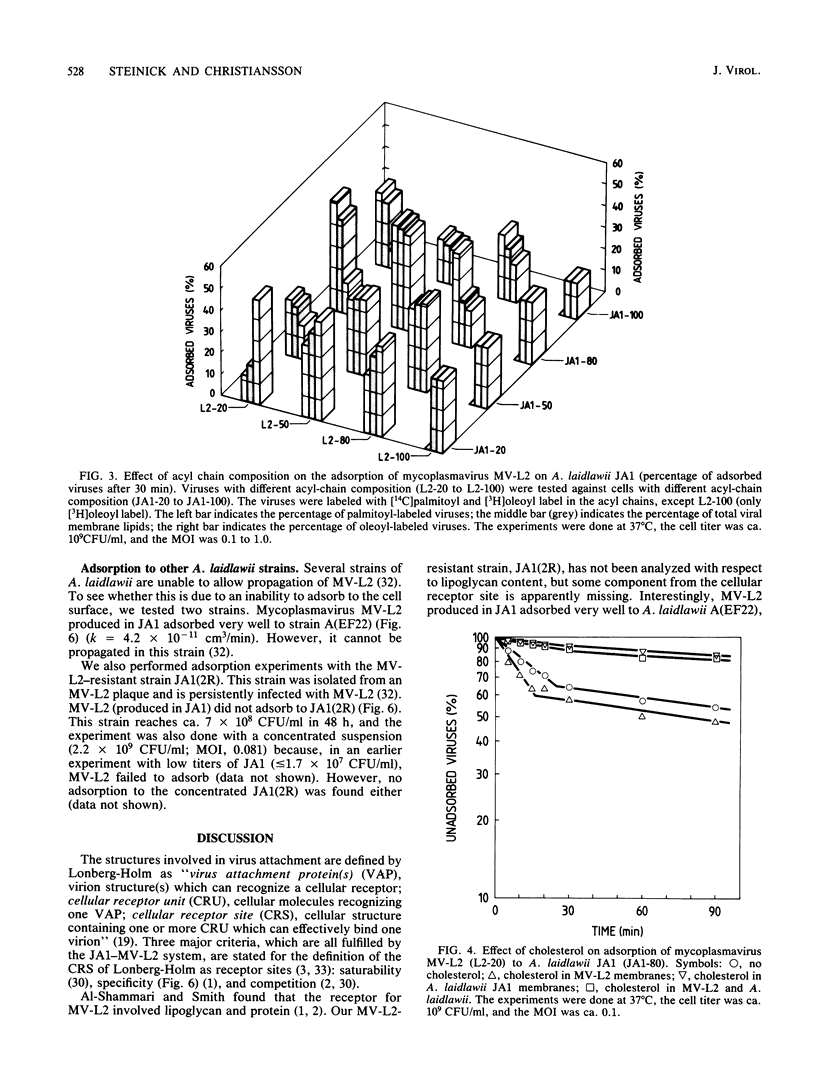
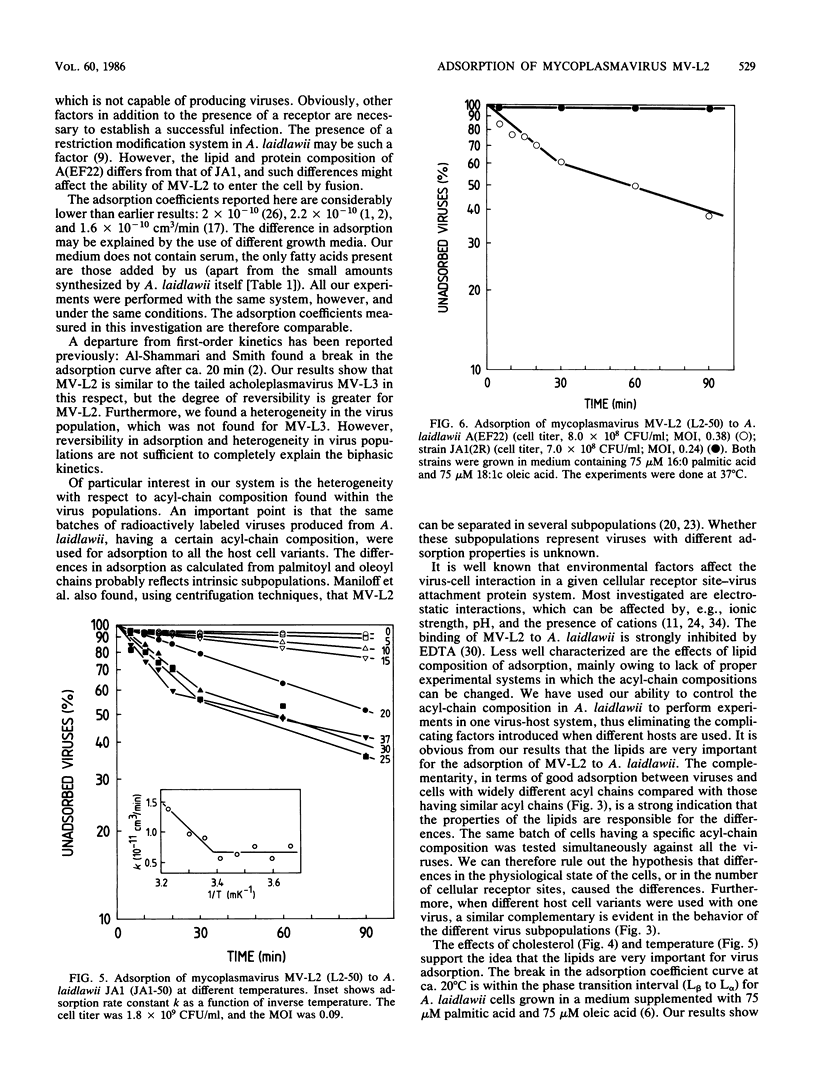
The enveloped mycoplasmavirus MV-L2 and its host Acholeplasma laidlawii JA1 were used to study the ways in which changes in the membrane lipid bilayer affect virus adsorption. The physical state of the membranes was altered by (i) using viruses and bacteria with different membrane lipid acyl-chain compositions, (ii) using incorporation of cholesterol, and (iii) changing the temperature. Adsorption of viruses was strongly dependent on the acyl-chain composition of the virus and the host. Adsorption to homologous hosts was poor, whereas adsorption to hosts with highly different membrane lipid acyl-chain composition was much stronger. We found a heterogeneity within virus populations produced from hosts with different acyl-chain compositions. In a given virus population, various subpopulations differing in acyl-chain composition were found that differed in their ability to adsorb to cells with a specific acyl-chain composition. The adsorption rate increased slightly when cholesterol was present in the viral membranes but decreased considerably when cholesterol was present in the bacterial membranes. The rate of adsorption was temperature dependent with an increase in adsorption rate above 20 degrees C (for hosts with equal amounts of palmitoyl and oleoyl acyl chains). MV-L2 did not adsorb to the persistently L2-infected strain JA1(2R) but adsorbed very well to the virus-resistant strain A(EF22). The physicochemical properties of the lipid matrix of both virus and host are obviously important factors in the adsorption process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Shammari A. J., Smith P. F. Interaction of mycoplasma virus type 2 with cellular components of Acholeplasma laidlawii strain JA1. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):120–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.120-124.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shammari A. J., Smith P. F. Receptor sites for mycoplasmal viruses on Acholeplasma laidlawii. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S109–S114. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. R. The kinetics of reversible and irreversible attachment of bacteriophage T-1. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):727–737. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansson A., Wieslander A. Control of membrane polar lipid composition in Acholeplasma laidlawii a by the extent of saturated fatty acid synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansson A., Wieslander A. Membrane lipid metabolism in Acholeplasma laidlawii A EF 22. Influence of cholesterol and temperature shift-down on incorporation of fatty acids and synthesis of membrane lipid species. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementz T., Christiansson A., Wieslander A. Transmembrane electrical potential affects the lipid composition of Acholeplasma laidlawii. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):823–830. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybvig K., Swinton D., Maniloff J., Hattman S. Cytosine methylation of the sequence GATC in a mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1420-1424.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D., Fleischmann C. Interaction of mycoplasma with viruses. I. Primary adsorption of virus is ionic in mechanism. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1067-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., PUCK T. T. The first two steps of the invasion of host cells by bacterial viruses. II. J Exp Med. 1951 Sep;94(3):177–189. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberer K., Maniloff J. Adsorption of the tailed mycoplasma virus L3 to cell membranes. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):501–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.501-507.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Rilfors L., Wieslander A., Lindblom G. The effect of cholesterol on the phase structure of glucolipids from Acholeplasma laidlawii membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(2):215–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Lipids of plasma membranes of monkey and hamster kidney cells and of parainfluenza virions grown in these cells. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):255–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Plasma membrane lipids and parainfluenza virus assembly. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss A., Heiland R. A. Characterization of the enveloped plasmavirus MVL2 after propagation on three Acholeplasma laidlawii hosts. Arch Virol. 1983;75(1-2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01314132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss A., Maniloff J. Infection of Acholeplasma laidlawii by MVL51 virus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Cadden S. P., Putzrath R. M. Maturation of an enveloped budding phage: mycoplasmavirus L2. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;64:503–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Das J., Christensen J. R. Viruses of mycoplasmas and spiroplasmas. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:343–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Haberer K., Gourlay R. N., Das J., Cole R. Mycoplasma viruses. Intervirology. 1982;18(4):177–188. doi: 10.1159/000149323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., GAREN A., CLINE J. The mechanism of virus attachment to host cells. I. The role of ions in the primary reaction. J Exp Med. 1951 Jan;93(1):65–88. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddar S. K., Cadden S. P., Das J., Maniloff J. Heterogeneous progeny viruses are produced by a budding enveloped phage. Intervirology. 1985;23(4):208–221. doi: 10.1159/000149607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzrath R. M., Cadden S. P., Maniloff J. Effect of cell membrane composition on the growth and composition of a nonlytic enveloped mycoplasmavirus. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):162–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzrath R. M., Maniloff J. Growth of an enveloped mycoplasmavirus and establishment of a carrier state. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.308-314.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilfors L., Wieslander A., Ståhl S. Lipid and protein composition of membranes of Bacillus megaterium variants in the temperature range 5 to 70 degrees C. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1043-1052.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Greenberg N. Binding of MVL-2 virus to A. laidlawii cells. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):765–769. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinick L. E., Wieslander A. Effects of acyl chain composition on production of mycoplasmavirus MV-L2 by Acholeplasma laidlawii. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinick L. E., Wieslander A., Johansson K. E., Liss A. Membrane composition and virus susceptibility of Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1200–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1200-1207.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOLMACH L. J. Attachment and penetration of cells by viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1957;4:63–110. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Weiner H. L. Interaction of viruses with cell surface receptors. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;80:27–61. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60366-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLS M. A., DITTMER J. C. THE USE OF SEPHADEX FOR THE REMOVAL OF NONLIPID CONTAMINANTS FROM LIPID EXTRACTS. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1259–1263. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander A., Christiansson A., Rilfors L., Lindblom G. Lipid bilayer stability in membranes. Regulation of lipid composition in Acholeplasma laidlawii as governed by molecular shape. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3650–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander A., Rilfors L. Qualitative and quantitative variations of membrane lipid species in Acholeplasma laidlawii A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 18;466(2):336–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


