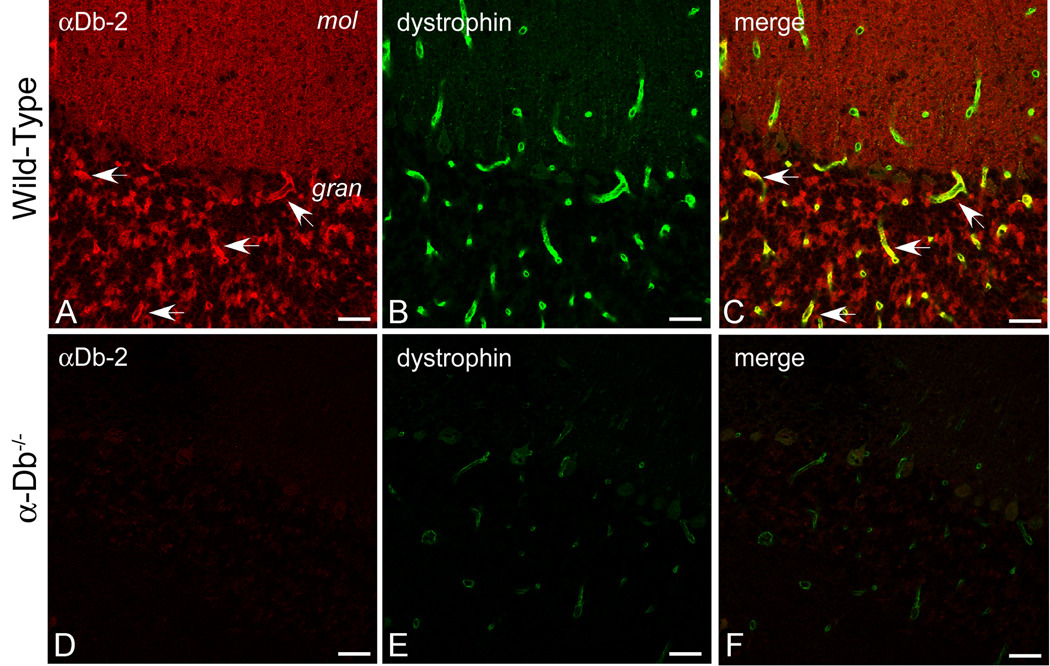
Figure 3. Dystrophin is Reduced at the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Absence of α-Dystrobrevin.
We performed double-immunolabeling for α-dystrobrevin-2 (red, A, D) and dystrophin (green, B, E) in wild type (A–C) and α-dystrobrevin-null (D–F) adult mouse cerebellum. αDB-2 is restricted to the blood-brain barrier in the granular layer of cerebellum (see arrows, A), whereas dystrophin localizes to the blood-brain barrier throughout the cerebellar cortex (B). In α-dystrobrevin null cerebellum (D–F), labeling for αDB-2 is absent (D), and immunolocalization of dystrophin is reduced (E). Arrows in C denote co-localization of αDB-2 and dystrophin in the granular layer of cerebellum. C and F are merged images of [A, B] and [D, E], respectively. mol, molecular layer; gran, granular layer. Scale bar, 25 µm.