Abstract
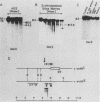
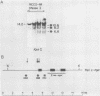
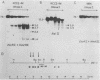
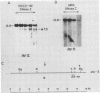
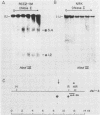
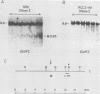
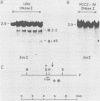
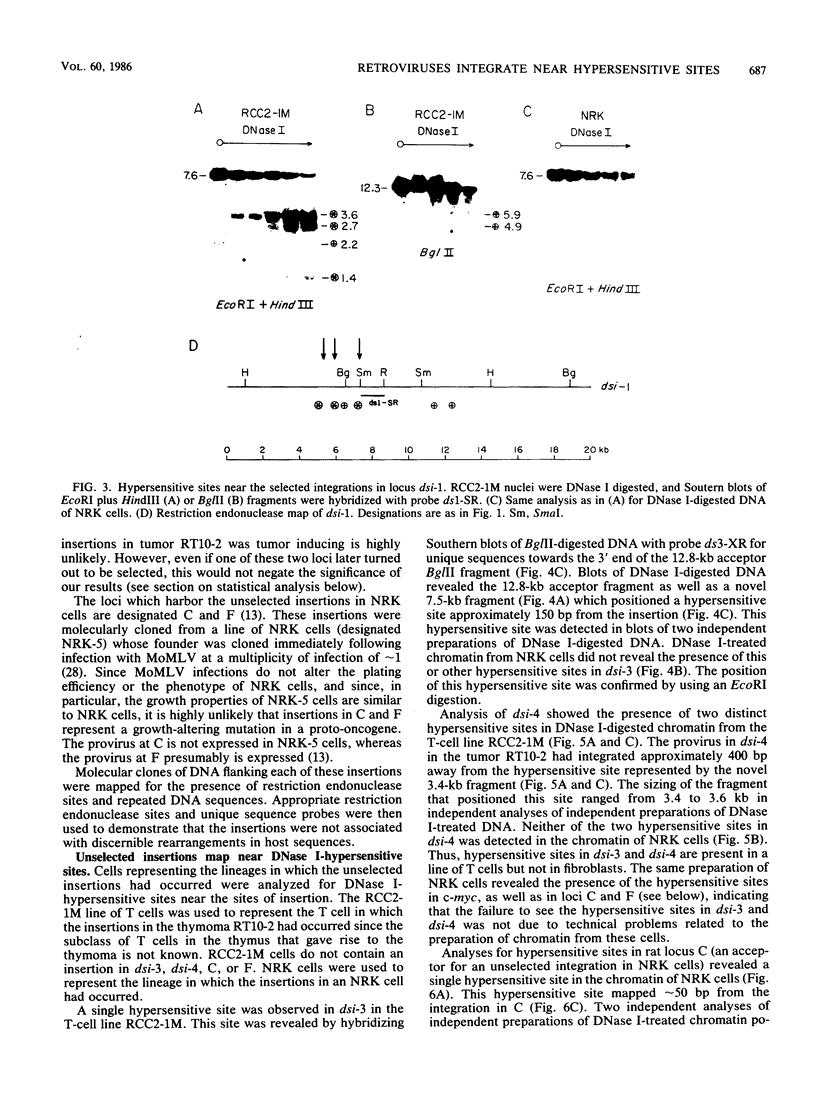
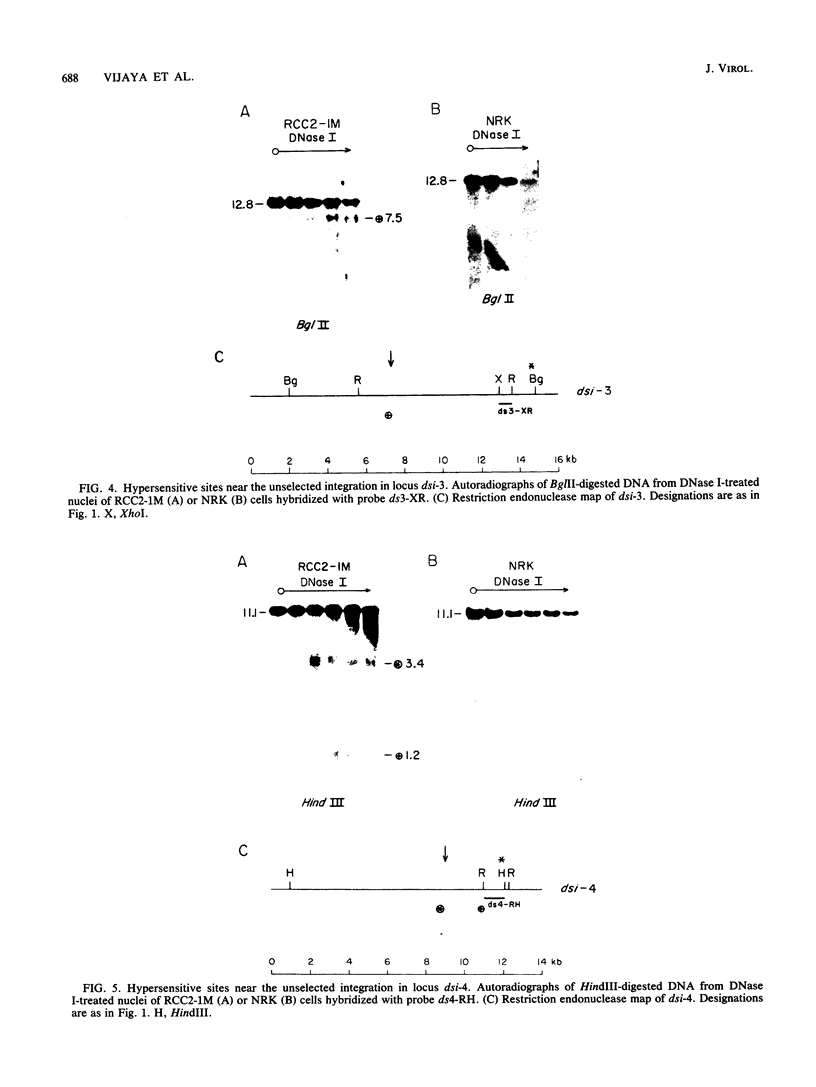
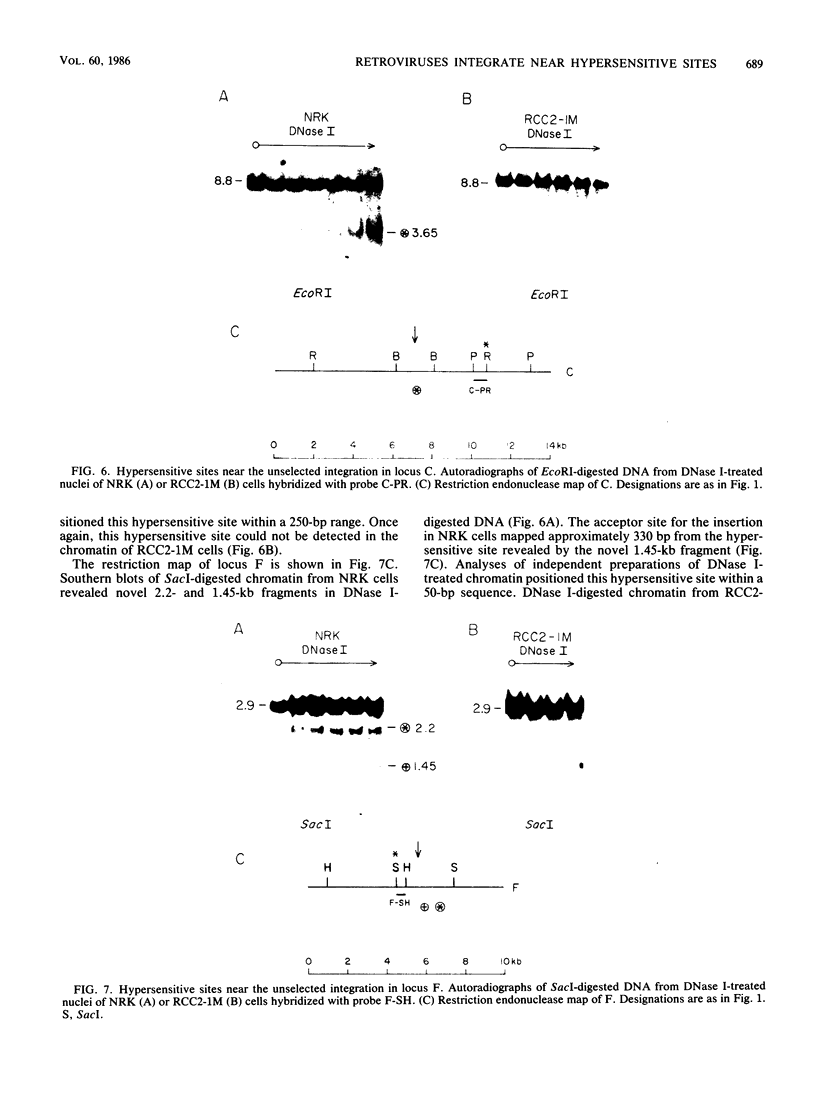
Seven cellular loci with acceptor sites for retroviral integrations have been mapped for the presence of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Integrations in three of these loci, chicken c-erbB, rat c-myc, and a rat locus, dsi-1, had been selected for in retrovirus-induced tumors. Of the remaining four, two, designated dsi-3 and dsi-4, harbored acceptor sites for apparently unselected integrations of Moloney murine leukemia virus in a Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymoma, and two, designated C and F, harbored unselected acceptor sites for Moloney murine leukemia virus integrations in a rat fibroblast cell line. Each acceptor site mapped to within 500 base pairs of a DNase I-hypersensitive site. In the analyses of the unselected integrations, six hypersensitive sites were observed in 39 kilobases of DNA. The four acceptor sites in this DNA were localized between 0.05 and 0.43 kilobases of a hypersensitive site. The probability of this close association occurring by chance was calculated to be extremely low. Hypersensitive sites were mapped in cells representing the lineage in which integration had occurred as well as in an unrelated lineage. In six of the seven acceptor loci hypersensitive sites could not be detected in the unrelated lineage. Our results indicate that retroviruses preferentially integrate close to DNase I-hypersensitive sites and that many of these sites are expressed in some but not all cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Roush C. L., Gelinas R. E. DNA and chromatin structure of the human alpha 1 (I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14906–14913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Tissue-specific DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking sequences of the tryptophan oxygenase and the tyrosine aminotransferase genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2015–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced lethal mutation in collagen I gene of mice is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G., Longiaru M., Cobrinik D., Kowal R., deHaseth P., Skalka A. M., Leis J. Circles with two tandem long terminal repeats are specifically cleaved by pol gene-associated endonuclease from avian sarcoma and leukosis viruses: nucleotide sequences required for site-specific cleavage. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):589–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.589-599.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Philippsen P. Preferential integration of yeast transposable element Ty into a promoter region. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):386–388. doi: 10.1038/307386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of acceptor site and termini of integrated avian endogenous provirus ev1: integration creates a 6 bp repeat of host DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. W., Steffen D., Gusella J., Tabin C., Bird S., Cowing D., Weinberg R. A. DNA methylation affecting the expression of murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):144–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.144-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the long terminal repeat (LTR) of avian retroviruses: structural similarities with transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Ravetch J. V., Kwan S. P., Max E. E., Ney R. L., Leder P. Multiple immunoglobulin switch region homologies outside the heavy chain constant region locus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):585–587. doi: 10.1038/293585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Kruiger W., Stolarsky L. S., Weber W., Evans R. M., Verma I. M., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression cloning of human EGF receptor complementary DNA: gene amplification and three related messenger RNA products in A431 cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):843–848. doi: 10.1126/science.6326261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequences at host-proviral junctions for mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):253–258. doi: 10.1038/289253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles B. D., Robinson H. L. High-frequency transduction of c-erbB in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):295–303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.295-303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Gagnon G. C. Patterns of proviral insertion and deletion in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.28-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W., Groudine M. Alteration of c-myc chromatin structure by avian leukosis virus integration. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):702–708. doi: 10.1038/307702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Sequence of retrovirus provirus resembles that of bacterial transposable elements. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):550–554. doi: 10.1038/285550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Hoffman J., Goff S. P., Baltimore D. Intramolecular integration within Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):164–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.164-172.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. Proviruses are adjacent to c-myc in some murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Weinberg R. A. The integrated genome of murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Arp B., Wilson R. The switch region associated with immunoglobulin C mu genes is DNase I hypersensitive in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):90–92. doi: 10.1038/294090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Padgett T., Heasley S., Simon G., Bishop J. M. Cellular functions are required for the synthesis and integration of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Gilbert W. Tissue-specific exposure of chromatin structure at the 5' terminus of the rat preproinsulin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1577–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]