Abstract
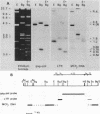
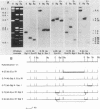
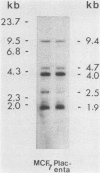
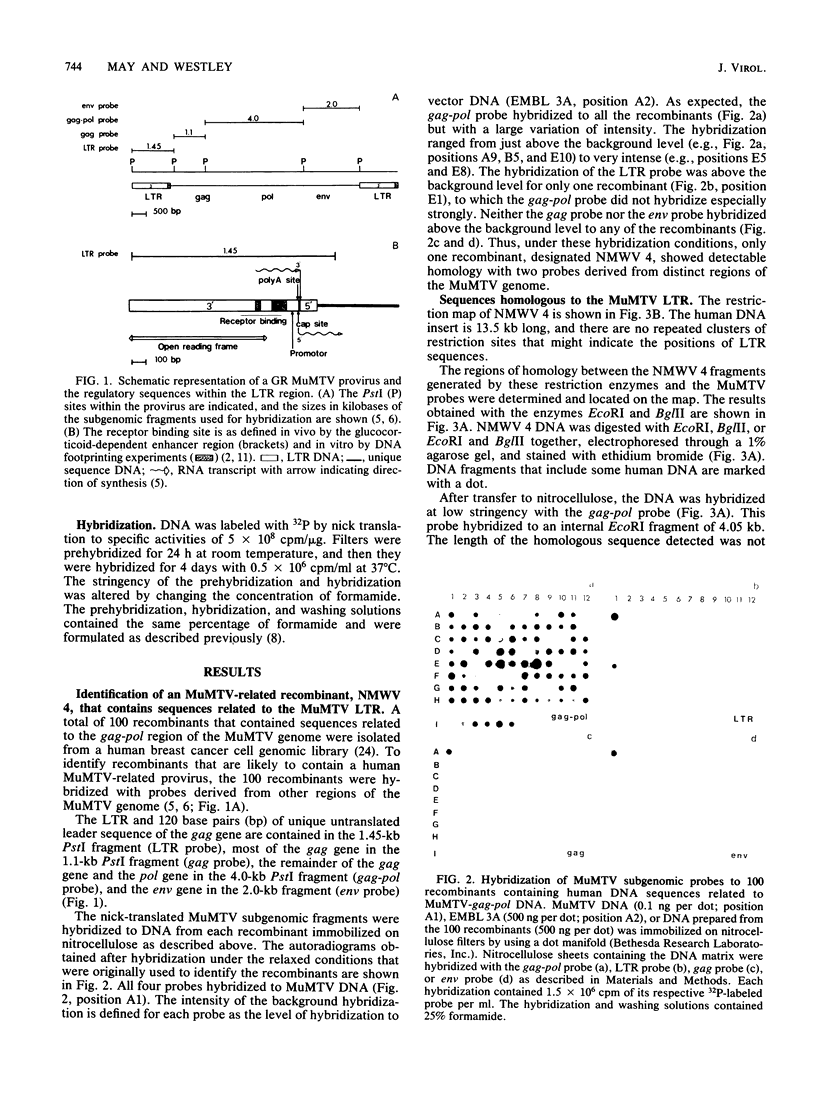
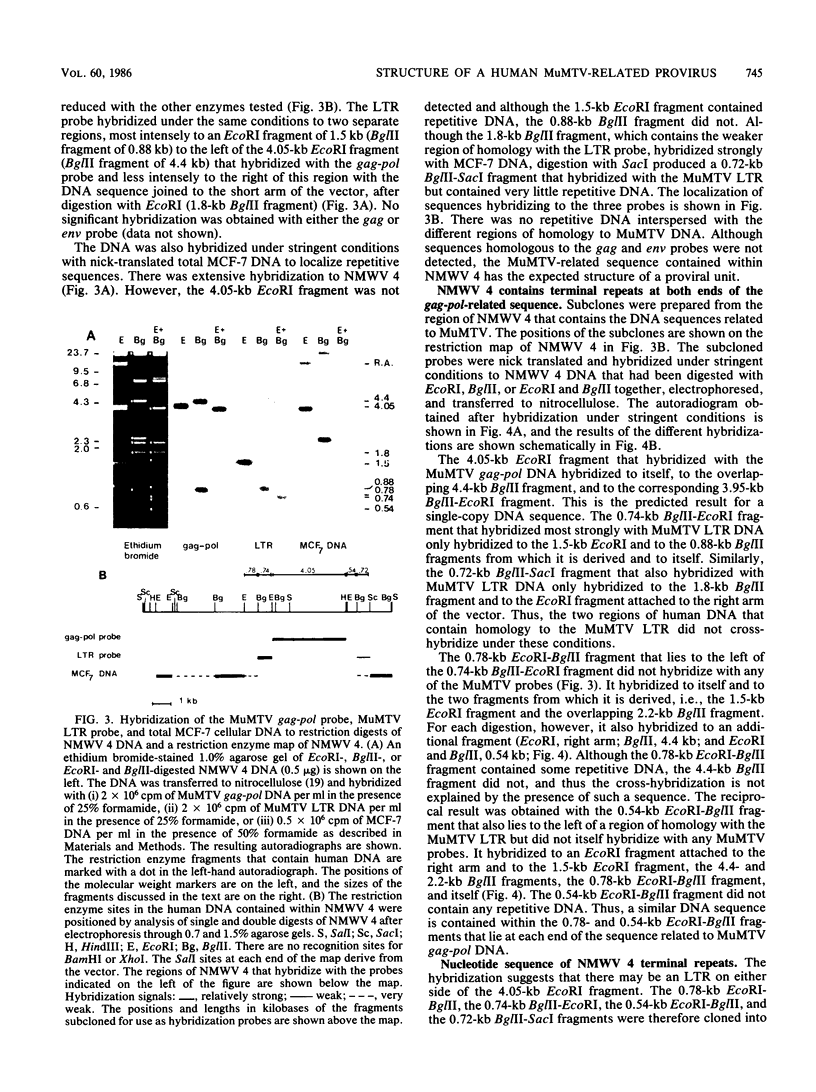
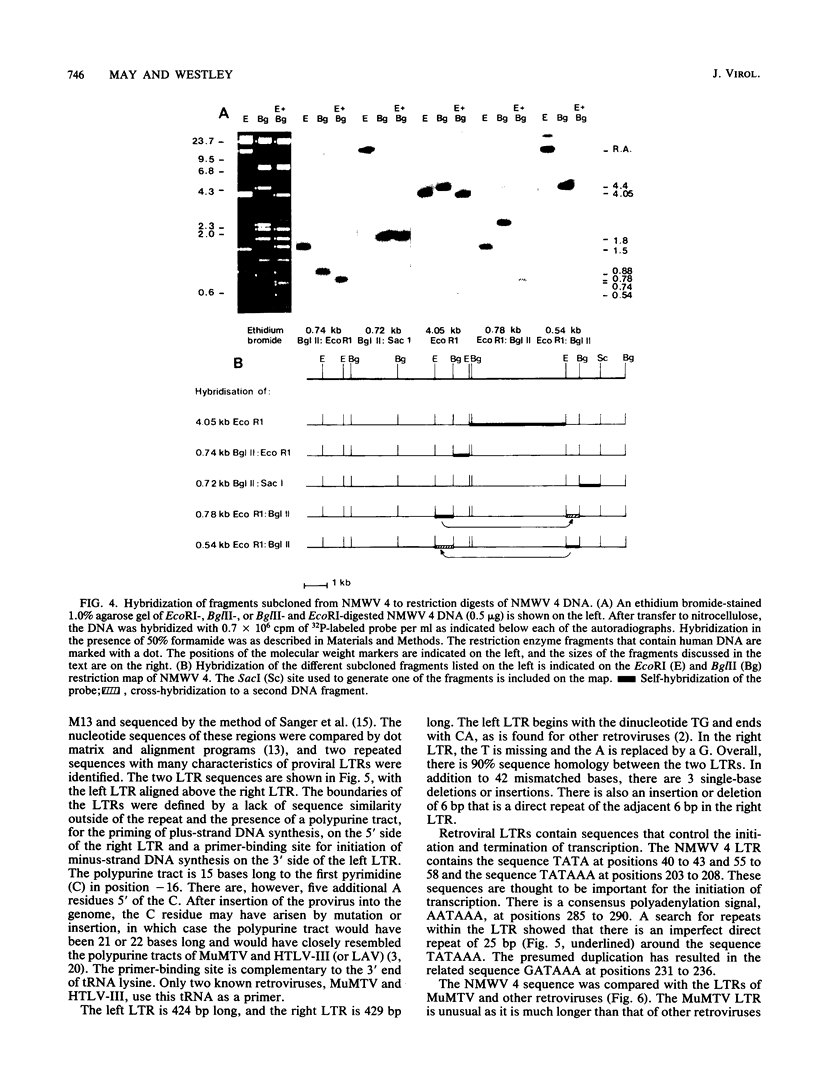
Human sequences that are related to the mouse mammary tumor virus (MuMTV) genome were cloned from breast tumor cell DNA. Of 100 recombinants, only 1 hybridized with two different probes from separate regions of the MuMTV genome (gag-pol and long terminal repeat [LTR]). This sequence, NMWV 4, was shown to have a proviruslike structure. Hybridization to digests of normal and tumor cell DNA indicated that NMWV 4 and a few closely related sequences are endogenous to the human genome. The regions that contain homology to the MuMTV LTR were sequenced. Long repeated sequences with the hallmarks of retroviral LTRs were identified. The NMWV 4 LTR contains transcription initiation and termination signals and is flanked by a polypurine tract (5' LTR) and a primer-binding site (3' LTR). The primer-binding site is complementary to tRNA lysine, the primer used by MuMTV and HTLV-III. The polypurine tract is also similar to those of these two retroviruses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callahan R., Chiu I. M., Wong J. F., Tronick S. R., Roe B. A., Aaronson S. A., Schlom J. A new class of endogenous human retroviral genomes. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1208–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.2408338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. R., Barker W. C. Nucleotide sequences of the retroviral long terminal repeats and their adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1767–1778. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., Sweet R. W. Murine mammary tumor virus pol-related sequences in human DNA: characterization and sequence comparison with the complete murine mammary tumor virus pol gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):422–432. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.422-432.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasel N., Pearson K., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. The region of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA containing the long terminal repeat includes a long coding sequence and signals for hormonally regulated transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H., Hynes N. E. Characterization of endogenous and exogenous mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA with site-specific molecular clones. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):734–745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.734-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S. Identification of a retrovirus-like repetitive element in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7510–7514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Westley B. R., Rochefort H., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Mouse mammary tumour virus related sequences are present in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4127–4139. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M. Molecular cloning and long terminal repeat sequences of human endogenous retrovirus genes related to types A and B retrovirus genes. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.937-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Brookes S., Smith R., Dickson C. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: evidence for a common region for provirus integration in mammary tumors. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Golde D. W., Miwa M., Sugimura T., Chen I. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. D., Vazguez J., Long A., Albert S., Brennan M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B., Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Okamoto T., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Characterization of long terminal repeat sequences of HTLV-III. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):538–540. doi: 10.1126/science.2981438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P. E., Rabson A. B., Bryan T., Martin M. A. Distinctive termini characterize two families of human endogenous retroviral sequences. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):943–947. doi: 10.1126/science.6089336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Miyata T. Is the AIDS virus recombinant? Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):21–22. doi: 10.1038/316021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., May F. E. The human genome contains multiple sequences of varying homology to mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):395–403. doi: 10.1038/317395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]