Abstract
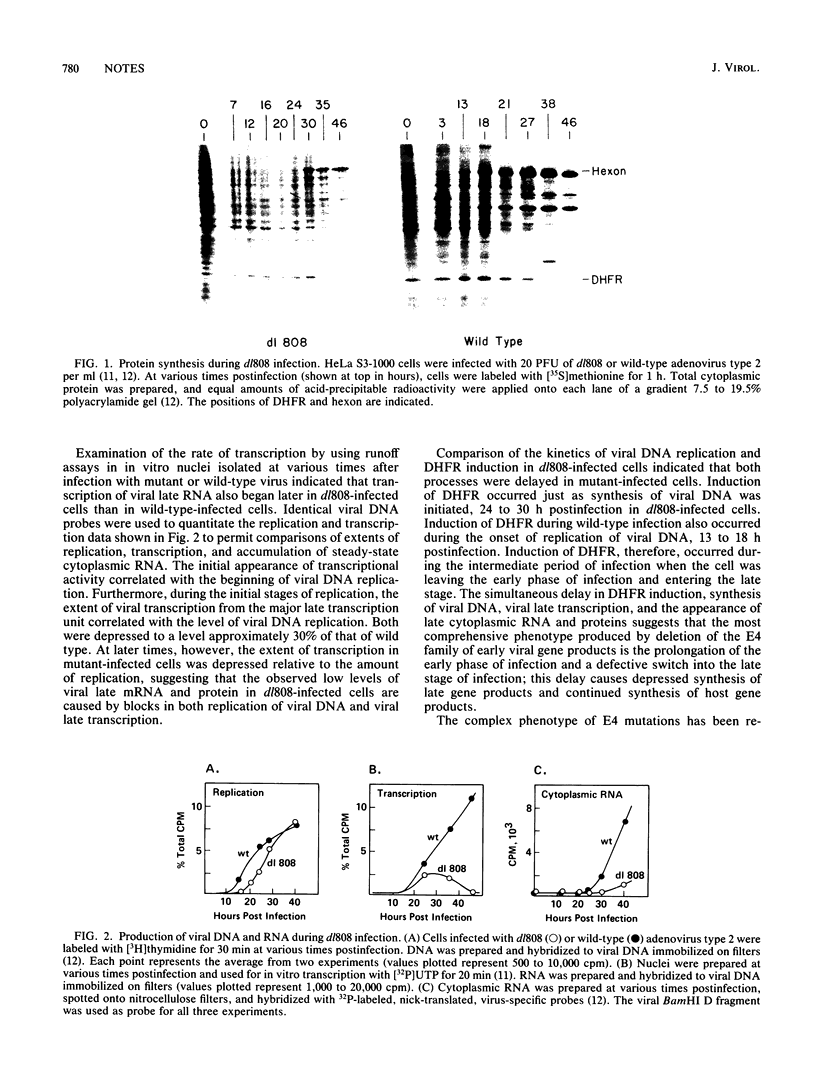
Deletion of 98% of the adenovirus type 2 E4 transcription unit resulted in a delay of several events characteristic of the intermediate stage of infection, including viral DNA synthesis, induction of the cellular gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase, and the onset of the switch from viral early to late gene expression. Although delayed, both viral DNA replication and dihydrofolate reductase induction eventually approached wild-type levels. Events characteristic of the late stage of infection were both delayed and diminished in mutant-infected cells. Therefore, the viral E4 gene family is involved in the transition from the early to late stages of infection, and events whose timing is coincident or dependent upon the early-to-late switch are delayed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beltz G. A., Flint S. J. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis during adenovirus infection. Restriction of cellular messenger RNA sequences to the nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):353–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Cutt J. R., Shenk T. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes functions required for efficient DNA replication, late gene expression, and host cell shutoff. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.250-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Capasso O., Heintz N., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle control of the human HSP70 gene: implications for the role of a cellular E1A-like function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):628–633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Levine A. J. Studies on the regulation of deoxypyrimidine kinases in normal, SV40-transformed and SV40- and adenovirus-infected mouse cells in culture. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):404–420. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Ketner G. A cell line that supports the growth of a defective early region 4 deletion mutant of human adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5383–5386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Ketner G. Adenoviral early region 4 is required for efficient viral DNA replication and for late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.833-838.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Berget S. M. Posttranscriptional control of DHFR gene expression during adenovirus 2 infection. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.72-77.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Robberson B. L., Leys E. J., Hook A. G., Al-Ubaidi M., Yeung C. Y., Kellems R. E., Berget S. M. Control of cellular gene expression during adenovirus infection: induction and shut-off of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression by adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):819–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]