Abstract
Phosphoinositides are essential lipid regulators of trafficking and signaling pathways of all eukaryotic cells. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) is an intermediate in the synthesis of several important phosphoinositide species but also serves as a regulatory molecule in its own right. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases are most abundant in the Golgi but are also found in the plasma membrane and in endocytic compartments. To investigate the role of Golgi PtdIns4P in orchestrating trafficking events, we used a unique drug-inducible molecular approach to rapidly deplete PtdIns4P from Golgi membranes by a recruitable Sac1 phosphatase enzyme. The utility of the system was shown by the rapid loss of Golgi localization of PH domains known to bind PtdIns4P after Sac1 recruitment to the Golgi. Acute PtdIns4P depletion prevented the exit of cargo from the Golgi destined to both the plasma membrane and the late endosomes and led to the loss of some but not all clathrin adaptors from the Golgi membrane. Rapid PtdIns4P depletion in the Golgi also impaired but did not eliminate the replenishment of the plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 during phospholipase C activation revealing a hitherto unrecognized contribution of Golgi PtdIns4P to this process. This unique approach will allow further studies on the role of phosphoinositides in endocytic compartments that have evaded detection using the conventional long-term manipulations of inositide kinase and phosphatase activities.
Keywords: phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, PI 4-kinase, Sac1 phosphatase, vesicular trafficking, green fluorescent protein
Phosphoinositides (PIs) are best known as substrates of phospholipase C (PLC) enzymes during activation of cell surface receptors yielding the second messengers inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) (1). However, PIs also function as membrane-delimited docking sites to recruit and regulate a variety of signaling proteins, including kinases, ion channels, nucleotide exchange factors, and GTPase activating proteins as well as several actin binding proteins (2–4). PtdIns 4-kinases (PI4Ks) and their lipid product, PtdIns4P, represent the first committed step in the synthesis of multiphosphorylated PIs, most notably PtdIns(4,5)P2. Because of this role, PI4Ks were expected to function primarily in the plasma membrane. Surprisingly, all four isoforms of PI4K have been localized (at least partially) to the Golgi, and a significant fraction of cellular PtdIns4P is also found to be Golgi associated (5, 6).
Yeast studies have clarified nonredundant and essential roles of type III PI4Ks, namely the importance of Pik1p in Golgi to plasma membrane secretion (7, 8) and that of Stt4p in the maintenance of the plasma membrane PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools (9, 10). Golgi PtdIns4P is responsible for the recruitment of clathrin adaptors such as AP-1 (11) or the Golgi-localized, gamma-ear-containing, Arf-binding family of proteins (GGAs) (12, 13) in mammalian cells and critical for lipid transport (14) as well as delivery of cargos from the Golgi to the cell surface (15, 16). These conclusions were mostly based on expression of kinase-dead mutant forms or on RNAi-mediated silencing of the various PI4Ks in mammalian cells. However, these are long procedures and it is hard to know whether the phenotypic changes are directly linked to PtdIns4P or due to complex trafficking or signaling defects developing during this time. Moreover, eliminating any one of the four PI4Ks could leave significant amounts of PtdIns4P formed by the remaining PI4Ks. To overcome these problems, we have been working toward a system by which PtdIns4P can be rapidly and completely eliminated from specific compartments within a cell. This system is based on the rapamycin-inducible heterodimerization of the FKBP12 protein and the FRB domain of mTOR (17). Targeting the FRB domain to a specific membrane compartment allows the rapamycin-induced recruitment to that compartment of any PI modifying enzyme fused with FKBP12 (Fig. 1A). For this the enzyme of interest has to be stripped of its own localization domains. This principle has been successfully used to rapidly alter the levels of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane (18, 19) and of PtdIns3P in sorting endosomes (20).
Fig. 1.
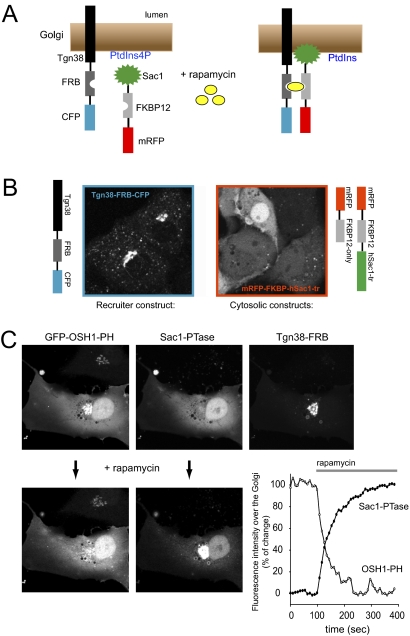
Rapamycin-induced elimination of PtdIns4P from Golgi membranes. (A) Principle of rapamycin-induced modification of membrane lipid composition. (B) Distribution of the Tgn38-FRB-CFP and cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-fused Sac1 phosphatase expressed in COS-7 cells. (C) Recruitment of the cytosolic Sac1 phosphatase to the Golgi decreases the localization of the PtdIns4P reporter, GFP-OSH1-PH domain. The decrease in the OSH1-PH domain intensity over the Golgi parallels the increase in the mRFP-FKBP12-Sac1 signal over the same area.
In the present study we report on the development of a Golgi recruiting strategy to acutely alter the levels of PtdIns4P in the Golgi. Our results demonstrate that Golgi PtdIns4P levels are acutely critical for cargo delivery to both the plasma membrane and the late endosomal compartment and that some but not all GGA adaptors require PtdIns4P for membrane targeting. This approach also allowed us to address the long-standing question of how much contribution the Golgi PtdIns4P makes to the maintenance of the signaling pool of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane.
Results
Recruitment of a Cytosolic Sac1 Phosphatase to the Golgi Eliminates Golgi PtdIns4P.
To recruit PtdIns4P modifying enzymes to the Golgi, we used the type I Golgi protein, Tgn38 (21) and fused FRB and CFP modules to its C terminus. When expressed in COS-7 cells, this construct showed both a tight Golgi localization and presence in the Tgn as expected (Fig. 1B). At high expression levels it also affected the Golgi structure making it very tight and compact but this could be managed with controlled expression (see Materials and Methods).
To eliminate PtdIns4P from the Golgi, we used the human Sac1 phosphatase, which is a key regulator of PtdIns4P both in yeast (22–24) and mammalian cells (25). Deletion of the short C-terminal hydrophobic sequence that localizes Sac1 to the ER rendered the enzyme cytoplasmic. This cytoplasmic Sac1 was then fused to an mRFP-FKBP12 module with various linkers (mRFP-FKBP12-cytoSac1 or recruitable Sac1 for short). Expression of this enzyme alone in the cytosol yielded large vesicles, suggesting that the enzyme was active also against PtdIns3P. This was not unexpected as the substrate specificity of Sac1 is poor (22), mainly determined by its localization. Despite its limited specificity, the human Sac1 construct was still suitable when its expression level was kept at moderate levels.
The effects of the recruitable Sac1 were followed with GFP-fused PH domains whose Golgi localization is known to depend on PtdIns4P (26, 27). Because many of these PH domains (OSBP, FAPP1, OSH1, or CERT) distort the Golgi structure due to their PtdIns4P binding and sequestration of protein binding partners such as Arf1, we replaced the CMV promoter with a thymidine kinase (TK) promoter in some cases. With these modifications it was possible to fine-tune the expression of the recruiter, the enzyme, and the reporter so that enough cells could be analyzed with intact Golgi morphology (see Materials and Methods) (Fig. 1C). Addition of rapamycin to such selected cells caused a rapid translocation of the recruitable Sac1 from the cytosol to the Golgi and caused a parallel dissociation of the PtdIns4P reporters from the same sites, which took place within 5–8 min in most cases (Fig. 1C). This was true for all of the PtdIns4P reporters tested although there was a small residual localization found with the FAPP1 PH domain consistent with its strong Arf1 binding (27) (Fig. S1). Recruitment of the mRFP-FKBP12 construct not containing the Sac1 domain failed to elicit any such response (Fig. S1).
Functional Relevance of PtdIns4P in Vesicular Trafficking.
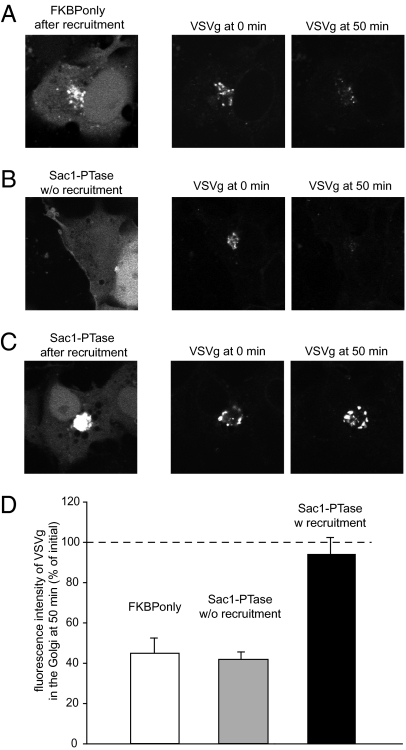
Next we assessed to what extent PtdIns4P determines the rate of vesicular trafficking out of the Golgi compartments. The temperature-sensitive trafficking of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)g is widely used to follow the transport of vesicular cargo from the ER to the plasma membrane. However, large cell-to-cell variation in the VSVg-GFP trafficking responses after the temperature switch prevented a reliable quantitative comparison of this process between cells with or without Golgi PtdIns4P depletion. Therefore, we generated a VSVg fusion construct with a photoactivable GFP and used a protocol allowing the transport and accumulation of VSVg in the Golgi (see Materials and Methods for details). Cells were then released from the Golgi block at the microscope stage and the Golgi area was immediately photoactivated. The fluorescence intensity decrease in the photoactivated area was used as a measure of VSVg leaving the Golgi. As shown in Fig. 2, when this protocol was used in cells where the Sac1 phosphatase was recruited to the Golgi (5–10 min was allowed after rapamycin to find the cell to be followed), only a negligible decrease in the fluorescent intensity over the photoactivated area was observed during a 50-min period. This contrasted with the substantial drop in fluorescence in the cells where the FKBP-only construct was recruited to the Golgi. These experiments suggested that VSVg trafficking from the Golgi rapidly declines after removal of PtdIns4P from the Golgi membrane.
Fig. 2.
The effect of PtdIns4P elimination on VSVg trafficking in COS-7 cells. Cells were transfected with Tgn38-FRB (without a fluorescent tag) together with either the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP only (A) or the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-Sac1 phosphatase (B and C) and the VSVg protein fused to photoactivable GFP. Cells were kept at 39.5 °C overnight and shifted to 20 °C the next day for 1 h. This allowed the refolded VSVg to enter and accumulate in the Golgi. Cells were then mounted on the microscope's heated stage (35 °C) and treated immediately with rapamycin to induce recruitment of the cytosolic constructs to the Golgi (A and C). Cells that showed Golgi recruitment (within 5–10 min of rapamycin) were selected and the Golgi area was photoactivated using a 405-nm laser line. The intensity change in the photoactivated VSVg was then followed in the GFP channel. VSVg trafficking was also recorded in cells expressing the Sac1 phosphatase but without recruitment to the Golgi (B). Representative images are shown at 0 min (after photoactivation) and at 50 min. The bar diagram (D) shows the summary calculated from seven cells expressing FKBP only or the recruitable Sac1 without recruitment, and from six cells in the case of recruited Sac1 phosphatase (means ± SEM).
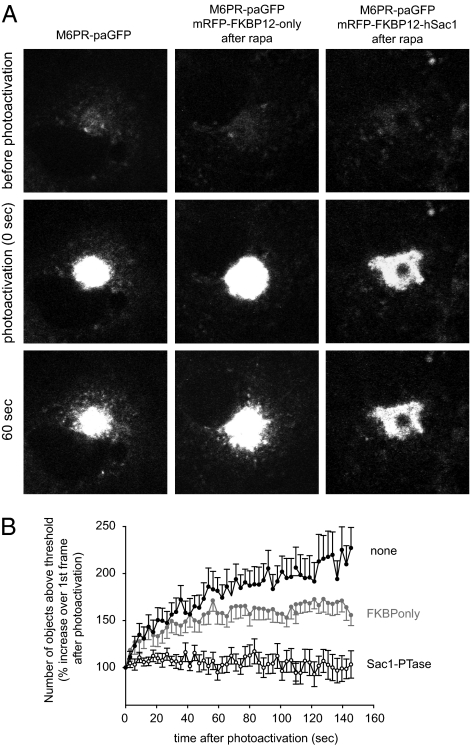
Next we studied the effect of PtdIns4P depletion on the trafficking of the cation independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor (CI-M6PR), which shuttles between the Golgi and the multivesicular body (MVB) to deliver acid hydrolases to the lysosome (28). For this, we also tagged the CI-M6PR with a photoactivable GFP. This construct expressed at a higher level than the VSVg reporter (in the combined transfection regime) allowing a better resolution of the vesicular outflow from the photoactivated Golgi area (Fig. 3). A complex morphometric analysis showed that the vesicular budding of M6PR positive vesicles was essentially shut down in the cells where the Sac1 phosphatase was acutely recruited to the Golgi (Fig. 3). A slight decrease in the number of fluorescent vesicles appearing outside the Golgi was also seen in cells where the FKBP-only construct was recruited to the Golgi compared to control cells that only expressed the photoactivable M6PR (Fig. 3). This was attributed to the expression of the Tgn38-FRB-CFP recruiter, which is expected to slightly alter Golgi function even at the expression level in the chosen cells. Nevertheless, these data suggested that the vesicular trafficking pathways linking the Golgi to the late endosomal/MVB compartment also required the presence of PtdIns4P in the Golgi membranes.
Fig. 3.
The effect of PtdIns4P elimination on mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking in COS-7 cells. Cells were transfected with the CI-M6PR fused to photoactivable-GFP (A Left) either alone or together with the Golgi-targeted Tgn38-FRB (nonfluorescent) and the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-only (A Middle) or the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-Sac1 phosphatase (A Right). The next day the mounted live cells were preincubated for 10 min with rapamycin (100 nM) and the Golgi region of cells that showed recruitment was photoactivated. Time-lapse images were followed for 5 min with GFP excitation. (A) Representative images of each group of cells at the indicated time points. (B) Combined result of morphometric analysis of the recordings using MetaMorph software. The graphs show the number of objects around the Golgi that are above an arbitrary threshold normalized to the value found right after photoactivation (at 0 min). The graph illustrates the first 2.5 min of the recordings. (Means ± SEM of 12, 12, and 21 cells for the black, gray, and open symbol traces, respectively.)
The Importance of PtdIns4P in the Recruitment of Clathrin Adaptors and Arf1 to the Golgi Membrane.
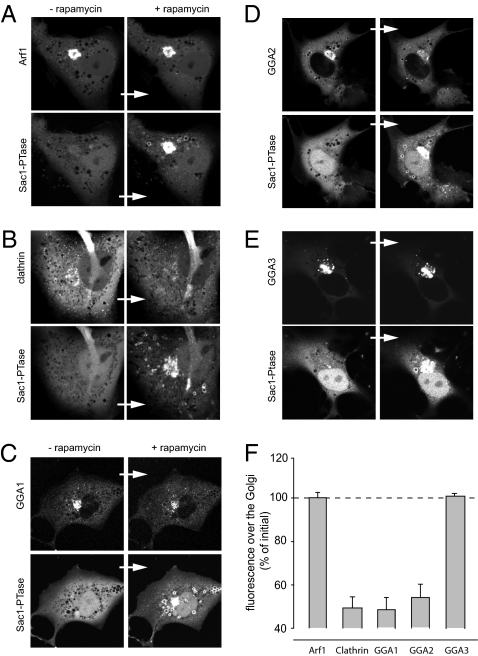
Next we evaluated the contribution of PtdIns4P to the Golgi localization of the small GTP binding protein, Arf1, as well as several clathrin adaptor proteins. Arf1 is a key regulator of the association of coat proteins with budding membranes and was also shown to recruit PI4KIIIβ to the Golgi and stimulate its activity (16). Fig. 4A shows that acute PtdIns4P depletion was without effect on the steady-state level of Arf1-GFP associated with the Golgi. We also tested whether PtdIns4P elimination influenced the rate of Arf1 dissociation from the Golgi (after BFA treatment) or the rate of recovery after photobleaching (FRAP). However, the expression level of Arf1-GFP impacted these dynamic parameters more than the presence or absence of PtdIns4P, indicating that PtdIns4P may not be a major factor in Arf1 regulation. Nevertheless, we cannot rule out that PtdIns4P or PtdIns(4,5)P2 affects Arf-GAP or Arf-GEF activities as suggested by in vitro studies (29, 30).
Fig. 4.
Changes in the localization of Arf1, clathrin and the monomeric clathrin adaptor GGAs to the Golgi upon acute Sac1-phosphatase recruitment. Cells were transfected with the Golgi-targeted Tgn38-FRB-CFP (not displayed) together with the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP12-Sac1 and one of the following constructs: Arf1-GFP (A), clathrin light chain-GFP (B), thimidine kinase (TK) promoter driven GGA1-GFP (C), GGA2-GFP (D), and GGA3-GFP proteins (E). Pictures were taken before and after (5–8 min) rapamycin (100 nM). (F) Summary of intensity changes observed over the Golgi upon Sac1-phosphatase recruitment. Means ± SEM of number (n) of cells: Arf1 (n = 3), Golgi clathrin (n = 6), GGA1 (n = 6), GGA2 (n = 7), and GGA3 (n = 4). (Because the cytosolic background intensity increases after delocalization, a complete loss of Golgi localization in most constructs does not cause more than a 60% decrease in the initial intensity.)
The effect of PtdIns4P removal on the Golgi localization of clathrin was examined by using the GFP-tagged clathrin light chain, which showed its characteristic localization both in the Golgi and the plasma membrane (Fig. 4B). Recruitment of the Sac1 phosphatase rapidly decreased the Golgi-associated fraction of clathrin with no effects on the PM-associated puncta (Fig. 4B). The effects of PtdIns4P removal on the distribution of the monomeric GGA adaptors were quite prominent but not uniform. Both GFP-GGA1 and GFP-GGA2 showed rapid dissociation from the Golgi after rapamycin-induced recruitment of the Sac1 phosphatase, but not of the FKBP-only control construct (Fig. 4 C and D). In contrast, the same manipulation failed to affect the Golgi localization of GGA3 (Fig. 4E). Note that because of significant cytoplasmic intensities of all of these constructs after they are released from the Golgi, even in the case of complete delocalization the intensity values do not drop to zero levels but stay at around 40–50% of the initial intensity values (Fig. 4F). Nevertheless, these findings showed that some but not all of the clathrin adaptors use PtdIns4P in the Golgi in a similar manner as they use PtdIns(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane (31, 32).
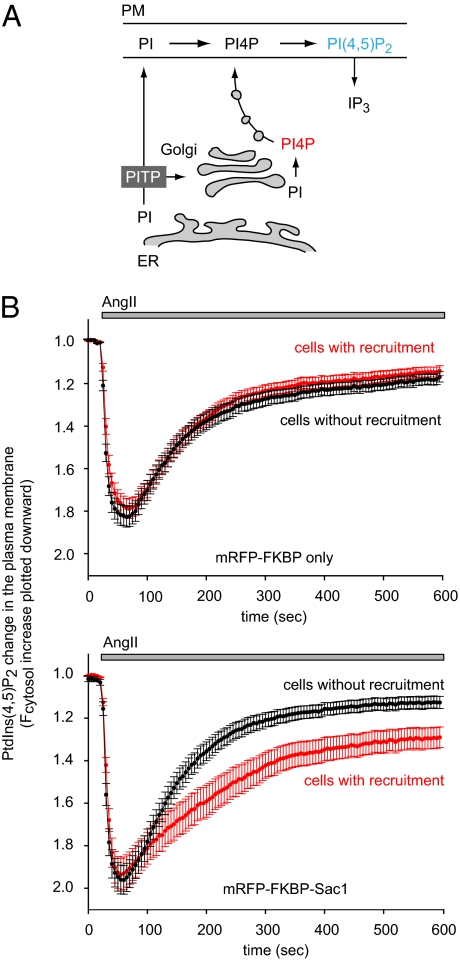
Golgi PtdIns4P Contributes to the Maintenance of Plasma Membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 Pools.
Lastly, we wanted to determine whether the Golgi pool of PtdIns4P has any role in the maintenance of the PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels in the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 is rapidly exhausted during PLC activation without a steady supply generated via PtdIns4P from the larger PtdIns pools. According to classical views, PtdIns4P is produced in the plasma membrane from PtdIns, which is transported there from the ER by PI-transfer proteins (PITPs) (33, 34) (Fig. 5A). However, the high abundance of PtdIns4P and the PI4K enzymes in the Golgi and the prominent role of PITPs in the same compartment (33, 34) also raised the possibility that the plasma membrane receives its PtdIns4P content through vesicular trafficking from the Golgi and perhaps from recycling endocytic vesicles (as none of the known PITPs would transfer PtdIns4P). Rapid selective depletion of the Golgi PtdIns4P pool seemed like an appropriate system to address these questions. We used HEK-293 cells stably transfected with the AT1a receptor because these cells show large angiotensin II (AngII)-induced changes in PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels in the plasma membrane (35). PtdIns(4,5)P2 was monitored with the PLCδ1PH-GFP construct and for simplicity we followed the cytoplasmic fluorescence as a measure of translocation of the reporter from the membrane to the cytosol, indicating the falling PtdIns(4,5)P2 in the membrane. Ang II stimulation induced a rapid decrease in PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels in the plasma membrane, which started to return to levels slightly below prestimulatory values after a few minutes (Fig. 5B). When cells were also transfected with the recruitable Sac1 and the Tgn38-FRB-CFP constructs and rapamycin was applied 10 min before stimulation with AngII, a clear difference was observed in the kinetics of PtdIns(4,5)P2 changes between the cells that showed visible Golgi recruitment of the Sac1 enzyme compared to those without recruitment (Fig. 5B, lower panel). The PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels recovered significantly slower in cells where the Golgi PtdIns4P was eliminated but there was still a significant PtdIns(4,5)P2 synthesis taking place in those cells. No difference was observed, however, when the FKBP-only construct was recruited to the Golgi membrane (Fig. 5B, upper curves). These data have collectively shown that Golgi PtdIns4P makes a sizeable contribution to the plasma membrane supply of PtdIns4P but it is dispensable in the maintenance of PtdIns(4,5)P2.
Fig. 5.
The effects of PtdIns4P elimination on the resynthesis of the plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools during phospholipase C activation. (A) Current model of how the PM is supplied with PtdIns(4,5)P2 in mammalian cells. Because a large fraction of PtdIns4P is found in the Golgi (PI4P with red), some PtdIns4P may reach the PM via vesicular transport. (B) HEK-293 cells stably expressing AT1a receptors were cotransfected with the PtdIns(4,5)P2 reporter PLCδ1PH-GFP, the Tgn38-FRB-CFP, and either the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-only or the cytosolic mRFP-FKBP-Sac1-phosphatase constructs. Next day cells were examined on the stage of Zeiss LSM 510-META confocal microscope at room temperature. Rapamycin (100 nM) was added 10 min before stimulation with 100 nM AngII. The cytoplasmic fluorescence of the cells was calculated from ROIs drawn in the cytosol (outside the nucleus) from time-lapse images. Curves were normalized to their initial prestimulatory values and averaged either from cells showing Golgi recruitment or from cells without recruitment. Means ± SEM are shown from 60 to 80 cells recorded in multiple dishes from two independent experiments. The curves are plotted such that an increase in cytosolic PLCδ1PH-GFP fluorescence is shown as a downward change to better conceptualize that it reflects a drop in the plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2. Also note that in all of the cells expressing the Sac1 construct there are larger changes in PtdIns(4,5)P2 than in those expressing the FKPB-only construct (compare black traces in the Upper and Lower panels), but a significantly slower recovery is observed only in the cells that showed Golgi recruitment of the Sac1 phosphatase (Lower trace).
Discussion
The significance of PtdIns4P regulation of Golgi function was realized about 10 years ago in yeast using temperature-sensitive alleles of PI4Ks (7, 8). More difficult is to study the roles of PtdIns4P in various Golgi functions in mammalian cells. Most manipulations of PI4Ks or their lipid products, other than by the use of inhibitors, (knockdown of enzymes, overexpression of active or dominant negative enzymes, or PtdIns4P binding protein domains) require several hours (at least 6–12 h) to develop. During this period, cells will adapt to the new situation and the changes observed are often secondary to PtdIns4P manipulations. Unfortunately, specific PI4K inhibitors have not been developed as of today and many studies relied upon PI3K inhibitors that also inhibit the type III PI4Ks at higher concentrations (36) or very nonspecific drugs like PAO (37). Moreover, no inhibitors exist for the type II PI4Ks, enzymes that show significant presence in Golgi/Tgn (11). Because of these difficulties, we felt the need to adapt the drug-induced heterodimerization system to alter PIs (19) to address the role of Golgi PtdIns4P in cell regulation. Using the Sac1 phosphatase stripped of its ER localization signal and the Tgn38 molecule as a scaffold to serve as a Golgi/Tgn recruiter we were able to acutely eliminate PtdIns4P from Golgi membranes. An advantage of this method is that it can detect an acute change in a matter of seconds to minutes in single cells. At the same time, it requires analysis of many individual cells that express the constructs in the right proportion, making it unsuitable at this point for cell population or longer-term studies.
Vesicular budding from the Golgi membrane requires the assembly and disassembly of several proteins working together. A common feature of these processes is their regulation by the small GTP binding protein, Arf1 (38) and in some cases PIs (6). Moreover, in vitro evidence suggests that PIs can regulate the activation state of Arf1 (29). Arf1 not only regulates the recruitment of clathrin adaptors such as the GGAs and other coat proteins to the Golgi membrane but also helps recruit and activate PI4KIIIβ (16) and hence facilitates PtdIns4P production. PtdIns4P works together with Arf1 in the recruitment (and most likely also in inducing a conformational change) of several PH domain-containing proteins to the Golgi/Tgn membrane. This dual signal requirement—also referred to as coincidence detection—is a hallmark of many phosphoinositide-recognizing domains and -regulatory paradigms (39). The present studies allowed analysis of the PtdIns4P requirement of several of these steps yielding clear conclusions. The results showed that clathrin recruitment to the Golgi membrane requires PtdIns4P as does GGA1 and -2 but not GGA3. They also indicated that substantial differences could exist in the PI regulation of proteins that are structurally highly related. Elimination of PtdIns4P very rapidly terminated the formation of transport vesicles from the Golgi. This was true for the transports of both VSVg and the CI-M6PR. These results unequivocally show that PtdIns4P is crucial for vesicular budding from the Golgi also in mammalian cells. Previous studies using knockdown of individual PI4K enzymes achieved only a partial PtdIns4P depletion allowing the cells to survive (because there are multiple forms of PI4Ks in the Golgi).
Importantly, these studies provided clear evidence that although Golgi PtdIns4P does contribute to the maintenance of plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools to some extent, it is not essential for this process. Even though classical views placed PtdIns4P generation to the plasma membrane from a larger pool of PtdIns, delivered from the ER by the PITP proteins (33), Golgi involvement has been a recurring question ever since the type III PI4Ks, found primarily in the Golgi and ER membranes (5), were identified as the important enzymes to synthesize PtdIns4P the precursor of PtdIns(4,5)P2 (36, 40). It is noteworthy that the PtdIns(4,5)P2 decrease was larger and the resynthesis occurred more rapidly in cells expressing the recruitable Sac1 than in those expressing the FKBP-only even without rapamycin addition (compare black traces in Fig. 5B Upper and Lower). This may be due to the partial depletion of the plasma membrane pool of PtdIns4P by the cytosolic Sac1 as the enzyme clearly showed significant activity against its substrates even before recruitment. This shows the ability of cells to cope with sustained alterations in phosphoinositide balance and the importance of appropriate controls and the need to compare cells before and after rapamycin addition as has been done in the present study.
In summary, the present studies described the functional consequences of rapid and selective manipulations of PtdIns4P from Golgi membranes by enzymatic means in intact living cells. The results clearly show a direct regulation by PtdIns4P of the recruitment of clathrin and several clathrin adaptor proteins to the Golgi membrane and the essential role of this lipid in the generation of transport vesicles out of the Golgi compartment. The present findings also revealed a small but nonessential contribution of the Golgi PtdIns4P in the maintenance of the PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels in the plasma membrane during PLC activation. These data unequivocally place PtdIns4P as the most important regulatory phosphoinositide in the center of Golgi function.
Materials and Methods
Materials.
Rapamycin was purchased from Calbiochem and angiotensin II (human) from Peninsula Laboratories. All other chemicals were of the highest purity grades. Description of the DNA constructs is listed in SI Materials and Methods.
Transfection of Cells for Confocal Microscopy.
COS-7 cells were used for most confocal microscopy studies. Cells were plated onto 25-mm-diameter circular glass coverslips at a density of 3 × 105 cells/dish 1 day before transfection with plasmid DNAs (0.2–1 μg/dish) using the Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen) and OPTI-MEM (Invitrogen). One day (16–24 h) after transfection cells were washed twice with a modified Krebs-Ringer solution, containing 120 mM NaCl, 4.7 mM KCl, 1.2 mM CaCl2, 0.7 mM MgSO4, 10 mM glucose, 10 mM Na-Hepes, pH 7.4 and the coverslip was placed into a metal chamber that was mounted on a heated stage with the medium (1 mL) kept at 33 °C. Cells were examined in an inverted microscope under a 60× oil-immersion objective (LSM 510-META; Carl Zeiss MicroImaging). Cells were selected for analysis on the basis of the following criteria: the expression of Tgn38-FRB-CFP was sufficiently high yet it showed no compacting or vesicular fragmentation of the Golgi. The mRFP-FKBP12-Sac1 expression has not caused the development of large vacuoles indicative of PtdIns3P depletion. The GFP-tagged reporter construct (PH domain, Arf1, GGA, or clathrin) showed its characteristic distribution and its expression did not distort the Golgi morphology. To increase the number of cells meeting these criteria, a careful fine-tuning of the amounts of DNA constructs was necessary that differed for each individual reporter. Images were processed for final figures in Adobe Photoshop, and no manipulations other than expanding to the full dynamic range (linear) were allowed.
Measurements of PLCδ1PH Domain Translocation.
HEK-293 cell stably expressing the rat AT1a angiotensin receptor were transfected with the PLCδ1PH-GFP construct together with the Tgn38-FRB construct and either one of the mRFP-FKBP12-only or the mRFP-FKBP12-hSac1 plasmids. After 24 h, cells were imaged in a Zeiss LSM 510-META confocal microscope at room temperature. After addition of rapamycin (100 nM) for 10 min, fields with many cells showing Golgi-localized mRFP were selected and stimulated with AngII (100) nM. The cytosolic GFP intensity was monitored and in each cell using ROIs outside the nucleus and plotted against time using the Zeiss software. The responses of cells showing Golgi recruitment were averaged and compared to those in which no recruitment to the Golgi was visible.
VSVg Trafficking and Morphometric Analysis.
Cells were transfected with the photoactivable VSVg and the respective DNA constructs and kept at 39.5 °C overnight. At this restrictive temperature the VSVg remains in the ER. Next morning the cells were shifted to 20 °C for 2 h. This temperature change releases the protein from the ER block and allows it to move to the Golgi. The Golgi area was immediately photoactivated after placing the cells at the 35 °C microscope stage, which allowed the protein to traffic to the PM. The intensity of the VSVg fluorescence in the Golgi was then recorded in time. The sprouting out of the photoactivated M6PR from the Golgi area was assessed using the integrated morphometric analysis of the Metamorph software (Molecular Dynamics). Here the sequential time-lapse pictures were thresholded (using same values in all images within a series) and the number of objects exceeding the threshold were calculated and plotted against time. In each case the increase in object number over the one immediately after photoactivation was calculated and averaged from several experiments as indicated in the figure legends.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Drs. Juan Bonifacino, Julie Donaldson, Lois Greene, Mark Lemmon, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Philip W. Majerus (Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO), Jeffry Pessin, Alexander Sorkin, and Roger Y. Tsien (University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA) for DNA constructs. Confocal imaging was performed at the Microscopy and Imaging Core of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), National Institutes of Health (NIH), with the kind assistance of Drs. Vincent Schram and James T. Russell. P.V. was supported by grants from the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA NF-68563) and the Medical Research Council (ETT 494/2009) of Hungary. This research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD of NIH.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/1000157107/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984;220:345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di Paolo G, De Camilli P. Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature. 2006;443:651–657. doi: 10.1038/nature05185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hilgemann DW, Feng S, Nasuhoglu C. The complex and intriguing lives of PIP2 with ion channels and transporters. Sci STKE. 2001;2001(111):re19. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.111.re19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Balla T, Szentpetery Z, Kim YJ. Phosphoinositide signaling: New tools and insights. Physiology (Bethesda) 2009;24:231–244. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00014.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Balla A, Balla T. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases: Old enzymes with emerging functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:351–361. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.De Matteis MA, Di Campli A, Godi A. The role of the phosphoinositides at the Golgi complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1744:396–405. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Walch-Solimena C, Novick P. The yeast phosphatidylinositol-4-OH kinase pik1 regulates secretion at the Golgi. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:523–525. doi: 10.1038/70319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hama H, Schnieders EA, Thorner J, Takemoto JY, DeWald DB. Direct involvement of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in secretion in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:34294–34300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.48.34294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Audhya A, Foti M, Emr SD. Distinct roles for the yeast phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, Stt4p and Pik1p, in secretion, cell growth, and organelle membrane dynamics. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:2673–2689. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.8.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Audhya A, Emr SD. Stt4 PI 4-kinase localizes to the plasma membrane and functions in the Pkc1-mediated MAP kinase cascade. Dev Cell. 2002;2:593–605. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang YJ, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate regulates targeting of clathrin adaptor AP-1 complexes to the Golgi. Cell. 2003;114:299–310. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00603-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang J, et al. PI4P promotes the recruitment of the GGA adaptor proteins to the trans-Golgi network and regulates their recognition of the ubiquitin sorting signal. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:2646–2655. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-10-0897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Demmel L, et al. The clathrin adaptor Gga2p is a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate effector at the Golgi exit. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:1991–2002. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-10-0937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hanada K, et al. Molecular machinery for non-vesicular trafficking of ceramide. Nature. 2003;426:803–809. doi: 10.1038/nature02188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bruns JR, Ellis MA, Jeromin A, Weisz OA. Multiple roles for phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in biosynthetic transport in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2012–2018. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108571200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Godi A, et al. ARF mediates recruitment of PtdIns-4-OH kinase-beta and stimulates synthesis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 on the Golgi complex. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:280–287. doi: 10.1038/12993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Belshaw PJ, Ho SN, Crabtree GR, Schreiber SL. Controlling protein association and subcellular localization with a synthetic ligand that induces heterodimerization of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:4604–4607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Suh BC, Inoue T, Meyer T, Hille B. Rapid chemically induced changes of PtdIns(4,5)P2 gate KCNQ ion channels. Science. 2006;314:1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.1131163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varnai P, Thyagarajan B, Rohacs T, Balla T. Rapidly inducible changes in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate levels influence multiple regulatory functions of the lipid in intact living cells. J Cell Biol. 2006;175:377–382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200607116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fili N, Calleja V, Woscholski R, Parker PJ, Larijani B. Compartmental signal modulation: Endosomal phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate controls endosome morphology and selective cargo sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:15473–15478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607040103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Banting G, Ponnambalam S. TGN38 and its orthologues: roles in post-TGN vesicle formation and maintenance of TGN morphology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1355:209–217. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(96)00146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guo S, Stolz LE, Lemrow SM, York JD. SAC1-like domains of yeast SAC1, INP52, and INP53 and of human synaptojanin encode polyphosphoinositide phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12990–12995. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.12990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hughes WE, Cooke FT, Parker PJ. Sac phosphatase domain proteins. Biochem J. 2000;350:337–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Foti M, Audhya A, Emr SD. Sac1 lipid phosphatase and stt4 phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase regulate a pool of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate that functions in the control of the actin cytoskeleton and vacuole morphology. Mol Biol Cell. 2001;128:2396–2411. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Blagoveshchenskaya A, et al. Integration of Golgi trafficking and growth factor signaling by the lipid phosphatase SAC1. J Cell Biol. 2008;180:803–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200708109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dowler S, et al. Identification of pleckstrin-homology-domain-containing proteins with novel phosphoinositide-binding specificities. Biochem J. 2000;351:19–31. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3510019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Levine TP, Munro S. Targeting of Golgi-specific pleckstrin homology domains involves both PtdIns 4-kinase-dependent and -independent components. Curr Biol. 2002;12:695–704. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00779-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hirst J, Futter CE, Hopkins CR. The kinetics of mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking in the endocytic pathway in HEp-2 cells: The receptor enters and rapidly leaves multivesicular endosomes without accumulating in a prelysosomal compartment. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:809–816. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Terui T, Kahn RA, Randazzo PA. Effects of acid phospholipids on nucleotide exchange properties of ADP-ribosylation factor 1. Evidence for specific interaction with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28130–28135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Randazzo PA, Kahn RA. GTP hydrolysis by ADP-ribosylation factor is dependent on both an ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein and acid phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:10758–10763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zoncu R, et al. Loss of endocytic clathrin-coated pits upon acute depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:3793–3798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611733104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Abe N, Inoue T, Galvez T, Klein L, Meyer T. Dissecting the role of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in endocytosis and recycling of the transferrin receptor. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:1488–1494. doi: 10.1242/jcs.020792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cockcroft S, Carvou N. Biochemical and biological functions of class I phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1771:677–691. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Routt SM, Bankaitis VA. Biological functions of phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:254–262. doi: 10.1139/o03-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Balla A, et al. Maintenance of hormone-sensitive phosphoinositide pools in the plasma membrane requires phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIalpha. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:711–721. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-07-0713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nakanishi S, Catt KJ, Balla T. A wortmannin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase that regulates hormone-sensitive pools of inositolphospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:5317–5321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wiedemann C, Schäfer T, Burger MM. Chromaffin granule-associated phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity is required for stimulated secretion. EMBO J. 1996;15:2094–2101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Donaldson JG, Honda A, Weigert R. Multiple activities for Arf1 at the Golgi complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1744:364–373. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carlton JG, Cullen PJ. Coincidence detection in phosphoinositide signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:540–547. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Willars GB, Nahorski SR, Challiss RA. Differential regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-sensitive polyphosphoinositide pools and consequences for signaling in human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5037–5046. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.9.5037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.