Abstract
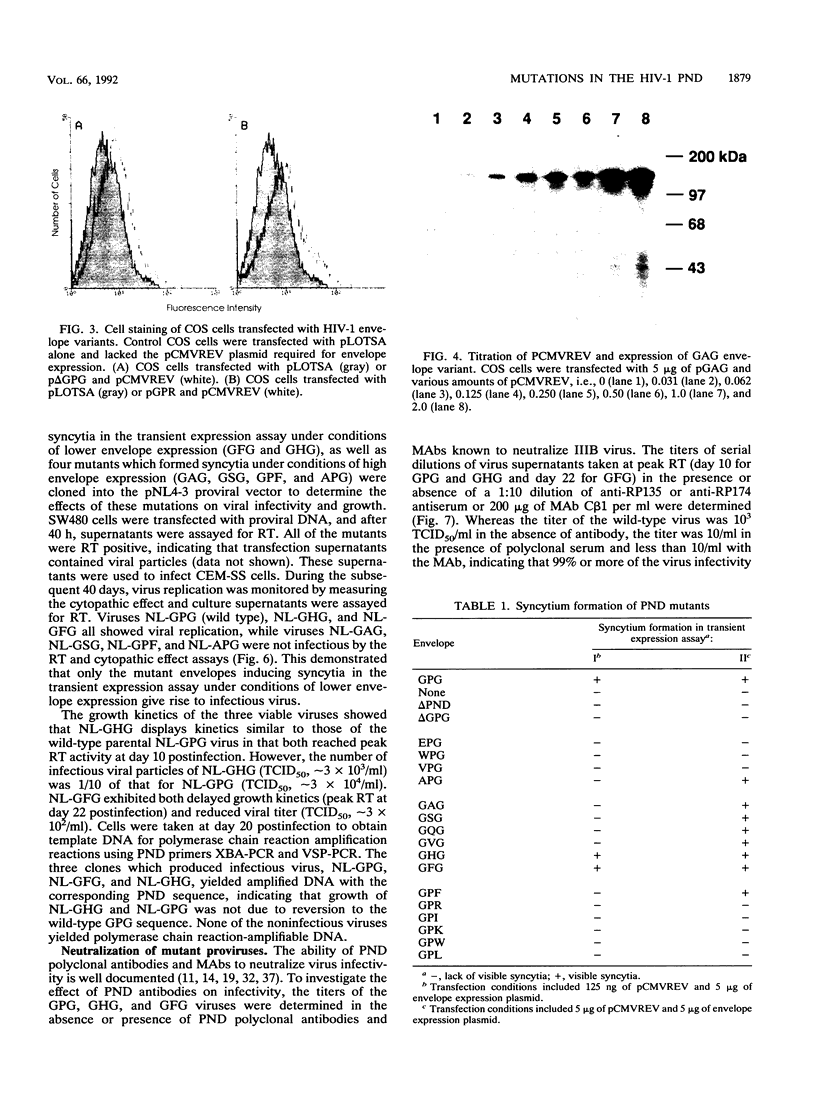
The principal neutralization determinant (PND) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 contains a conserved GPG sequence. The effects of a 29-amino-acid deletion of most of the PND, a 3-amino-acid deletion in the GPG sequence, and 16 single-amino-acid substitutions in the GPG sequence were determined in a transient expression assay. All mutant envelope glycoproteins were expressed at levels comparable to that of the wild-type envelope, and mutations in the GPG sequence did not affect processing to gp120 or, except for the 29-amino-acid deletion, binding to CD4. Of all of the mutants, only the GHG and GFG mutants induced formation of syncytia similar in size and number to those induced by the wild-type envelope. When the envelope expression level was increased 10-fold or more, several additional mutants (APG, GAG, GSG, GQG, GVG, and GPF) also induced syncytium formation. Transfection with infectious proviral molecular clones containing the GHG, GFG, APG, GAG, GSG, or GPF mutations induced production of viral particles; however, only the GPG, GHG, and GFG viruses produced active infections in CD4-bearing cells. Furthermore, whereas the wild-type virus was efficiently neutralized by PND polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies, the GHG- and GFG-containing viruses were not. These results show that mutations in the GPG sequence found within the PND do not affect envelope expression and do not significantly affect CD4 binding or production of viral particles but that they do affect the ability of the envelope to induce syncytia and those of the viral particles to infect CD4 cells and be neutralized by PND antibodies.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Evans L. H., Sevoian M., Chesebro B. Role of the host immune response in selection of equine infectious anemia virus variants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3783–3789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3783-3789.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. J., Price-Jones M. J., Stephens P. E., Sutton C., Schulz T. F., Clapham P. R., McKeating J. A., McClure M. O., Thomson S., Marsh M. The V3 loops of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface glycoproteins contain proteolytic cleavage sites: a possible function in viral fusion? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):3–16. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier A., Montagnier L., Emerman M. Single amino-acid changes in HIV envelope affect viral tropism and receptor binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):571–574. doi: 10.1038/340571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier A., Rivière Y., Montagnier L., Emerman M. Effects of mutations in hyperconserved regions of the extracellular glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on receptor binding. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4464–4468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4464-4468.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Nara P. L., Schleif W. A., Lewis J. A., Davide J. P., Lee D. R., Kessler J., Conley S., Matsushita S., Putney S. D. Antibody-mediated in vitro neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 abolishes infectivity for chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3674–3678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3674-3678.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennie C., Lasky L. A. Model for intracellular folding of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.639-646.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenyö E. M., Morfeldt-Månson L., Chiodi F., Lind B., von Gegerfelt A., Albert J., Olausson E., Asjö B. Distinct replicative and cytopathic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus isolates. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4414–4419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4414-4419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Identification of the principal neutralizing determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 as a fusion domain. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):190–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.190-194.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Looney D. J., McDanal C., Morris J. F., Wong-Staal F., Langlois A. J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Matthews T. J. Alteration of HIV-1 infectivity and neutralization by a single amino acid replacement in the V3 loop domain. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jul;7(7):595–603. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koito A., Hattori T., Murakami T., Matsushita S., Maeda Y., Yamamoto T., Takatsuki K. A neutralizing epitope of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 has homologous amino acid sequences with the active site of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor. Int Immunol. 1989;1(6):613–618. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.6.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. K., Spellman M. W., Riddle L., Harris R. J., Thomas J. N., Gregory T. J. Assignment of intrachain disulfide bonds and characterization of potential glycosylation sites of the type 1 recombinant human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein (gp120) expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10373–10382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Williams J., Rekosh D., Hammarskjöld M. L. Identification of a cis-acting element in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) that is responsive to the HIV-1 rev and human T-cell leukemia virus types I and II rex proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1690–1697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1690-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Kinney-Thomas E., Hu S. L. Effects of anti-gp120 monoclonal antibodies on CD4 receptor binding by the env protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3695–3702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3695-3702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Rusche J., Koito A., Hattori T., Hoshino H., Javaherian K., Takatsuki K., Putney S. Characterization of a human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the neutralizing epitope. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2107-2114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B. Equine infectious anemia: detection of infections virus-antibody complexes in the serum. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(6):545–551. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Gow J., Goudsmit J., Pearl L. H., Mulder C., Weiss R. A. Characterization of HIV-1 neutralization escape mutants. AIDS. 1989 Dec;3(12):777–784. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198912000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hatch W. C., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Fischinger P. J. Simple, rapid, quantitative, syncytium-forming microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):283–302. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Smit L., Dunlop N., Hatch W., Merges M., Waters D., Kelliher J., Gallo R. C., Fischinger P. J., Goudsmit J. Emergence of viruses resistant to neutralization by V3-specific antibodies in experimental human immunodeficiency virus type 1 IIIB infection of chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3779–3791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3779-3791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Clements J. E., Griffin D. E., Wolinsky J. S. Neutralizing antibody spectrum determines the antigenic profiles of emerging mutants of visna virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1045-1050.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Virus mutation during 'slow infection': temporal development and characterization of mutants of visna virus recovered from sheep. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):343–352. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Sheffer D., Griffin D. E., Clements J., Hess J. Lack of neutralizing antibodies to caprine arthritis-encephalitis lentivirus in persistently infected goats can be overcome by immunization with inactivated Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.349-355.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Jr, Wilson C., Naugle C., Gallo R. C., Robert-Guroff M. Generation of a neutralization-resistant variant of HIV-1 is due to selection for a point mutation in the envelope gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D., Nygren A., Flodby P., Hammarskjöld M. L., Wigzell H. Coexpression of human immunodeficiency virus envelope proteins and tat from a single simian virus 40 late replacement vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):334–338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Dewhurst S., Ma X. Y., Volsky D. J. Differences in cytopathogenicity and host cell range among infectious molecular clones of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 simultaneously isolated from an individual. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4078–4085. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4078-4085.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L. Rapid emergence of novel antigenic and genetic variants of equine infectious anemia virus during persistent infection. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.71-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Macrophage and T cell-line tropisms of HIV-1 are determined by specific regions of the envelope gp120 gene. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):167–169. doi: 10.1038/349167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Langlois A. J., McDanal C. B., McDougal J. S., Bolognesi D. P., Matthews T. J. Neutralizing antibodies to an immunodominant envelope sequence do not prevent gp120 binding to CD4. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4195–4200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4195-4200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Clements G., Yarranton G. T., Moore J. A chink in HIV's armour? Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):219–219. doi: 10.1038/343219b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Akutsu M., Murayama K., Shimizu N., Hoshino H. Host range mutant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: modification of cell tropism by a single point mutation at the neutralization epitope in the env gene. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1710–1718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1710-1718.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Lange J. M., de Goede R. E., de Wolf F., Eeftink-Schattenkerk J. K., Schellekens P. T., Coutinho R. A., Huisman J. G., Goudsmit J., Miedema F. Association between biological properties of human immunodeficiency virus variants and risk for AIDS and AIDS mortality. Lancet. 1989 May 6;1(8645):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92628-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L. Identification of a determinant within the human immunodeficiency virus 1 surface envelope glycoprotein critical for productive infection of primary monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]