Abstract
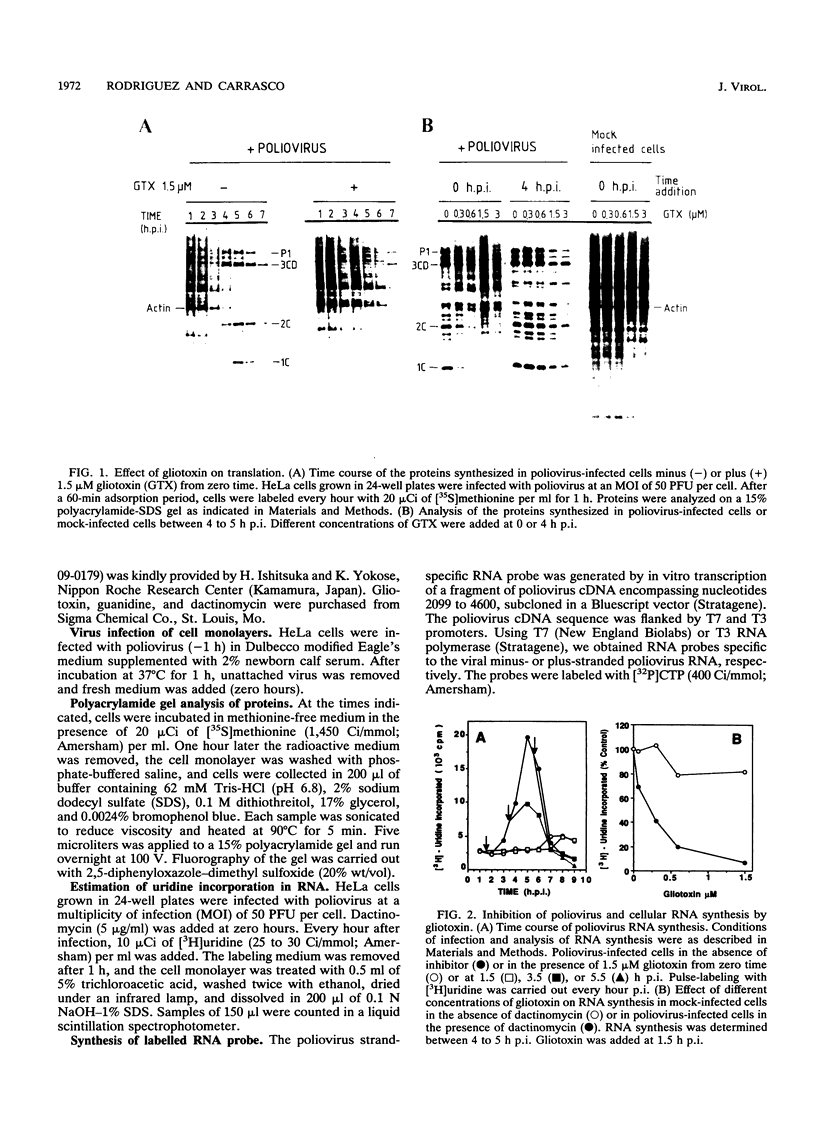
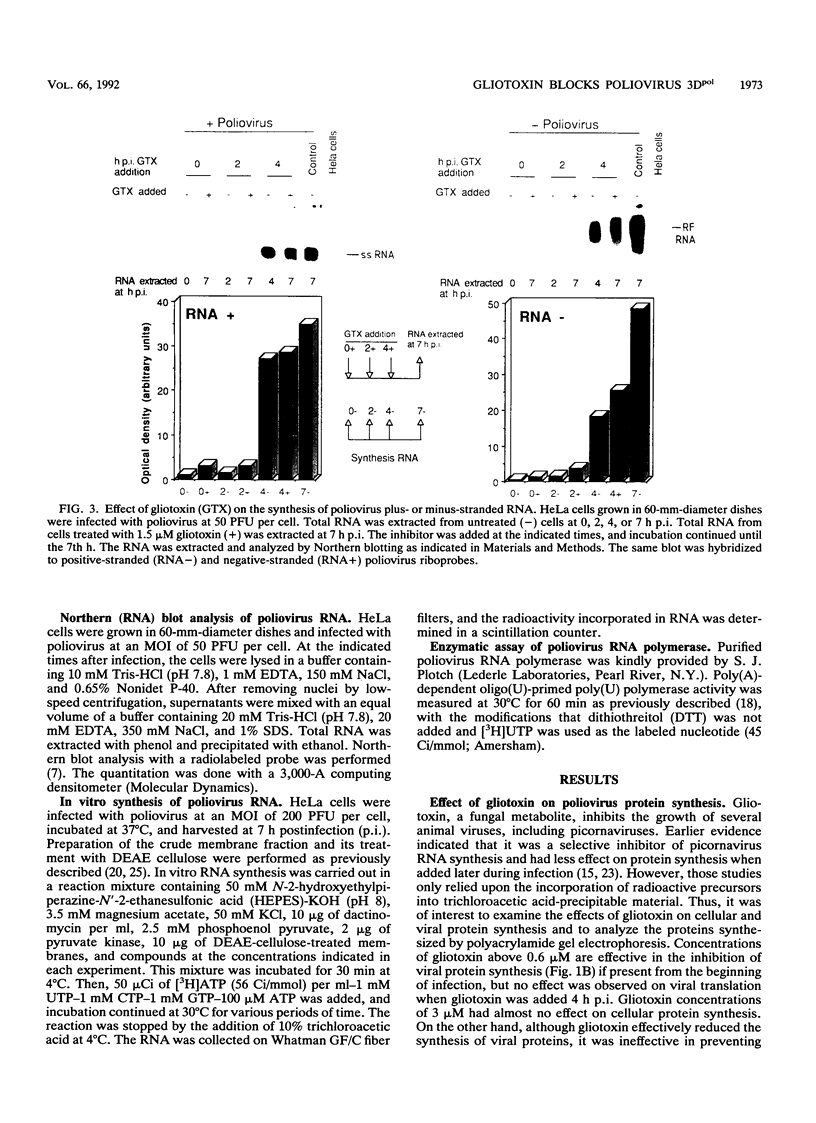
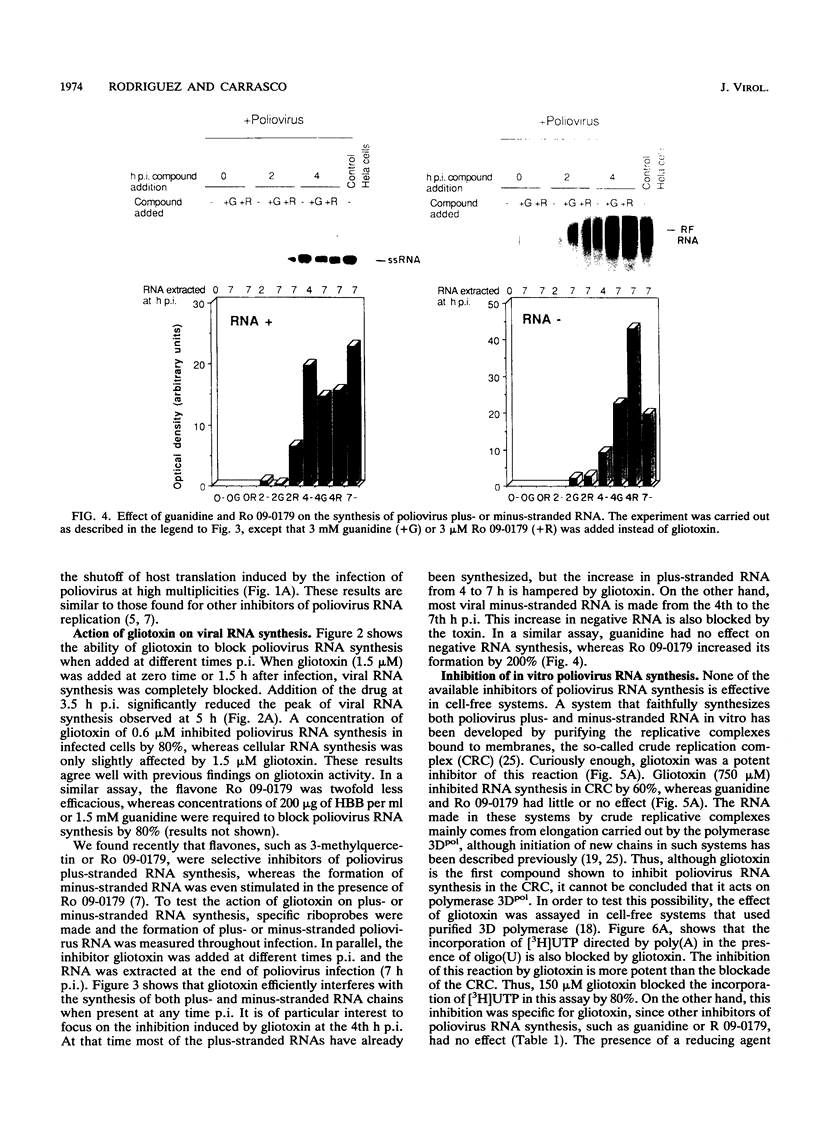
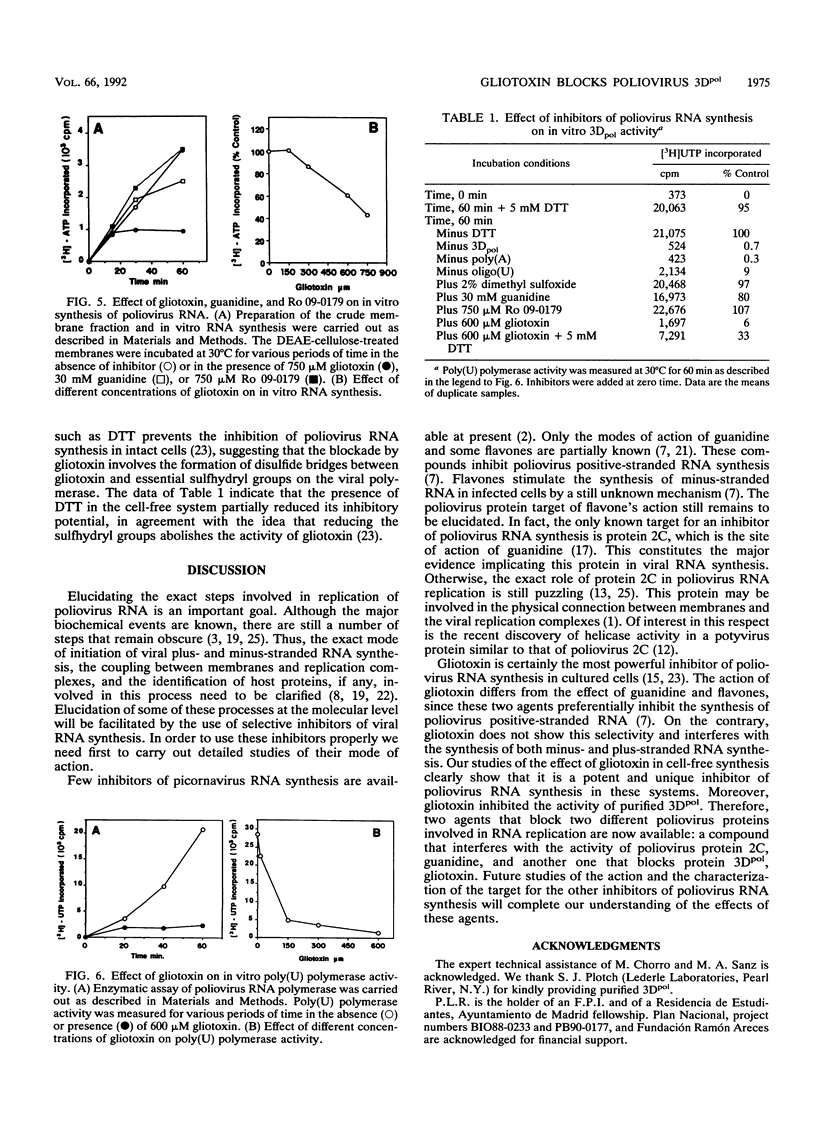
The mode of action of gliotoxin against poliovirus has been analyzed in detail. This fungal metabolite inhibits the appearance of poliovirus proteins when present from the beginning of infection but has no effect on viral translation when added at late times. In agreement with previous findings, this toxin potently inhibited the incorporation of [3H]uridine into poliovirus RNA soon after its addition to the culture medium. Analysis of the synthesis of poliovirus plus- or minus-stranded RNA in the presence of gliotoxin suggests that this compound effectively hampered both processes. This result contrasts with the mode of action of other inhibitors of poliovirus RNA synthesis, such as guanidine or flavones, that selectively block plus-stranded RNA synthesis and suggests that the target of gliotoxin differs from the target of guanidine, i.e., poliovirus protein 2C. Indeed, gliotoxin was found to be a potent inhibitor of poliovirus RNA synthesis in cell-free systems, using membranous crude replication complexes, a reaction that is not blocked by guanidine or Ro 09-0179. Moreover, in vitro activity of the purified poliovirus polymerase 3Dpol was efficiently inhibited by gliotoxin. These results indicate that this toxin acts on the poliovirus polymerase 3Dpol, providing the first description of an inhibitor of this viral enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz K., Egger D., Troxler M., Pasamontes L. Structural organization of poliovirus RNA replication is mediated by viral proteins of the P2 genomic region. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1156-1163.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Otero M. J., Castrillo J. L. Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Carrasco L. Action of 3-methylquercetin on poliovirus RNA replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3319–3321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3319-3321.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Vanden Berghe D., Carrasco L. 3-Methylquercetin is a potent and selective inhibitor of poliovirus RNA synthesis. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinea R., Carrasco L. Phospholipid biosynthesis and poliovirus genome replication, two coupled phenomena. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):2011–2016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Ohsawa C., Ohiwa T., Umeda I., Suhara Y. Antipicornavirus flavone Ro 09-0179. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):611–616. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Martín M. T., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. Novel catalytic activity associated with positive-strand RNA virus infection: nucleic acid-stimulated ATPase activity of the plum pox potyvirus helicaselike protein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.1-6.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merryman P., Jaffe I. A., Ehrenfeld E. Effect of D-penicillamine on poliovirus replication in HeLa cells. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):881–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.881-887.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. A., Milstrey K. P., Trown P. W. Specific inhibition of viral ribonucleic acid replication by Gliotoxin. Science. 1968 Jan 26;159(3813):431–432. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3813.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C. Proteolytic processing of picornaviral polyprotein. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:603–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Wimmer E. Production of guanidine-resistant and -dependent poliovirus mutants from cloned cDNA: mutations in polypeptide 2C are directly responsible for altered guanidine sensitivity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):793–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.793-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Palant O., Gluzman Y. Purification and properties of poliovirus RNA polymerase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):216–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.216-225.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trown P. W., Bilello J. A. Mechanism of action of gliotoxin: elimination of activity by sulfhydryl compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):261–266. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Kuhn R. J., Pincus S., Yang C. F., Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Takeda N. Molecular events leading to picornavirus genome replication. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:251–276. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






