Abstract
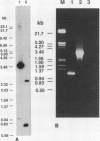
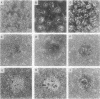
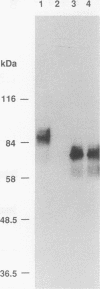
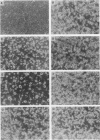
Most orthopoxviruses encode a functional hemagglutinin (HA), which is nonessential for virus growth in cell culture. However, inactivation of the HA gene leads to the formation of polykaryocytes (syncytia) by fusion of infected cells at neutral pH. Fusion is not observed when a functional HA gene is present. Deletion of open reading frames (ORFs) K2, K3, and K4 within the HindIII K fragment of the HA-positive (HA+) vaccinia virus strain WR also led to fusion of cells upon infection at neutral pH. A novel ORF inactivation procedure utilizing the polymerase chain reaction was used to specifically implicate the K2 ORF in this phenomenon. The K2 ORF (the viral SPI-3 gene) encodes a protein resembling serine protease inhibitors (serpins). Inactivation of the SPI-3 gene in any of the HA+ orthopoxviruses tested caused infected cells to fuse in a manner which appeared identical to that seen for HA- mutants, although fusion was most pronounced with cowpox virus. SPI-3-negative strains fused despite the fact that the HA was expressed and processed normally, i.e., cells infected with SPI-3 mutants remained functionally hemadsorption positive, and analysis of the HA protein by Western immunoblot suggested that posttranslational modifications of the HA protein appeared normal. Fusion triggered by SPI-3 mutants, like that for HA- mutants, was inhibited by the monoclonal antibody C3 directed against the vaccinia virus 14-kDa envelope protein. Therefore SPI-3- and HA-mediated fusion share a requirement for the 14-kDa protein, suggesting linkage of the seemingly disparate SPI-3 and HA genes through a common pathway which normally acts to prevent fusion of cells infected with wild-type virus.
Full text
PDF

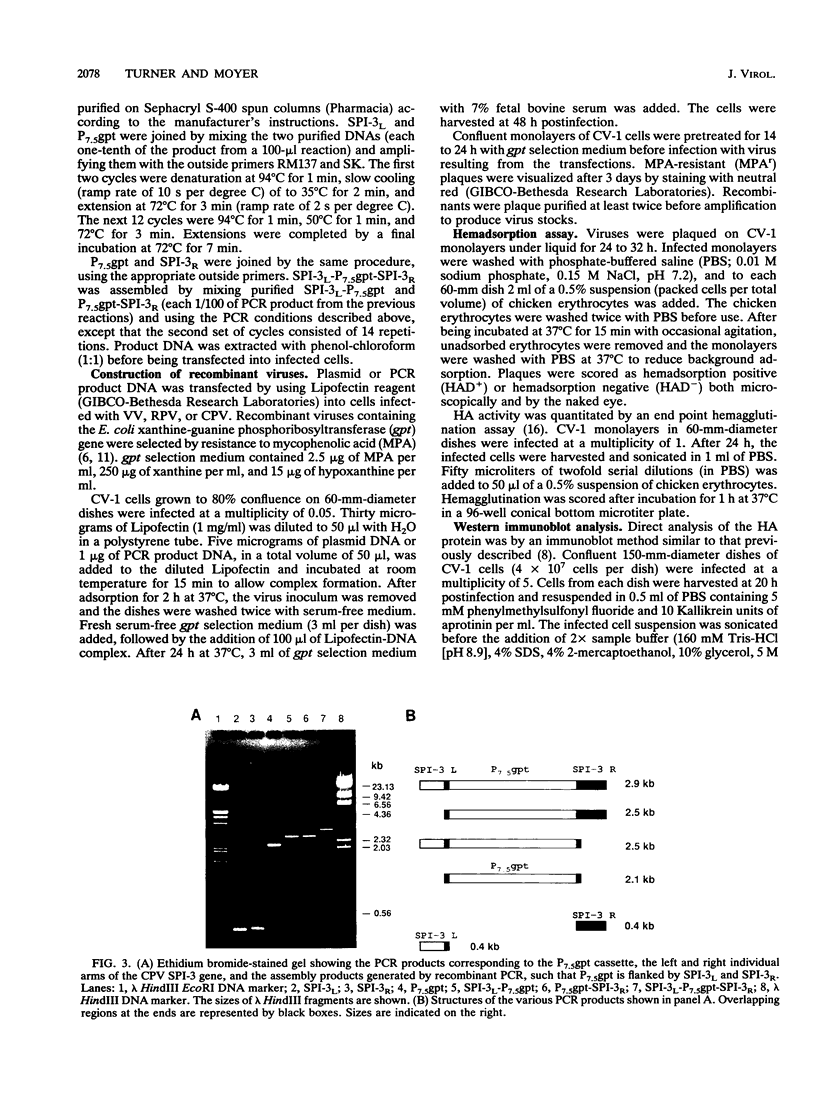

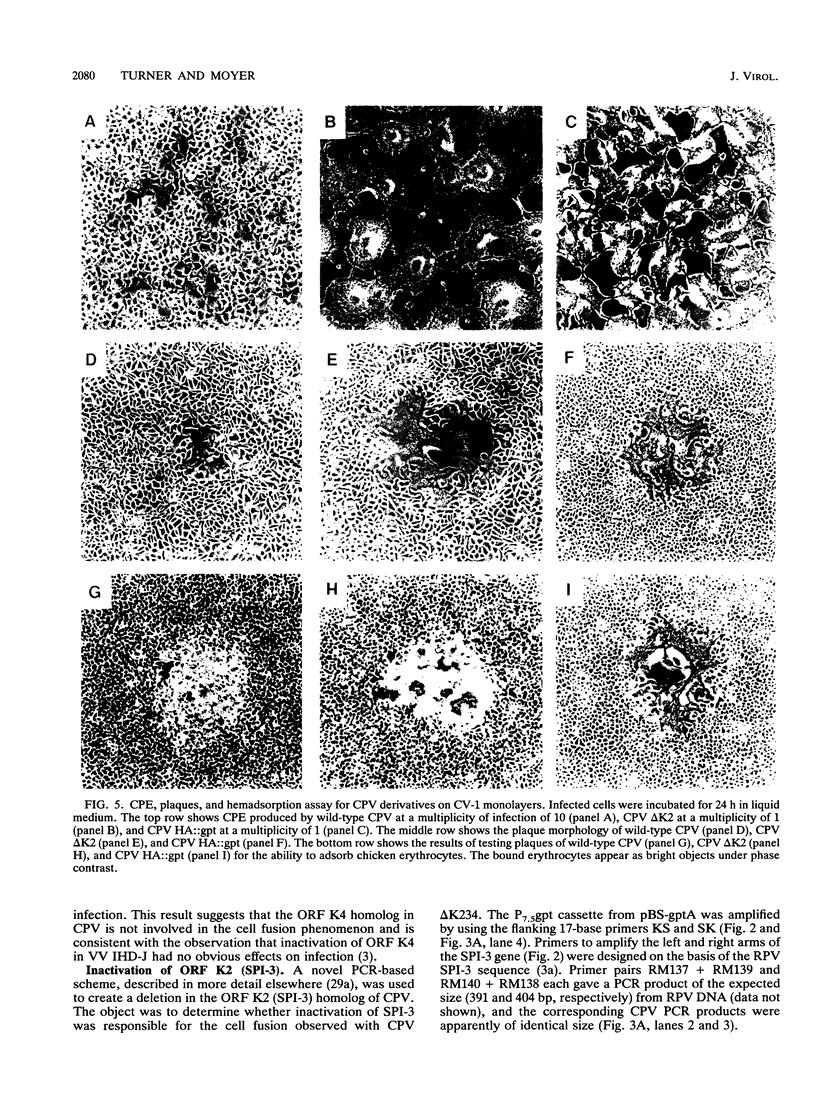
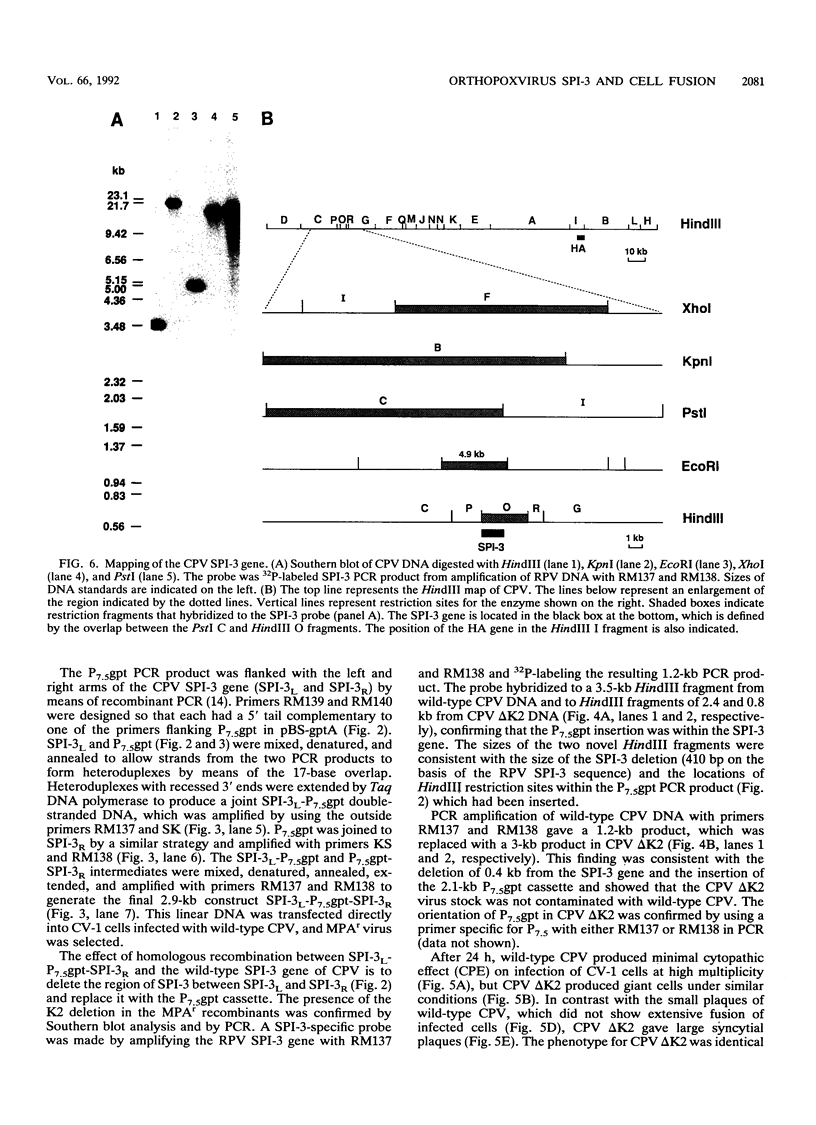

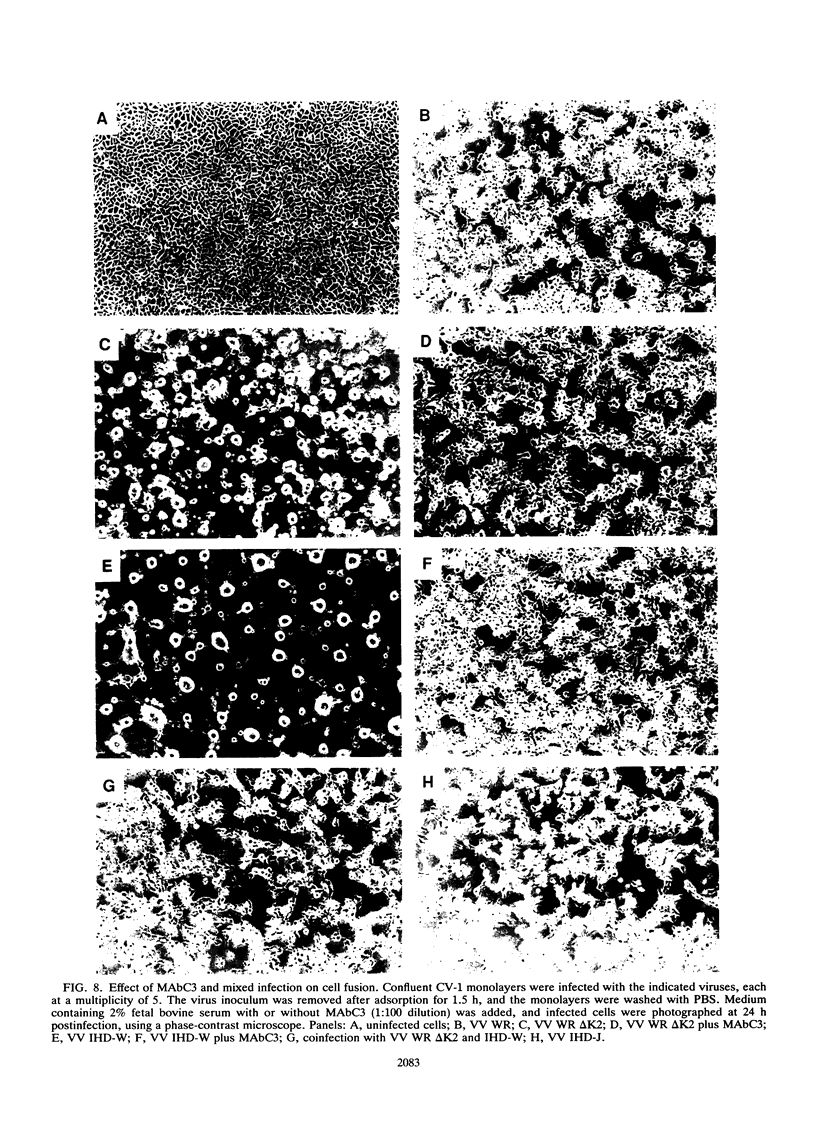


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archard L. C., Mackett M., Barnes D. E., Dumbell K. R. The genome structure of cowpox virus white pock variants. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):875–886. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie E., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus-encoded eIF-2 alpha homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., Moss B. Extracellular vaccinia virus formation and cell-to-cell virus transmission are prevented by deletion of the gene encoding the 37,000-Dalton outer envelope protein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5910–5920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5910-5920.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom D. C., Edwards K. M., Hager C., Moyer R. W. Identification and characterization of two nonessential regions of the rabbitpox virus genome involved in virulence. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1530–1542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1530-1542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Foulds I. J., Campbell J. I., Binns M. M. Non-essential genes in the vaccinia virus HindIII K fragment: a gene related to serine protease inhibitors and a gene related to the 37K vaccinia virus major envelope antigen. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2995–3003. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle D. B., Coupar B. E. A dominant selectable marker for the construction of recombinant poxviruses. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. K., Bloom D. C., Moyer R. W. The nature of naturally occurring mutations in the hemagglutinin gene of vaccinia virus and the sequence of immediately adjacent genes. Virus Genes. 1991 Jul;5(3):235–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00568973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. K., Turner P. C., Moyer R. W. Molecular characterization of the vaccinia virus hemagglutinin gene. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3598–3606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3598-3606.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito J. J., Knight J. C. Orthopoxvirus DNA: a comparison of restriction profiles and maps. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):230–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito J. J., Obijeski J. F., Nakano J. H. Orthopoxvirus DNA: strain differentiation by electrophoresis of restriction endonuclease fragmented virion DNA. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong S. C., Lai C. F., Esteban M. Vaccinia virus induces cell fusion at acid pH and this activity is mediated by the N-terminus of the 14-kDa virus envelope protein. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90381-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt P., Hiller G., Wittek R. Localization and fine structure of a vaccinia virus gene encoding an envelope antigen. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.757-764.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi Y., Dales S. Biogenesis of poxviruses: interrelationship between hemagglutinin production and polykaryocytosis. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Moss B. Vaccinia virus encodes two proteins that are structurally related to members of the plasma serine protease inhibitor superfamily. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.600-606.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Archard L. C. Conservation and variation in Orthopoxvirus genome structure. J Gen Virol. 1979 Dec;45(3):683–701. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-3-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie M., Shida H., Ichihashi Y. The function of the vaccinia hemagglutinin in the proteolytic activation of infectivity. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):494–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90019-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo G. J., Pickup D. J., Fredrickson T. N., McIntyre L. J., Buller R. M. Inhibition of an inflammatory response is mediated by a 38-kDa protein of cowpox virus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):262–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup D. J., Ink B. S., Hu W., Ray C. A., Joklik W. K. Hemorrhage in lesions caused by cowpox virus is induced by a viral protein that is related to plasma protein inhibitors of serine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup D. J., Ink B. S., Parsons B. L., Hu W., Joklik W. K. Spontaneous deletions and duplications of sequences in the genome of cowpox virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6817–6821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Janeczko R., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.482-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Paez E., Esteban M. A 14,000-Mr envelope protein of vaccinia virus is involved in cell fusion and forms covalently linked trimers. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):395–404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.395-404.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Oie M., Ichihashi Y., Shida H. Hemadsorption and fusion inhibition activities of hemagglutinin analyzed by vaccinia virus mutants. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90422-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: molecular basis for the hemagglutination-negative phenotype of the IHD-W strain. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):219–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Howard S. T., Chan Y. S. Vaccinia virus encodes a family of genes with homology to serine proteinase inhibitors. J Gen Virol. 1989 Sep;70(Pt 9):2333–2343. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-9-2333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomley F., Binns M., Campbell J., Boursnell M. Sequence analysis of an 11.2 kilobase, near-terminal, BamHI fragment of fowlpox virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 May;69(Pt 5):1025–1040. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., Macen J. L., Wishart D. S., McFadden G. Myxoma virus and malignant rabbit fibroma virus encode a serpin-like protein important for virus virulence. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90129-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]