Abstract
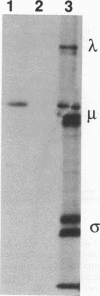
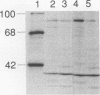
N-myristoylated viral polypeptide mu 1 was produced in COS cells transfected with a transient expression vector containing a DNA copy of the reovirus M2 gene. The mu 1 product was specifically cleaved to polypeptide mu 1C in cells that were cotransfected with the reovirus S4 gene and that expressed polypeptide sigma 3. Studies with site-specific mutants of the M2 gene demonstrated that conversion of mu 1 to mu 1C was dependent on myristoylation and the presence of the proteolytic cleavage sequence asparagine 42-proline 43 in mu 1, as well as on the presence of polypeptide sigma 3. The mu 1C product and polypeptide sigma 3 formed complexes that were immunoprecipitated by sigma 3-directed antibody, and a myristoylation-negative M2 double mutant, G2A-N42T, yielded mu 1 that did not undergo cleavage to mu 1C or bind sigma 3. However, the N42T single mutant did form immunoprecipitable complexes with sigma 3, indicating that binding can occur in the absence of cleavage. Polypeptide sigma 3 alternatively can bind double-stranded RNA and in COS cells stimulates translation of reporter chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation, presumably by blocking double-stranded RNA-mediated activation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit kinase which inhibits the initiation of protein synthesis. Consistent with these observations and with the formation of mu 1C-sigma 3 complexes, coexpression of M2 with S4 DNA prevented the translational stimulatory effect of polypeptide sigma 3.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Svensson C., Nygård O. A mechanism by which adenovirus virus-associated RNAI controls translation in a transient expression assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):549–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M., Ratner L. Myristoylation-dependent replication and assembly of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):523–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Seliger L. S., Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus type 3 genome segment S4: nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding a major virion surface protein. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):984–987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.984-987.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation by reovirus capsid polypeptide sigma 3 in cotransfected COS cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2415-2421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Duronio R. J., Rudnick D. A., Adams S. P., Gokel G. W. Protein N-myristoylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8647–8650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Association of p60src with Triton X-100-resistant cellular structure correlates with morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasuriya A. K., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the M2 gene segment of reovirus type 3 dearing and analysis of its protein product mu 1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Hölscher C., Reuer Q., Harber J., Wimmer E. Myristoylation of the poliovirus polyprotein is required for proteolytic processing of the capsid and for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2433–2436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2433-2436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Characterization of anti-reovirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Masson G., Girard M., van der Werf S. Lack of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP0 prevents the formation of virions or results in the assembly of noninfectious virus particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4099–4107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4099-4107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Simons J., Chow M. Myristoylation is important at multiple stages in poliovirus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2372–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2372-2380.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M. L., Schiff L. A., Fields B. N. Mammalian reoviruses contain a myristoylated structural protein. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1960–1967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1960-1967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. The preS1 protein of hepatitis B virus is acylated at its amino terminus with myristic acid. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1672-1677.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pett D. M., Vanaman T. C., Joklik W. K. Studies on the amino and carboxyl terminal amino acid sequences of reovirus capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):174–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is inhibited in extracts from vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.229-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roner M. R., Sutphin L. A., Joklik W. K. Reovirus RNA is infectious. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):845–852. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90153-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Co M. S., Brown E. G., Fields B. N. Distinct binding sites for zinc and double-stranded RNA in the reovirus outer capsid protein sigma 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger L. S., Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Translational effects and sequence comparisons of the three serotypes of the reovirus S4 gene. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Griffin B. E. Myristic acid is coupled to a structural protein of polyoma virus and SV40. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):619–622. doi: 10.1038/326619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Joklik W. K. Evolution of reovirus genes: a comparison of serotype 1, 2, and 3 M2 genome segments, which encode the major structural capsid protein mu 1C. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]