Abstract
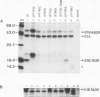
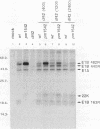
To analyze the structure and function of the E1B 19,000-molecular-weight protein (19K protein) (163R) of human adenovirus type 12, mutants were produced at various positions across the 163R-coding sequence. Viruses bearing mutations within the first 100 or so amino acids yielded unstable 163R-related products, induced DNA degradation and enhanced cytopathic effect (cyt/deg phenotype) in KB cells, and transformed primary rodent cells at much lower efficiencies than wild-type (wt) virus. Deletion of the final 16 residues at the carboxy terminus had no phenotypic effect. Alteration of residue 105 reduced transforming efficiency significantly, suggesting that this region of 163R is functionally important. Disruption of the AUG initiation codon at nucleotide 1542 blocked production of 163R completely but resulted in higher levels of E1B 55K-482R protein synthesis and a transforming efficiency similar to that of wt virus. These data suggested that while 163R is of some importance, normal transforming efficiencies can be obtained in its absence if 482R is overexpressed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Schmitt R. C., Smart J. E., Lewis J. B. Early region 1B of adenovirus 2 encodes two coterminal proteins of 495 and 155 amino acid residues. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):387–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.387-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Fisher P. B., Ginsberg H. S. Effect on transformation of mutations in the early region 1b-encoded 21- and 55-kilodalton proteins of adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.389-395.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S. Adenovirus type 5 early region 1b gene product is required for efficient shutoff of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Adenovirus E1B proteins are required for accumulation of late viral mRNA and for effects on cellular mRNA translation and transport. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2552–2558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus proteins from both E1B reading frames are required for transformation of rodent cells by viral infection and DNA transfection. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90441-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., de Leeuw M. G., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Role of the adenovirus early region 1B tumor antigens in transformation and lytic infection. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):126–139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Polder L. J., Bernards R., Schrier P. I., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J., van Ormondt H. The 2.2 kb E1b mRNA of human Ad12 and Ad5 codes for two tumor antigens starting at different AUG triplets. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Nelson C. C., Bellett A. J. E1a revisited: the case for multiple cooperative trans-activation domains. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton P. E., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Transformation by human adenoviruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(1):67–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(84)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiding D. E., Edbauer C. A., Tong J. Y., Byrd P., Grand R. J., Gallimore P. H., Williams J. Isolation and characterization of adenovirus type 12 E1 host-range mutants defective for growth in nontransformed human cells. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd P. J., Grand R. J., Breiding D., Williams J. F., Gallimore P. H. Host range mutants of adenovirus type 12 E1 defective for lytic infection, transformation, and oncogenicity. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Allart C., Cousin C., Boulanger P. A., Martin G. R. Adenovirus early function required for protection of viral and cellular DNA. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):61–71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.61-71.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbauer C., Lamberti C., Tong J., Williams J. Adenovirus type 12 E1B 19-kilodalton protein is not required for oncogenic transformation in rats. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3265–3273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3265-3273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezoe H., Fatt R. B., Mak S. Degradation of intracellular DNA in KB cells infected with cyt mutants of human adenovirus type 12. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):20–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.20-27.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Saito I., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Isolation of transformation-defective, replication-nondefective early region 1B mutants of adenovirus 12. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.154-161.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Föhring B., Gallimore P. H., Mellow G. H., Raska K., Jr Adenovirus type 12 specific cell surface antigen in transformed cells is a product of the E1b early region. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., PINA M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. IV. Isolation, purification, and chemical analysis of adenovirus. Virology. 1963 May;20:199–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Roberts C., Gallimore P. H. Acylation of adenovirus type 12 early region 1b 18-kDa protein. Further evidence for its localisation in the cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Yew P. R., Berk A. J. Domains required for in vitro association between the cellular p53 and the adenovirus 2 E1B 55K proteins. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):806–814. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90148-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Regulation of protein synthesis in virus-infected animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:229–292. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60265-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Fatt R. B., Mak S. Mapping of an adenovirus function involved in the inhibition of DNA degradation. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):969–977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.969-977.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Identification of adenovirus type 2 early region 1B proteins that share the same amino terminus as do the 495R and 155R proteins. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3879–3888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3879-3888.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Galet H., Mak S. Adenovirus 12 nononcogenic mutants: oncogenicity of transformed cells and viral proteins synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):687–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.687-690.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Lai Fatt R. B., Mak S. Inhibition of protein synthesis enhances transformation of primary cells by viral DNA. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;64(3):256–263. doi: 10.1139/o86-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Mak S. Separate regions of an adenovirus E1B protein critical for different biological functions. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90026-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Mak S. Transformation of rat cells by cyt mutants of adenovirus type 12 and mutants of adenovirus type 5. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1107-1117.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Tremblay M. L., Yee S. P., Ross R., Branton P. E. Acylation of the 176R (19-kilodalton) early region 1B protein of human adenovirus type 5. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3227–3234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3227-3234.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLorie W., McGlade C. J., Takayesu D., Branton P. E. Individual adenovirus E1B proteins induce transformation independently but by additive pathways. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jun;72(Pt 6):1467–1471. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-6-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. Localization of the adenovirus early region 1B 55-kilodalton protein during lytic infection: association with nuclear viral inclusions requires the early region 4 34-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):424–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.424-429.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Katze M. G., Philipson L. Purification of a native membrane-associated adenovirus tumor antigen. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):905–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.905-917.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Logan J., Shenk T. Deletion of the gene encoding the adenovirus 5 early region 1b 21,000-molecular-weight polypeptide leads to degradation of viral and host cell DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.664-671.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Moore M., Logan J., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B-55K transforming polypeptide modulates transport or cytoplasmic stabilization of viral and host cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Graham F. L., Branton P. E. Intracellular localization of adenovirus type 5 tumor antigens in productively infected cells. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. mRNA species and proteins of adenovirus type 12 transforming regions: identification of proteins translated from multiple coding stretches in 2.2 kb region 1B mRNA in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):272–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Ohshima K., Fukui Y., Ariga H. The adenovirus type 12 early-region 1B 58,000-Mr gene product is required for viral DNA synthesis and for initiation of cell transformation. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):792–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.792-801.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Gallimore P. H., Grand R. J. The expression of Ad12 E1B 19K protein on the surface of adenovirus transformed and infected human cells. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):489–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Gysbers J., Mak S., Chinnadurai G. 19-kDa tumor antigen coded by early region E1b of adenovirus 2 is required for efficient synthesis and for protection of viral DNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11777–11783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Mak S., Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus cyt+ locus, which controls cell transformation and tumorigenicity, is an allele of lp+ locus, which codes for a 19-kilodalton tumor antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.336-343.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori N., Cladaras C., Bhat B., Conley A. J., Wold W. S. cyt gene of adenoviruses 2 and 5 is an oncogene for transforming function in early region E1B and encodes the E1B 19,000-molecular-weight polypeptide. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):793–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.793-805.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori N., Riggs J. L., Aldrich C. Genetic studies with tumorigenic adenoviruses. I. Isolation of cytocidal (cyt) mutants of adenovirus type 12. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):575–586. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Organization of early region 1B of human adenovirus type 2: identification of four differentially spliced mRNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):383–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.383-391.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Blose S. H., Stillman B. W. Nuclear envelope localization of an adenovirus tumor antigen maintains the integrity of cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2865–2875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):120–130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R., Sabbatini P., Denton A. Adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein overcomes the cytotoxicity of E1A proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2968–2978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2968-2978.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Specific disruption of intermediate filaments and the nuclear lamina by the 19-kDa product of the adenovirus E1B oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9886–9890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Faha B., Stillman B. Regulation of adenovirus gene expression in human WI38 cells by an E1B-encoded tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3763–3773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Grodzicker T., Stillman B. W. Mutations in the gene encoding the adenovirus early region 1B 19,000-molecular-weight tumor antigen cause the degradation of chromosomal DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):410–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.410-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequences of adenovirus DNAs. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:73–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]