Abstract
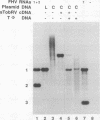
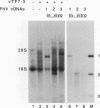
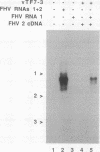
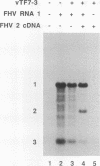
RNA replication provides a powerful means for the amplification of RNA, but to date it has been found to occur naturally only among RNA viruses. In an attempt to harness this process for the amplification of heterologous mRNAs, both an RNA replicase and its corresponding RNA templates have been expressed in functional form, using vaccinia virus-bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase vectors. Plasmids were constructed which contained in 5'-to-3' order (i) a bacteriophage T7 promoter; (ii) a full-length cDNA encoding either the RNA replicase (RNA 1) or the coat protein (RNA 2) of flock house virus (FHV), (iii) a cDNA sequence that encoded the self-cleaving ribozyme of satellite tobacco ringspot virus, and (iv) a T7 transcriptional terminator. Both in vitro and in vivo, circular plasmids of this structure were transcribed by T7 RNA polymerase to produce RNAs with sizes that closely resembled those of the two authentic FHV genomic RNAs, RNA 1 and RNA 2. In baby hamster kidney cells that expressed authentic FHV RNA replicase, the RNA 2 (coat protein) transcripts were accurately replicated. Moreover, the RNA 1 (replicase) transcripts directed the synthesis of an enzyme that could replicate not only authentic virion-derived FHV RNA but also the plasmid-derived transcripts themselves. Under the latter conditions, replicative amplification of the RNA transcripts ensued and resulted in a high rate of synthesis of the encoded proteins. This successful expression from a DNA vector of the complex biological process of RNA replication will greatly facilitate studies of its mechanism and is a major step towards the goal of harnessing RNA replication for mRNA amplification.
Full text
PDF


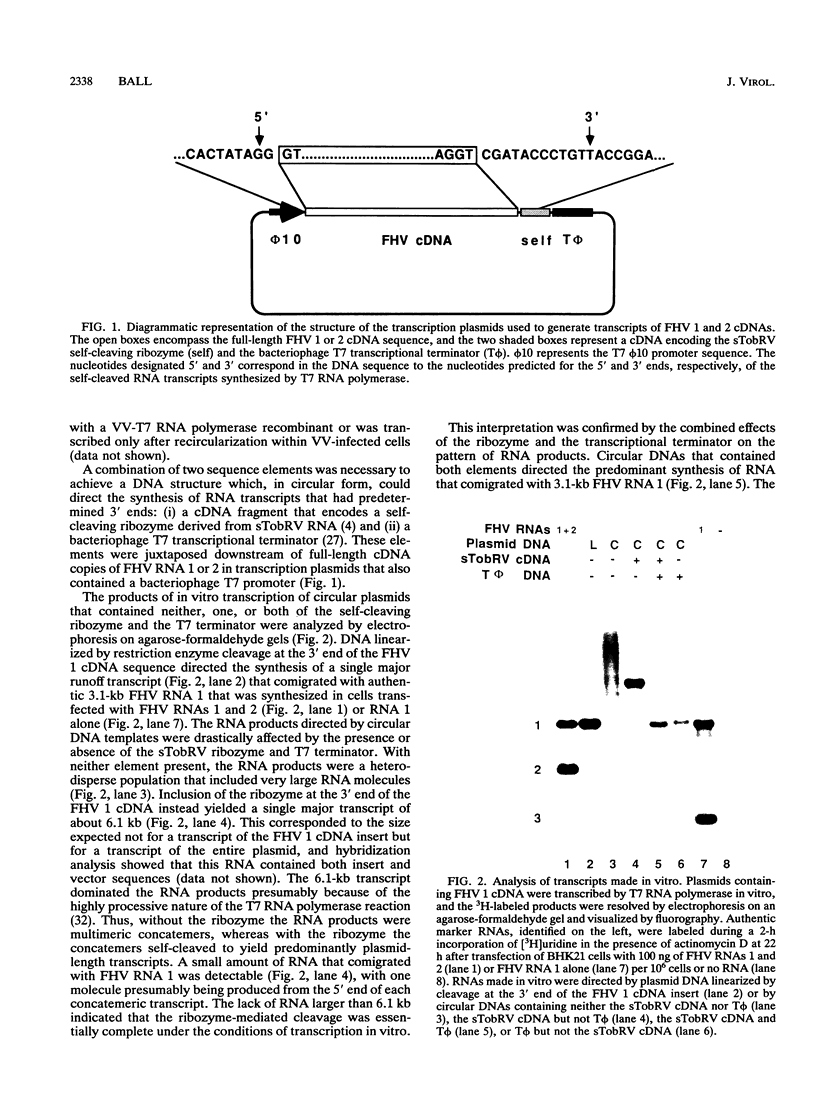

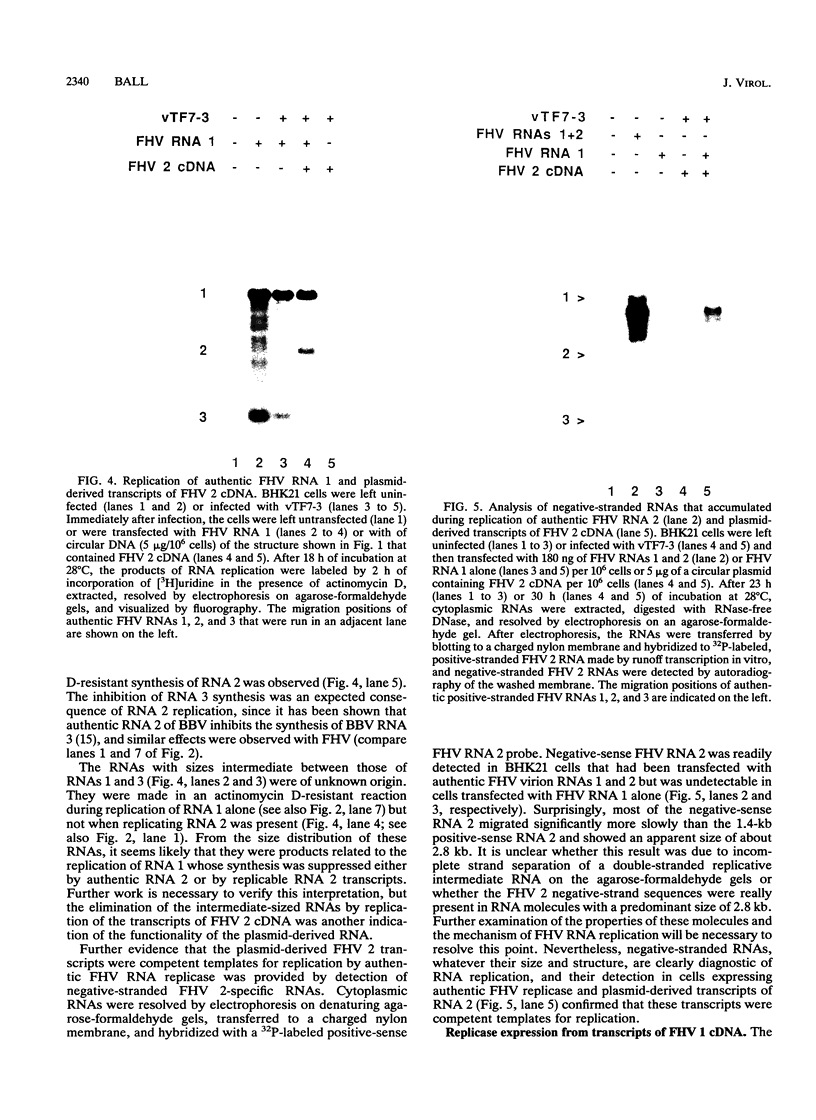




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison R. F., Janda M., Ahlquist P. Infectious in vitro transcripts from cowpea chlorotic mottle virus cDNA clones and exchange of individual RNA components with brome mosaic virus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3581–3588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3581-3588.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., Amann J. M., Garrett B. K. Replication of nodamura virus after transfection of viral RNA into mammalian cells in culture. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2326–2334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2326-2334.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruening G. Compilation of self-cleaving sequences from plant virus satellite RNAs and other sources. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:546–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzayan J. M., Gerlach W. L., Bruening G. Satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA: A subset of the RNA sequence is sufficient for autolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8859–8862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Ghosh A., Dasmahapatra B., Guarino L. A., Kaesberg P. Primary and secondary structure of black beetle virus RNA2, the genomic messenger for BBV coat protein precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7215–7223. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Ghosh A., Kaesberg P. Structure of the black beetle virus genome and its functional implications. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90337-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Saunders K., Selling B., Gallagher T., Kaesberg P. Infectious RNA derived by transcription from cloned cDNA copies of the genomic RNA of an insect virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):63–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzianott A. M., Bujarski J. J. An in vitro transcription vector which generates nearly correctly ended RNAs by self-cleavage of longer transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10940–10940. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzianott A. M., Bujarski J. J. Derivation of an infectious viral RNA by autolytic cleavage of in vitro transcribed viral cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Black beetle virus: messenger for protein B is a subgenomic viral RNA. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):986–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.986-995.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Synthesis of Black Beetle Virus Proteins in Cultured Drosophila Cells: Differential Expression of RNAs 1 and 2. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):876–886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.876-886.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P., Scotti P., Longworth J., Rueckert R. Black beetle virus: propagation in Drosophila line 1 cells and an infection-resistant subline carrying endogenous black beetle virus-related particles. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.741-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Autonomous replication and expression of RNA 1 from black beetle virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.481-489.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Ghosh A., Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Sequence of the black beetle virus subgenomic RNA and its location in the viral genome. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Guarino L. A., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication. I. Requirement for the host-cell nucleus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):705–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.705-715.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaesberg P., Dasgupta R., Sgro J. Y., Wery J. P., Selling B. H., Hosur M. V., Johnson J. E. Structural homology among four nodaviruses as deduced by sequencing and X-ray crystallography. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90191-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. Construction of a series of several self-cleaving RNA duplexes using synthetic 21-mers. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):228–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling M. L., Risman S. S., Klement J. F., McGraw N., McAllister W. T. Abortive initiation by bacteriophage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases under conditions of limiting substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1605–1618. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. V., Yang C. F., Jang S. K., Kuhn R. J., Tada H., Nicklin M., Kräusslich H. G., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Molecular events leading to poliovirus genome replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:343–352. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prody G. A., Bakos J. T., Buzayan J. M., Schneider I. R., Bruening G. Autolytic processing of dimeric plant virus satellite RNA. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4745.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K., Kaesberg P. Template-dependent RNA polymerase from black beetle virus-infected Drosophila melanogaster cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti P. D., Dearing S., Mossop D. W. Flock House virus: a nodavirus isolated from Costelytra zealandica (White) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Arch Virol. 1983;75(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01315272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selling B. H., Allison R. F., Kaesberg P. Genomic RNA of an insect virus directs synthesis of infectious virions in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selling B. H., Rueckert R. R. Plaque assay for black beetle virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):251–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.251-253.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]