Abstract
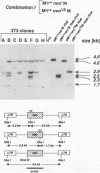
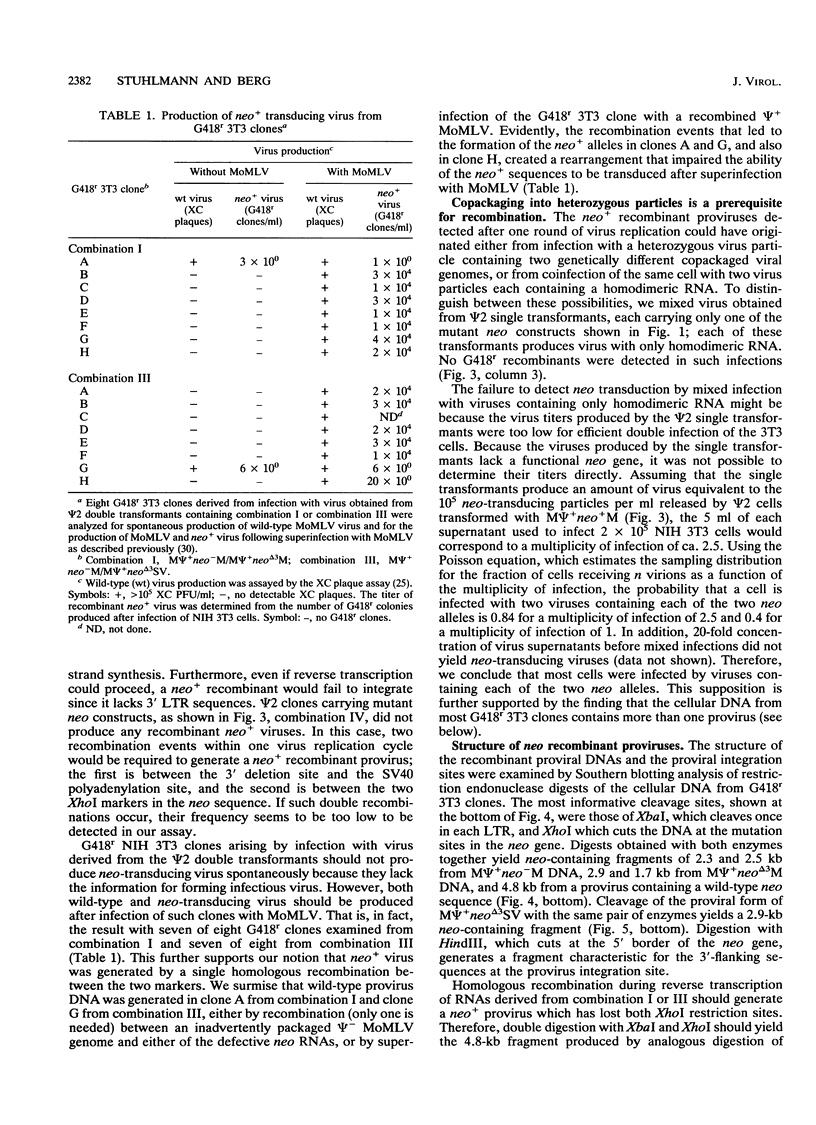
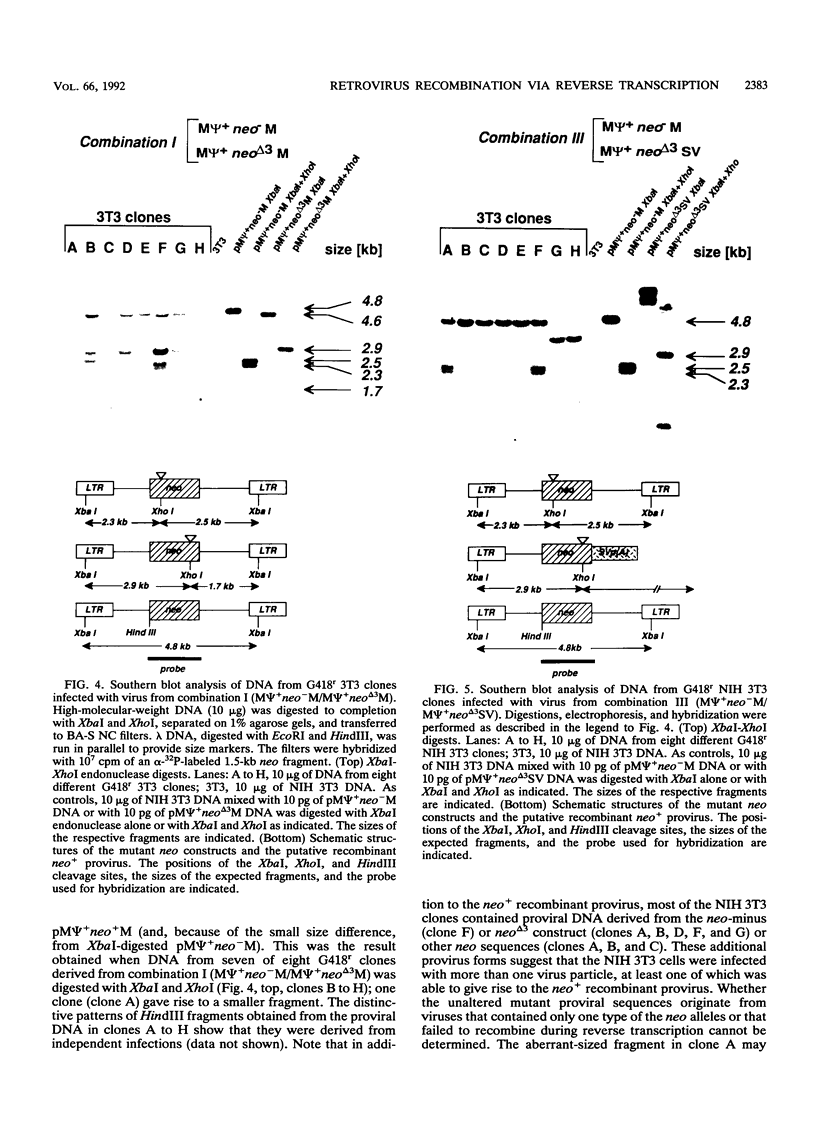
According to prevailing models, the high frequency of recombination in retroviruses occurs during reverse transcription of two genetically different genomes copackaged into virion particles. This view has been tested in our studies of the mechanism of recombination within homologous sequences of two retroviral genomes during a single round of virus replication and in the absence of helper virus. The recombination substrates were Moloney murine leukemia virus-based vectors, each of which contains an altered defective neomycin gene (neo) under the transcriptional control of the 5' long terminal repeat; the 3' sequences of each construct contain either the Moloney murine leukemia virus or simian virus 40 large-T polyadenylation sequence. One neo gene contained a linker insertion mutation at the 5' end (neo minus), and the other contained a deletion and linker insertion at the 3' end (neo delta 3). Each of the mutant neo constructs was introduced into the packaging helper cell line psi 2 by sequential cotransfection, and individual psi 2 double transformants were selected. Supernatant fluids from the cloned psi 2 double transformants were used to infect NIH 3T3 cells, and recombinant neo+ proviruses were detected by their ability to confer G418 resistance during infection of NIH 3T3 cells. Our results show that (i) recombination between a homologous sequence of about 560 bp occurred with a frequency of about 10(-4) per virus replication cycle; (ii) recombination occurred only after the viral RNAs had been packaged into particles, i.e., recombination between the two vector DNAs or between viral RNAs prior to packaging was not detected; and (iii) copackaging of two different genomic RNAs as a heterodimer is a prerequisite for recombination. Furthermore, our results indicate that recombination can occur during the DNA negative-strand synthesis of reverse transcription.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W., Chien Y. H., Chattopadhyay S., Vogt P. K., Gardner M. B., Davidson N. High-molecular-weight RNAs of AKR, NZB, and wild mouse viruses and avian reticuloendotheliosis virus all have similar dimer structures. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):888–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.888-896.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth E., Gabus C., Darlix J. L. A study of the dimer formation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA and of its effect on viral protein synthesis in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):119–127. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Mason W. S., Hunter E., Vogt P. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of avian sarcoma viruses: genetic recombination between multiple or coordinate mutants and avian leukosis viruses. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):48–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Stuhlmann H., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Cloning of two genetically transmitted Moloney leukemia proviral genomes: correlation between biological activity of the cloned DNA and viral genome activation in the animal. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1088–1098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1088-1098.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Hoggan M. D., Willey R. L., Strebel K., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Genetic recombination of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1455–1459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1455-1459.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Structure, replication, and recombination of retrovirus genomes: some unifying hypotheses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):1–26. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Hopkins N. T1 oligonucleotides that segregate with tropism and with properties of gp70 in recombinants between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):153–158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.153-158.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Duesberg P. H. Retroviral recombination during reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman S. C., Mulligan R. C. Two dominant-acting selectable markers for gene transfer studies in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8047–8051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Genetic consequences of packaging two RNA genomes in one retroviral particle: pseudodiploidy and high rate of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1556–1560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. The mechanism for genetic recombination in the avian retroviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:295–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans R. P., Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Retroviral DNA H structures: displacement-assimilation model of recombination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. Genetic recombination with avian tumor virus. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo G. X., Taylor J. Template switching by reverse transcriptase during DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4321–4328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4321-4328.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti K. G., Bondurant M., Tereba A. Secondary structural features in the 70S RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia and Rous sarcoma viruses as observed by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.411-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Roy C., Wang P. A., Erard M., Housset V., Gabus C., Paoletti C., Darlix J. L. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in dimer formation of murine leukemia virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.774-783.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Berg P. Homologous recombination between defective neo genes in mouse 3T6 cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:171–181. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Anderson G. R., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Evidence for genetic recombination between endogenous and exogenous mouse RNA type C viruses. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of murine leukemia virus. IV. Further physiological characterization and evidence for genetic recombination. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):918–923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.918-923.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Dieckmann M., Berg P. Transduction of cellular neo mRNA by retrovirus-mediated recombination. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5783–5796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5783-5796.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Jaenisch R., Mulligan R. C. Construction and properties of replication-competent murine retroviral vectors encoding methotrexate resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K. Genetically stable reassortment of markers during mixed infection with avian tumor viruses. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):947–952. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Mason W. S., Vogt P. K. Genetic recombinants and heterozygotes derived from endogenous and exogenous avian RNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):535–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., McCarter J. A. Genetic studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney-murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1973 Jun;53(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90209-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A., Beamand J. A. Genetic recombination in Rous sarcoma virus: the genesis of recombinants and lack of evidence for linkage between pol, env and src genes in three factor crosses. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):349–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A., Bell J. G., Beamand J. A. Genetic recombination among temperature-sensitive mutnats of Rous sarcoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):897–905. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]