Abstract
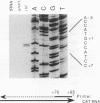
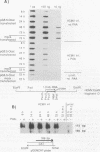
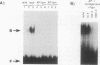
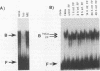
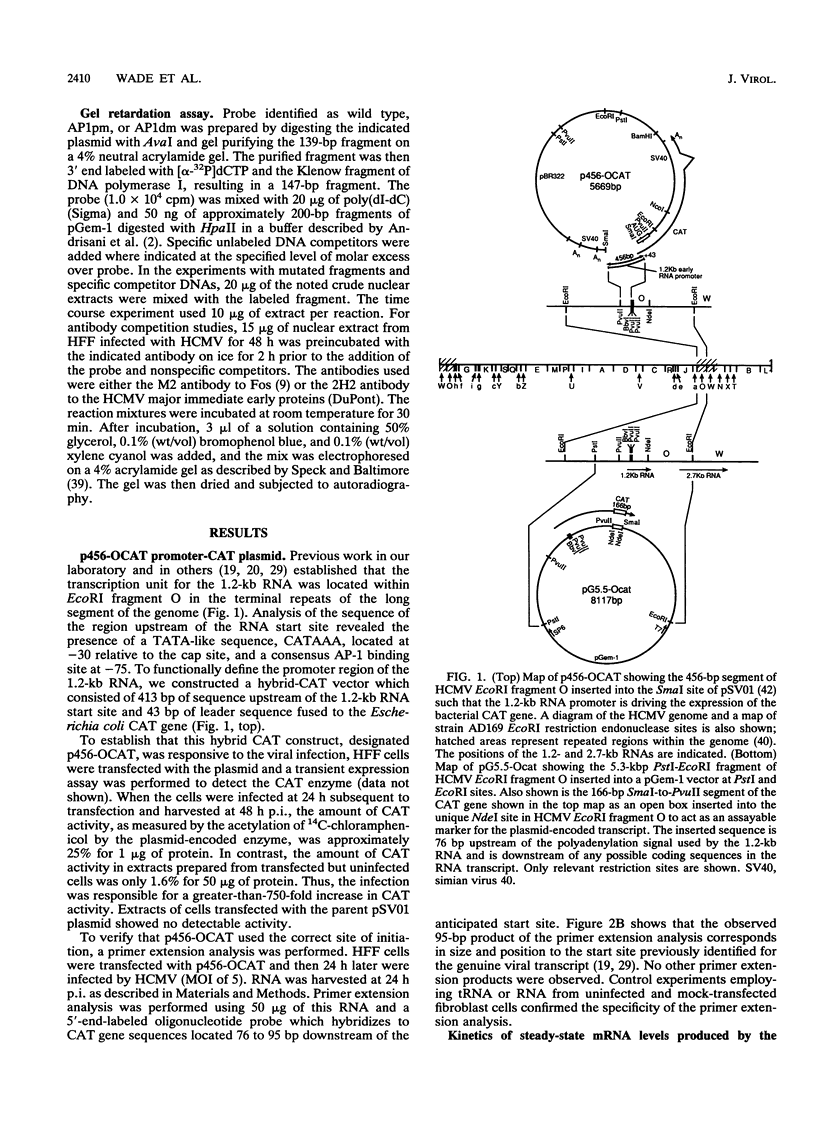
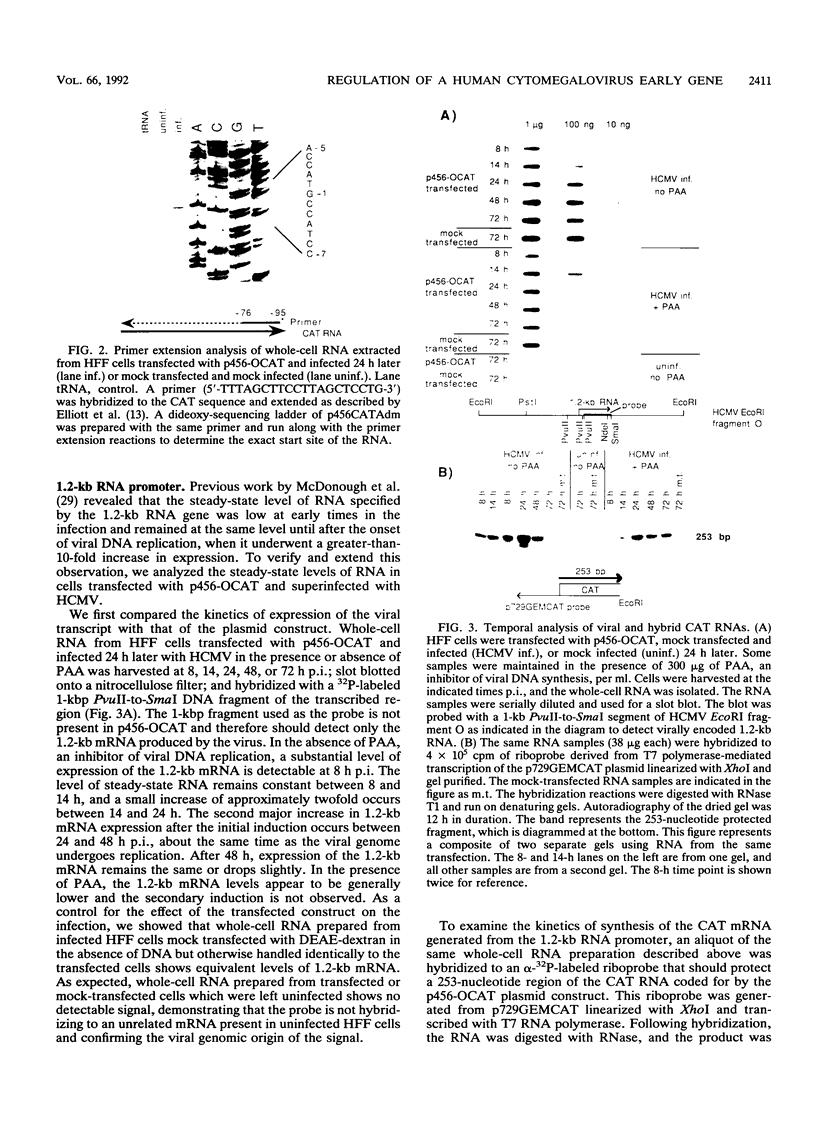
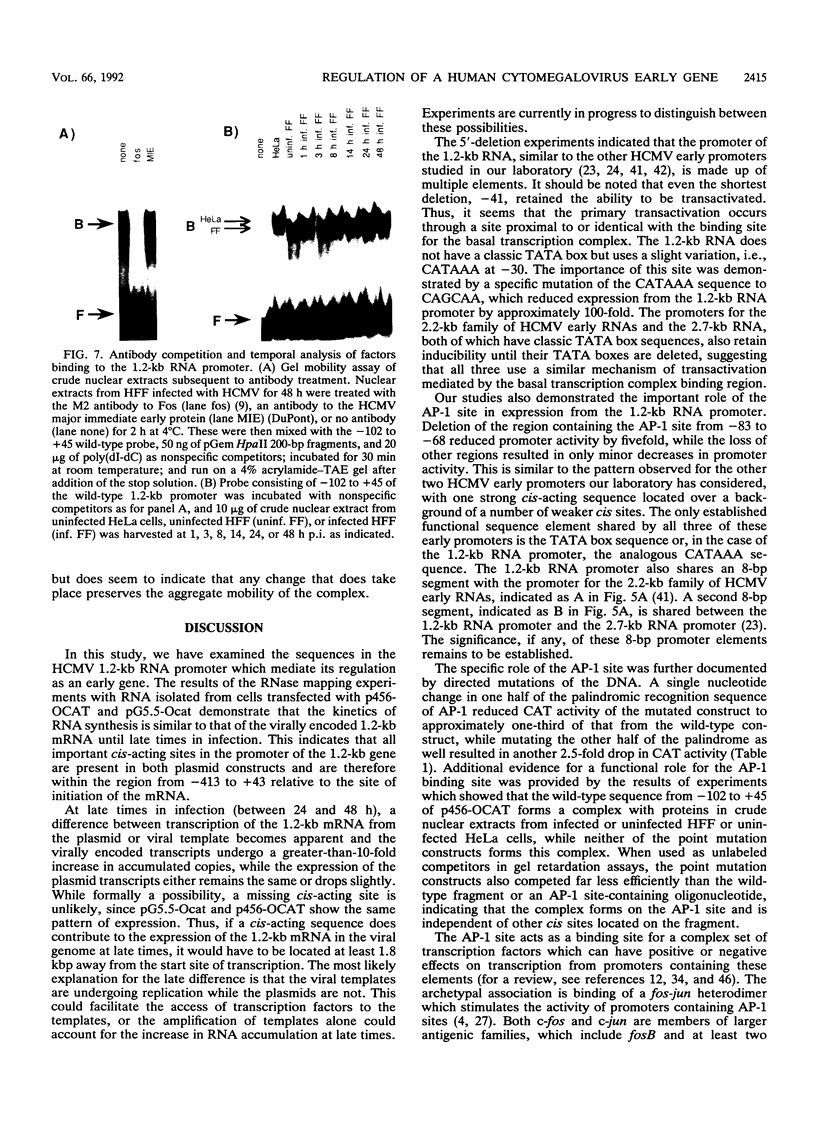
To extend our analysis of the regulation of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) early gene expression, we examined a transcription unit located in the terminal repeats of the long segment of the viral genome. This region encodes a major 1.2-kb RNA which is induced at early times in infection but undergoes its largest increase in abundance after the onset of viral DNA replication. To identify the important cis-acting regulatory elements for this gene, two constructs were prepared for use in transient expression assays. One contained 413 bp of the upstream sequence and 43 bp of the leader sequence fused to the gene for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). The second construct included 1,722 bp upstream of the start site of the 1.2-kb RNA, the entire transcribed region with an additional 166-bp insert derived from the CAT gene as an assayable marker, and 2,393 bp downstream of the polyadenylation signal. Both constructs were individually transfected into human fibroblast cells, and the cells were infected with HCMV. RNA specified by the hybrid construct was initiated at the correct position and accumulated with the same kinetics as the authentic viral transcript at early times in the infection but did not undergo the increase in abundance at late at late times. By 5'-end-deletion analysis, we determined that the promoter for the 1.2-kb RNA contains a number of cis-acting elements, the most significant of which are the TATA-like sequence CATAAA at -30 and a sequence corresponding to the binding site for the transcription factor AP-1 at -75. Using extracts prepared from HeLa cells as well as from infected and uninfected fibroblasts in gel retardation assays, we obtained evidence for the specific interaction of a cellular factor(s) with the AP-1 binding site. The pattern of binding differed in the HeLa and fibroblast cells but did not change as a function of the HCMV infection. However, the functional importance of the AP-1 binding site and its key role in the regulation of the 1.2-kb RNA was supported by analysis of constructs containing specific point mutations at this site in gel retardation and transient expression assays. Site-specific mutations in the AP-1 consensus sequence, which resulted in the complete loss of binding to cellular factors, eliminated the basal activity and reduced the inducible promoter activity by eightfold.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Wong S., Bristol G., Larkin B., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a factor in vivo to the metal-responsive elements of the metallothionein 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3574–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Pot D. A., Zhu Z., Dixon J. E. Three sequence-specific DNA-protein complexes are formed with the same promoter element essential for expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1947–1956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., AbuBakar S., Deng C. Z., Albrecht T. Transcriptional activation of cellular oncogenes fos, jun, and myc by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1568-1571.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Buckbinder L., Leza M. A., Rak N., Hearing P., Merino A., Reinberg D. EivF, a factor required for transcription of the adenovirus EIV promoter, binds to an element involved in EIa-dependent activation and cAMP induction. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Protooncogene c-fos as a transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:37–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R., Clark C., Jaquish D., Spector D. H. Transcription analysis and sequence of the putative murine cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):169–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Eckhart W. Transcriptional regulation of early-response genes during polyomavirus infection. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2193–2201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2193-2201.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Wilkinson G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the most abundantly transcribed early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1987 Feb;7(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson N. I., Sondermeyer R. T., Tocci M. J. Organization and expression of the major genes from the long inverted repeat of the human cytomegalovirus genome. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):160–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson N. I., Tocci M. J. Characterization of a major early gene from the human cytomegalovirus long inverted repeat; predicted amino acid sequence of a 30-kDa protein encoded by the 1.2-kb mRNA. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):172–182. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucher K. M., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Sequences in the human cytomegalovirus 2.7-kilobase RNA promoter which mediate its regulation as an early gene. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5334–5343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5334-5343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucher K. M., Spector D. H. The human cytomegalovirus 2.7-kilobase RNA promoter contains a functional binding site for the adenovirus major late transcription factor. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4189–4198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4189-4198.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. Analysis of the major transcripts encoded by the long repeat of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):711–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.711-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Montross L., Garcea R. L. Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1168–1176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1168-1176.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nankervis G. A., Kumar M. L. Diseases produced by cytomegaloviruses. Med Clin North Am. 1978 Sep;62(5):1021–1035. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31752-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina H., Sato H., Suzuki T., Sato M., Iba H. Isolation and characterization of fra-2, an additional member of the fos gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3619–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Verma I. M. Nuclear proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:539–557. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Hock L., Tamashiro J. C. Cleavage maps for human cytomegalovirus DNA strain AD169 for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII, and HindIII. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):558–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.558-582.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. 2.2-kilobase class of early transcripts encoded by cell-related sequences in human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):591–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.591-602.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Hock L. J., Spector D. H. Construction of a cloned library of the EcoRI fragments from the human cytomegalovirus genome (strain AD169). J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):547–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.547-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. jun: oncogene and transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. W., Akrigg A., Greenaway P. J. Transcription of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1984;1(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Szura L. L., Rushford C., Jackson D., Erickson J. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: the external transcribed spacer and adjacent regions. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Jan;34(1):32–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Toschi L., Ryseck R. P., Schuermann M., Müller R., Bravo R. The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):805–813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J., Stiles C. D., Garcea R. L. Regulation of c-myc and c-fos mRNA levels by polyomavirus: distinct roles for the capsid protein VP1 and the viral early proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]