Abstract
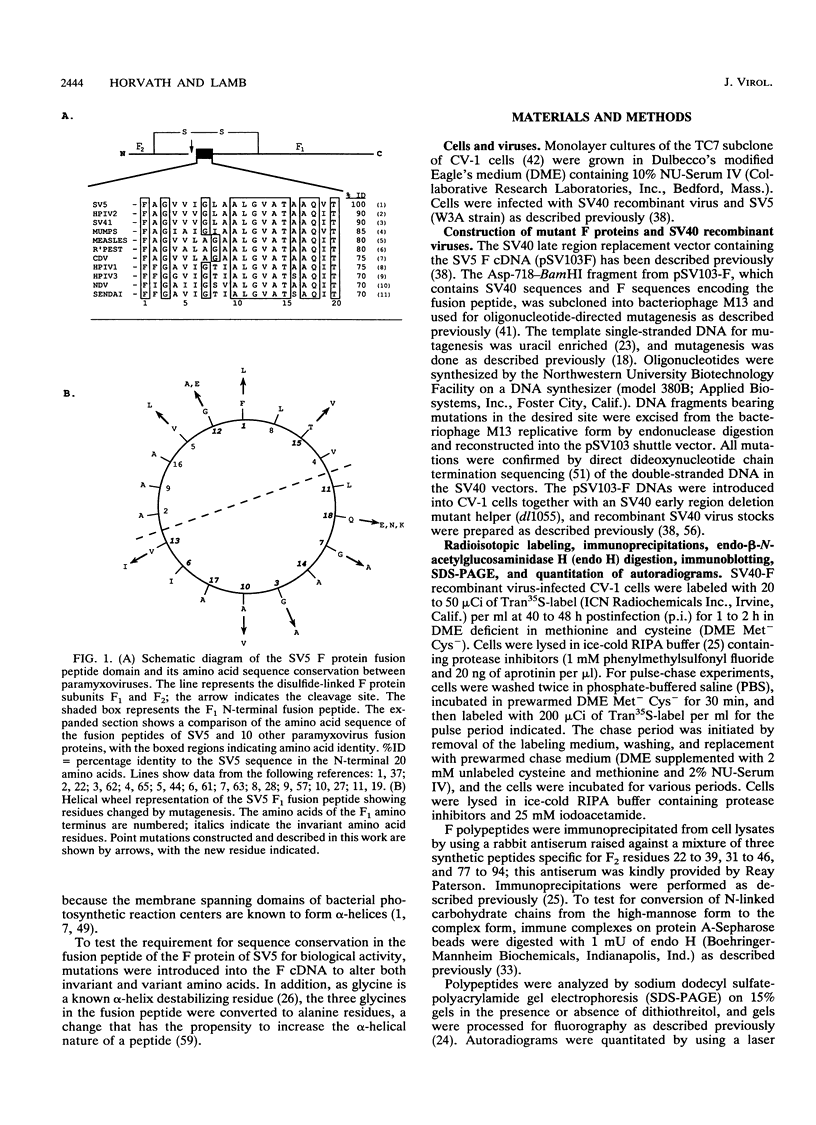
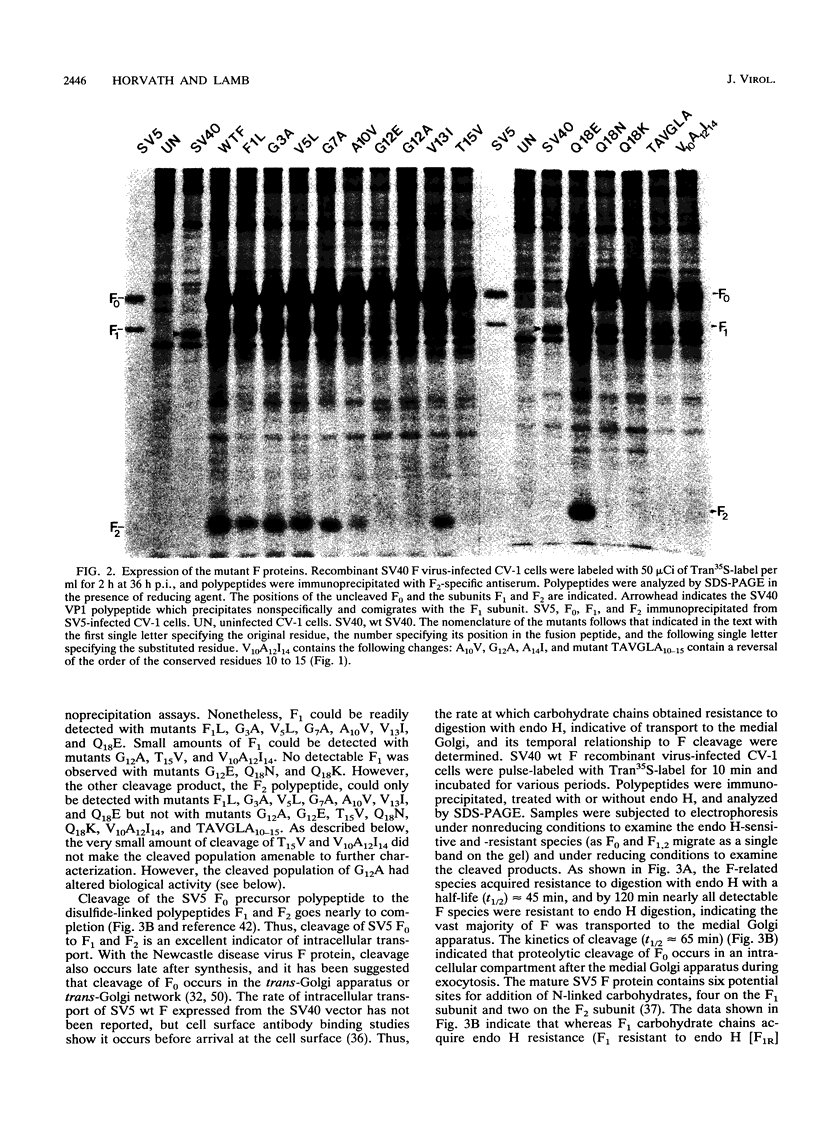
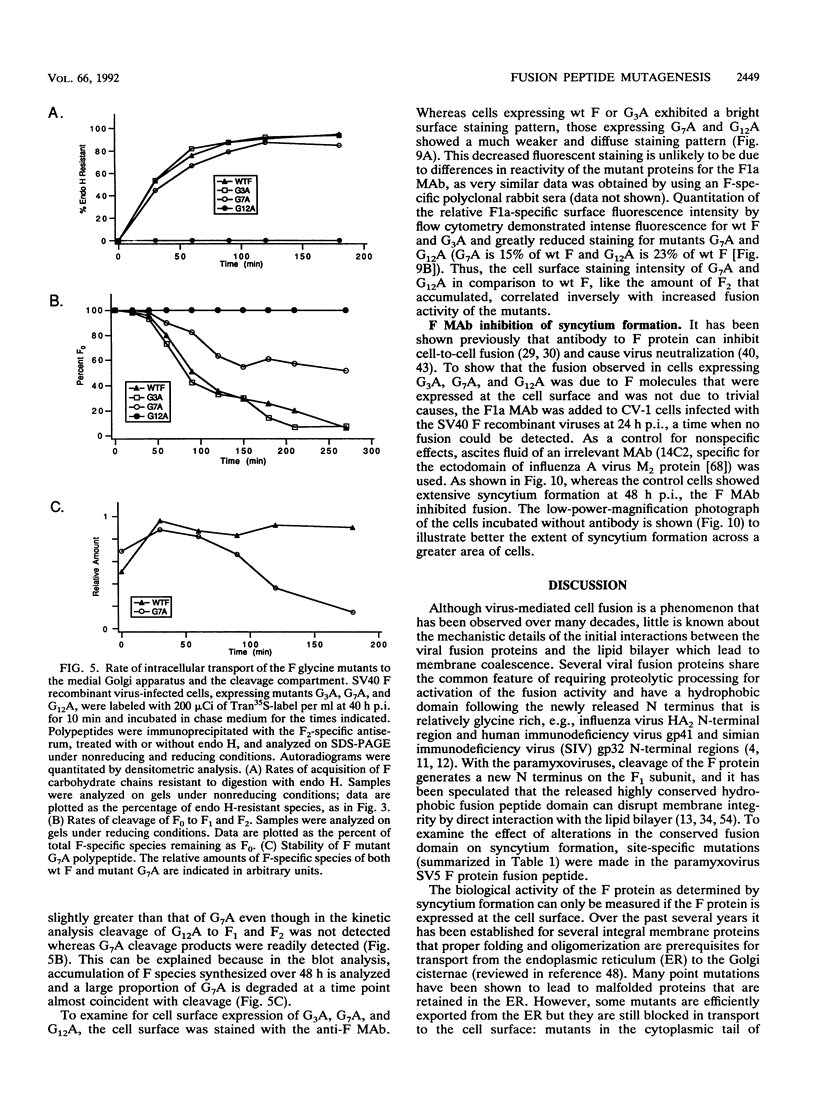
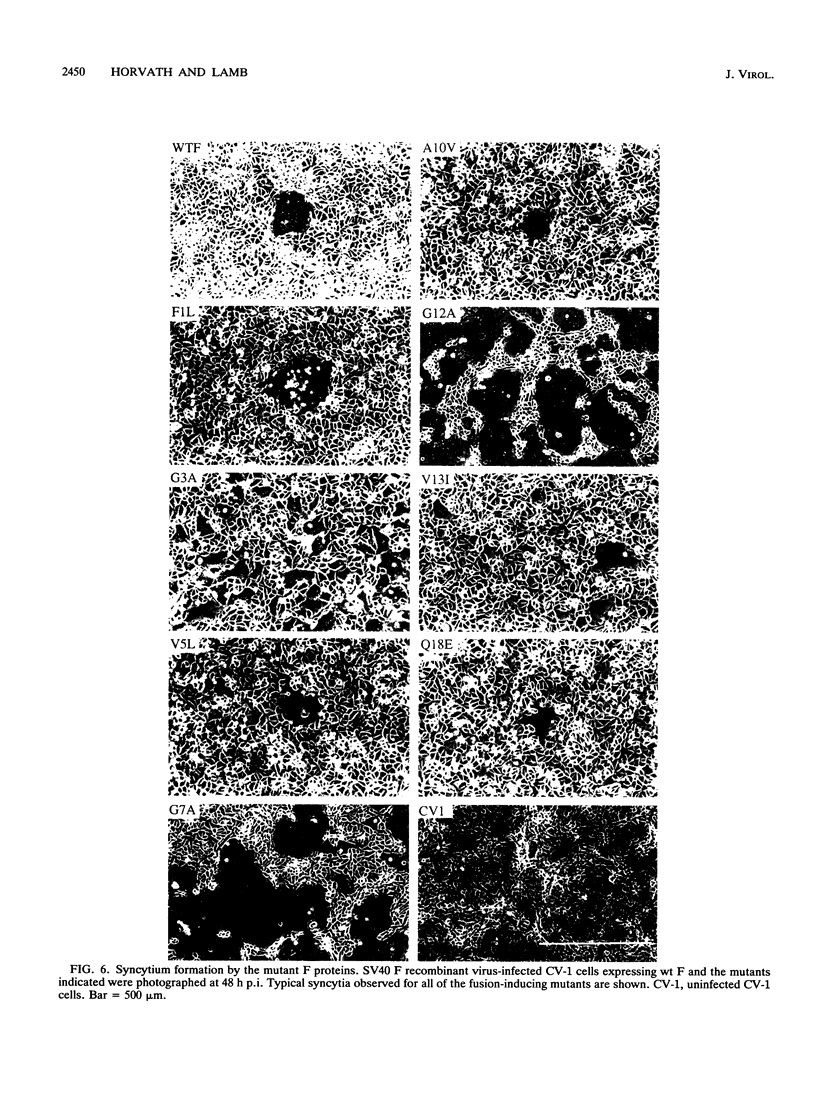
The role of residues in the conserved hydrophobic N-terminal fusion peptide of the paramyxovirus fusion (F) protein in causing cell-cell fusion was examined. Mutations were introduced into the cDNA encoding the simian virus 5 (SV5) F protein, the altered F proteins were expressed by using an eukaryotic vector, and their ability to mediate syncytium formation was determined. The mutant F proteins contained both single- and multiple-amino-acid substitutions, and they exhibited a variety of intracellular transport properties and fusion phenotypes. The data indicate that many substitutions in the conserved amino acids of the simian virus 5 F fusion peptide can be tolerated without loss of biological activity. Mutant F proteins which were not transported to the cell surface did not cause cell-cell fusion, but all of the mutants which were transported to the cell surface were fusion competent, exhibiting fusion properties similar to or better than those of the wild-type F protein. Mutant F proteins containing glycine-to-alanine substitutions had altered intracellular transport characteristics, yet they exhibited a great increase in fusion activity. The potential structural implications of this substitution and the possible importance of these glycine residues in maintaining appropriate levels of fusion activity are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the protein subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano K., Asano A. Why is a specific amino acid sequence of F glycoprotein required for the membrane fusion reaction between envelope of HVJ (Sendai virus) and target cell membranes? Biochem Int. 1985 Jan;10(1):115–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch M. L., Earl P. L., Fargnoli K., Picciafuoco S., Giombini F., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G. Identification of the fusion peptide of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.2541505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Lorge P., Goormaghtigh E., Ruysschaert J. M., Espion D., Burny A. The mode of insertion of the paramyxovirus F1 N-terminus into lipid matrix, an initial step in host cell/virus fusion. Virus Genes. 1988 Jul;1(4):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00257096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Schoch C., Blumenthal R. Delay time for influenza virus hemagglutinin-induced membrane fusion depends on hemagglutinin surface density. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2402-2407.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Roth M. G., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of the influenza virus hemagglutinin affect different stages of intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):704–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., James P., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the "fusion peptide". J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6459–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Choppin P. W. On the role of the response of the cell membrane in determining virus virulence. Contrasting effects of the parainfluenza virus SV5 in two cell types. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):501–520. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horth M., Lambrecht B., Khim M. C., Bex F., Thiriart C., Ruysschaert J. M., Burny A., Brasseur R. Theoretical and functional analysis of the SIV fusion peptide. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2747–2755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. M., Williams M. A., Lamb R. A. Eukaryotic coupled translation of tandem cistrons: identification of the influenza B virus BM2 polypeptide. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2639–2647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Protease activation mutants of Sendai virus: sequence analysis of the mRNA of the fusion protein (F) gene and direct identification of the cleavage-activation site. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Choppin P. W. Analysis of Sendai virus mRNAs with cDNA clones of viral genes and sequences of biologically important regions of the fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7732–7736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Activation of the Sendai virus fusion protein (f) involves a conformational change with exposure of a new hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3557–3563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Bando H., Ohgimoto S., Kondo K., Tsurudome M., Nishio M., Ito Y. Sequence of the fusion protein gene of human parainfluenza type 2 virus and its 3' intergenic region: lack of small hydrophobic (SH) gene. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90406-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Conformational preferences of amino acids in globular proteins. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4277–4285. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L. W., Morrison T. G. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein and comparisons of paramyxovirus fusion protein sequences. Virus Res. 1986 Sep;5(4):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson J. R., Hull R. A., Estes M. K., Kasel J. A. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the fusion protein gene of human parainfluenza virus type 1. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Immunological studies of the functions of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):94–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Importance of antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein of paramyxoviruses in the prevention of spread of infection. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):275–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Randall R. E., Lamb R. A. Intracellular maturation and transport of the SV5 type II glycoprotein hemagglutinin-neuraminidase: specific and transient association with GRP78-BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum and extensive internalization from the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3273–3289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick S. L., Hoekstra D. Membrane penetration of Sendai virus glycoproteins during the early stages of fusion with liposomes as determined by hydrophobic photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7433–7437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Defective assembly and intracellular transport of mutant paramyxovirus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase proteins containing altered cytoplasmic domains. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3605–3616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3605-3616.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Fusion protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of mRNA predicts a highly hydrophobic glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Expression at the cell surface of biologically active fusion and hemagglutinin/neuraminidase proteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Ability of the hydrophobic fusion-related external domain of a paramyxovirus F protein to act as a membrane anchor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A., Moss B., Murphy B. R. Comparison of the relative roles of the F and HN surface glycoproteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 in inducing protective immunity. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1972–1977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1972-1977.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Shaughnessy M. A., Lamb R. A. Analysis of the relationship between cleavability of a paramyxovirus fusion protein and length of the connecting peptide. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1293–1301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1293-1301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Polypeptide synthesis in simian virus 5-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):177–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.177-187.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Young D. F., Goswami K. K., Russell W. C. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to simian virus 5 and their use in revealing antigenic differences between human, canine and simian isolates. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2769–2780. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Choppin P. W. Oligopeptides that specifically inhibit membrane fusion by paramyxoviruses: studies on the site of action. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):518–532. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90517-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Specific inhibition of paramyxovirus and myxovirus replication by oligopeptides with amino acid sequences similar to those at the N-termini of the F1 or HA2 viral polypeptides. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Matsuda Y., Kiyokage R., Kawahara N., Kiyotani K., Katunuma N., Nagai Y., Yoshida T. Identification of endoprotease activity in the trans Golgi membranes of rat liver cells that specifically processes in vitro the fusion glycoprotein precursor of virulent Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90420-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Smith J. A., Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S., Goodman H. M. Purification and amino-terminal protein sequence analysis of the mumps virus fusion protein. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheshberadaran H., Lamb R. A. Simian virus 5 membrane protein maturation: expression in virus-infected cells and from a eukaryotic vector. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Olmsted R. A., Venkatesan S., Coligan J. E., Collins P. L. Fusion glycoprotein of human parainfluenza virus type 3: nucleotide sequence of the gene, direct identification of the cleavage-activation site, and comparison with other paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehlow K. G., Baldwin R. L. Effect of the substitution Ala----Gly at each of five residue positions in the C-peptide helix. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2130–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda T., Sakaguchi T., Imai K., Inocencio N. M., Gotoh B., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. Structural comparison of the cleavage-activation site of the fusion glycoprotein between virulent and avirulent strains of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama K., Yoshikawa Y., Yamanouchi K. Fusion glycoprotein (F) of rinderpest virus: entire nucleotide sequence of the F mRNA, and several features of the F protein. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurudome M., Bando H., Nishio M., Iwamoto Y., Kawano M., Kondo K., Komada H., Ito Y. Antigenic and structural properties of a paramyxovirus simian virus 41 (SV41) reveal a close relationship with human parainfluenza type 2 virus. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):738–748. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90141-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsanyi T. M., Jörnvall H., Orvell C., Norrby E. F1 polypeptides of two canine distemper virus strains: variation in the conserved N-terminal hydrophobic region. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Server A. C., Goodman H. M., Wolinsky J. S. Cloning and sequencing of the mumps virus fusion protein gene. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2762-2772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane proteins: the amino acid composition of membrane-penetrating segments. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]