Abstract
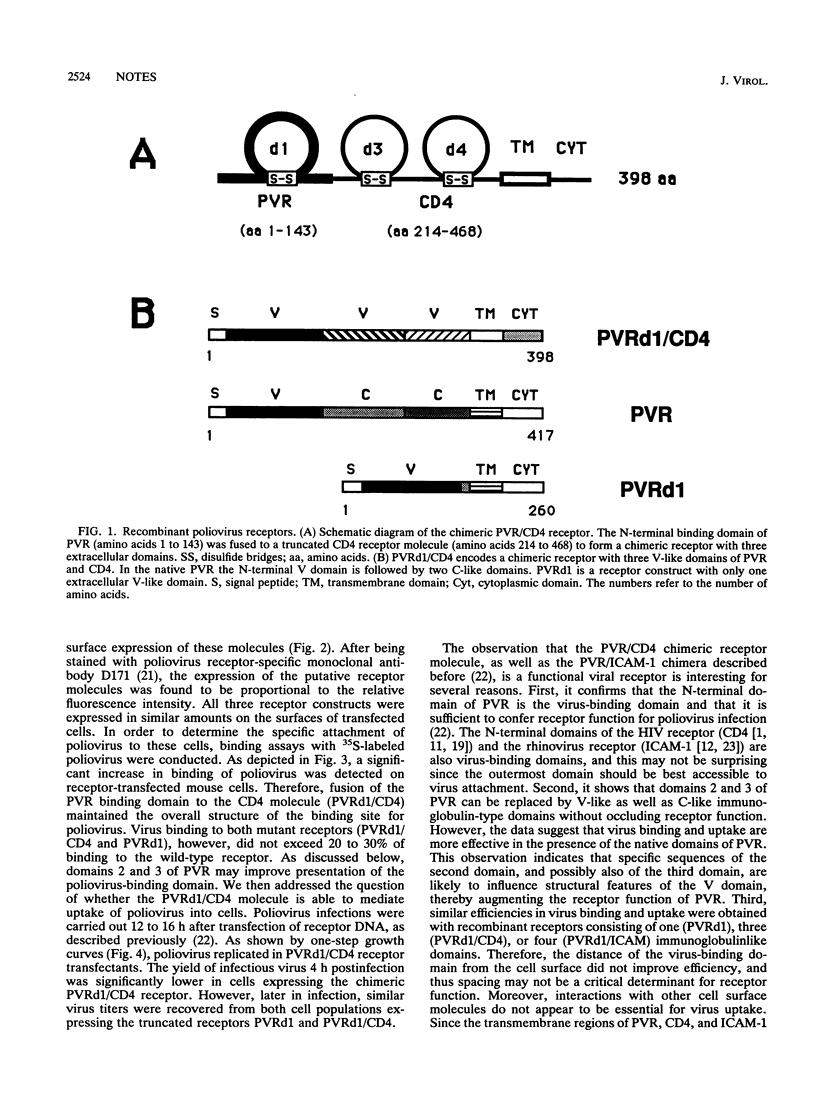
The human poliovirus receptor consists of three extracellular immunoglobulinlike domains, a transmembrane domain, and an intracytoplasmic domain. The amino-terminal variable-type domain (V domain) of the human poliovirus receptor is necessary and sufficient for its function as a viral receptor (H.-C. Selinka, A. Zibert, and E. Wimmer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:3598-3602, 1991). In this paper, data are presented showing that transfer of the putative poliovirus receptor-binding domain to a truncated receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus results in a functional receptor for poliovirus. After expression in mouse cells, this chimeric protein confers susceptibility to poliovirus. Thus, unlike human immunodeficiency virus, poliovirus can enter mouse cells by way of a truncated CD4 receptor if the specific binding domain for poliovirus is provided.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Blanc D., Weiss R. A. Specific cell surface requirements for the infection of CD4-positive cells by human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 and by Simian immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90904-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll P. C., Cyster J. G., Campbell I. D., Williams A. F. Structure of domain 1 of rat T lymphocyte CD2 antigen. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):762–765. doi: 10.1038/353762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Heterogeneous expression of poliovirus receptor-related proteins in human cells and tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5700–5706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Mutational analysis of the cellular receptor for poliovirus. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3873–3876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3873-3876.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromeier M., Wetz K. Kinetics of poliovirus uncoating in HeLa cells in a nonacidic environment. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3590–3597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3590-3597.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Neutralization of poliovirus by cell receptors expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4697-4702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Nomoto A. Functional domains of the poliovirus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Warton M., Littman D. R. The envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus binds to the immunoglobulin-like domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):159–162. doi: 10.1038/334159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lineberger D. W., Graham D. J., Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Antibodies that block rhinovirus attachment map to domain 1 of the major group receptor. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2582–2587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2582-2587.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Gosser L. B., Shimshick E. J. Interaction of liposomes with subviral particles of poliovirus type 2 and rhinovirus type 2. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):746–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.746-749.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Dalgleish A. G., Jamal S., Weiss R. A., Axel R. HIV infection does not require endocytosis of its receptor, CD4. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):865–874. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Molineaux S. M., Maddon D. E., Zimmerman K. A., Godfrey M., Alt F. W., Chess L., Axel R. Structure and expression of the human and mouse T4 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9155–9159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Johnson B., Lionetti K. A., Nobis P., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Transformation of a human poliovirus receptor gene into mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., Berger E. A., Moss B. Binding region for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and epitopes for HIV-blocking monoclonal antibodies of the CD4 molecule defined by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9273–9277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus can enter and infect mammalian cells by way of an intercellular adhesion molecule 1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3598–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Erickson H. P., Springer T. A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90805-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers P. Immunology. One hand clapping. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):393–394. doi: 10.1038/348393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibert A., Selinka H. C., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Wimmer E. Vaccinia virus-mediated expression and identification of the human poliovirus receptor. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90668-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


