Abstract
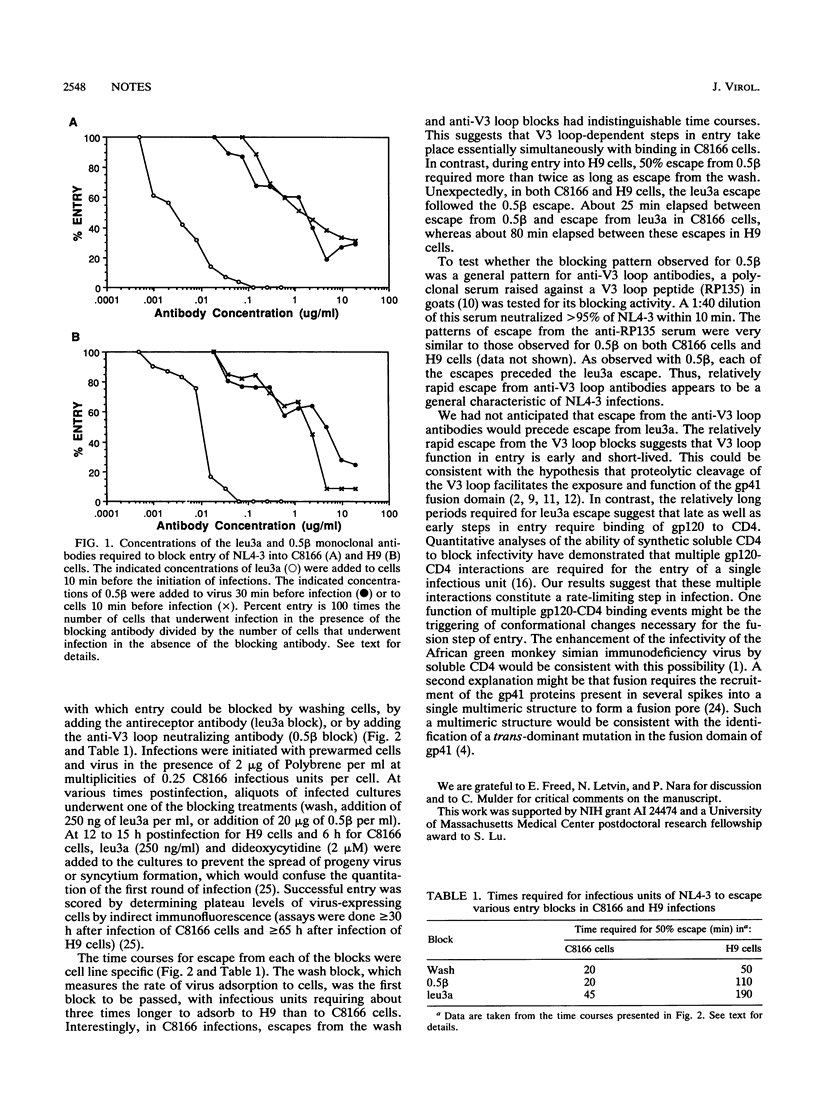
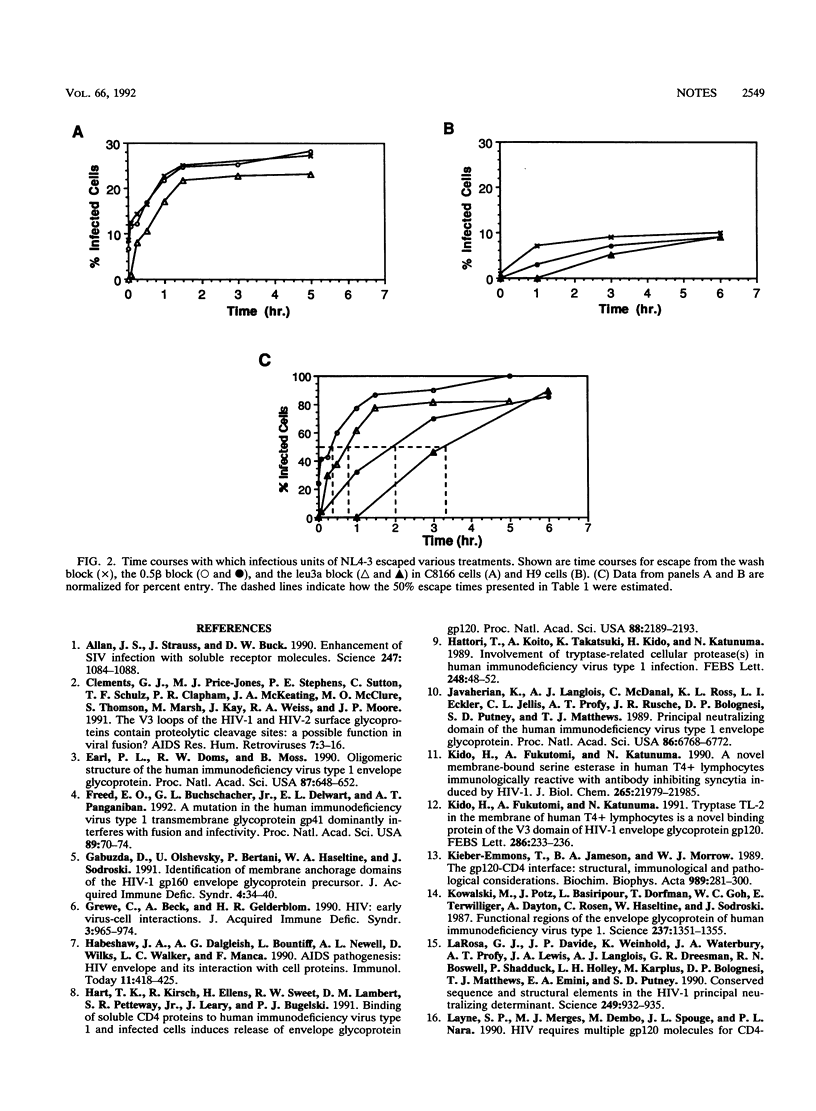
The entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 into two T-cell lines has been analyzed to determine the relative time courses with which virus entry can be blocked (i) by washing, (ii) by adding a monoclonal antibody to the V3 loop of gp120 that neutralizes without blocking CD4 binding (0.5 beta), or (iii) by adding an antireceptor monoclonal antibody that competes for virus binding (leu3a). During entry into C8166 cells, 50% escape from the wash as well as the anti-V3 loop antibody required 20 min, whereas 50% escape from the leu3a block required 45 minutes. In contrast, during entry into H9 cells, 50% escape from the wash block required 50 min, 50% escape from the anti-V3 loop antibody required 110 min, and 50% escape from the antireceptor antibody required 190 min. These results demonstrate that the times required for entering virus to escape each of the blocks were cell type specific. They also demonstrate that V3 loop-dependent steps occur relatively early in entry and suggest that binding of gp120 to CD4 is important for late as well as early steps in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 entry.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. S., Strauss J., Buck D. W. Enhancement of SIV infection with soluble receptor molecules. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1084–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.2309120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. J., Price-Jones M. J., Stephens P. E., Sutton C., Schulz T. F., Clapham P. R., McKeating J. A., McClure M. O., Thomson S., Marsh M. The V3 loops of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface glycoproteins contain proteolytic cleavage sites: a possible function in viral fusion? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):3–16. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Doms R. W., Moss B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Delwart E. L., Buchschacher G. L., Jr, Panganiban A. T. A mutation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein gp41 dominantly interferes with fusion and infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):70–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D., Olshevsky U., Bertani P., Haseltine W. A., Sodroski J. Identification of membrane anchorage domains of the HIV-1 gp160 envelope glycoprotein precursor. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(1):34–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewe C., Beck A., Gelderblom H. R. HIV: early virus-cell interactions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(10):965–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeshaw J. A., Dalgleish A. G., Bountiff L., Newell A. L., Wilks D., Walker L. C., Manca F. AIDS pathogenesis: HIV envelope and its interaction with cell proteins. Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):418–425. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Kirsh R., Ellens H., Sweet R. W., Lambert D. M., Petteway S. R., Jr, Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Binding of soluble CD4 proteins to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and infected cells induces release of envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukutomi A., Katunuma N. A novel membrane-bound serine esterase in human T4+ lymphocytes immunologically reactive with antibody inhibiting syncytia induced by HIV-1. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21979–21985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukutomi A., Katunuma N. Tryptase TL2 in the membrane of human T4+ lymphocytes is a novel binding protein of the V3 domain of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp 120. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80981-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieber-Emmons T., Jameson B. A., Morrow W. J. The gp120-CD4 interface: structural, immunological and pathological considerations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 27;989(3):281–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Rusche J., Koito A., Hattori T., Hoshino H., Javaherian K., Takatsuki K., Putney S. Characterization of a human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the neutralizing epitope. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2107-2114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Norton W. A., Sattentau Q. J. Direct measurement of soluble CD4 binding to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions: gp120 dissociation and its implications for virus-cell binding and fusion reactions and their neutralization by soluble CD4. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1133-1140.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Price T. M. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of T cells and monocytes proceeds via receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):959–968. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Rusche J., Javaherian K., Matthews T., Bolognesi D. Structural and functional features of the HIV envelope glycoprotein and considerations for vaccine development. Biotechnology. 1990;14:81–110. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-409-90116-0.50013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Langlois A. J., McDanal C. B., McDougal J. S., Bolognesi D. P., Matthews T. J. Neutralizing antibodies to an immunodominant envelope sequence do not prevent gp120 binding to CD4. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4195–4200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4195-4200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Iwata A., White J. M., Almers W. Patch clamp studies of single cell-fusion events mediated by a viral fusion protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):555–558. doi: 10.1038/342555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava K. K., Fernandez-Larsson R., Zinkus D. M., Robinson H. L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 NL4-3 replication in four T-cell lines: rate and efficiency of entry, a major determinant of permissiveness. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3900–3902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3900-3902.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


