Abstract
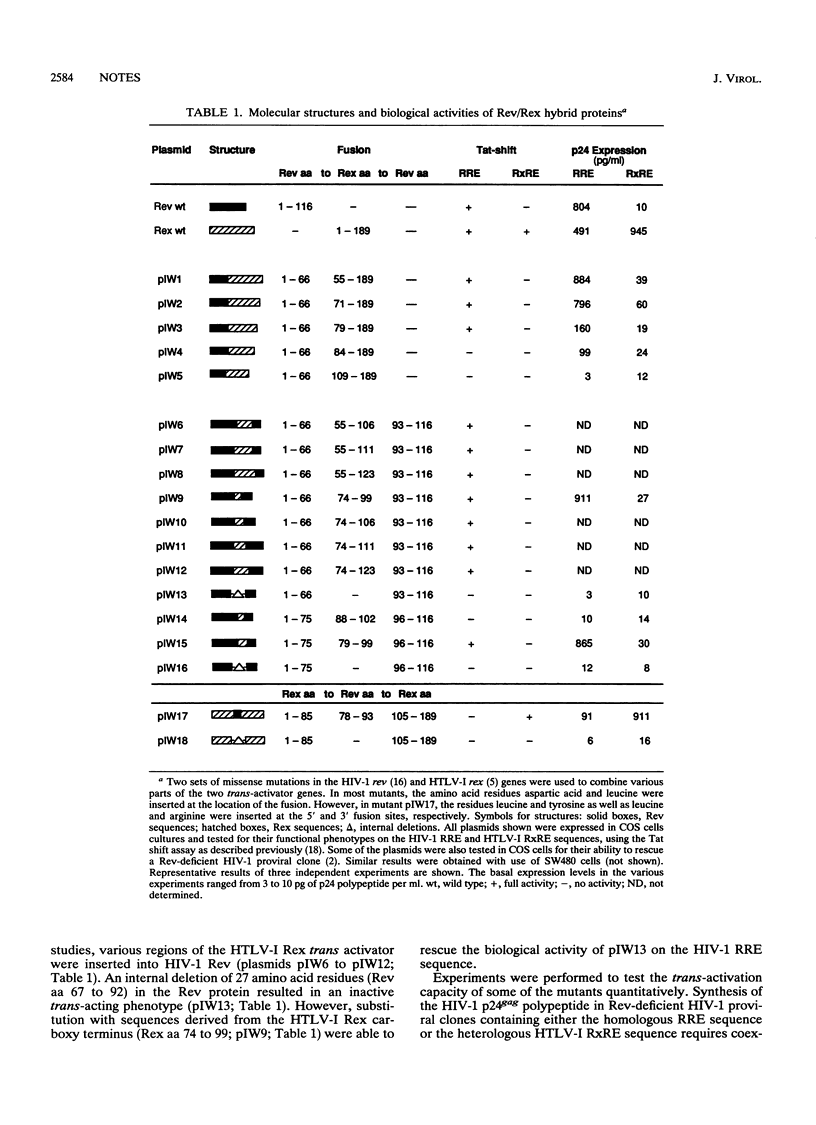
The human retroviruses human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) are characterized by complex regulation of gene expression. Each virus encodes a posttranscriptional regulator, the 19-kDa HIV-1 Rev protein and the 27-kDa HTLV-I Rex protein, which is required for viral replication. Expression of these trans activators results in the cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced or singly spliced viral mRNA which encode the gag, pol, and env gene products. The finding that the HTLV-I Rex protein is able to functionally substitute for the Rev protein of HIV-1 indicates that HIV-1 Rev and HTLV-I Rex may interact with the same component of a cellular pathway involved in either mRNA splicing or transport. In this study, we have generated functional Rev/Rex hybrid proteins by domain exchange. We have defined, using in vivo and in vitro analyses, the activation domains of Rev and Rex which are the putative targets of a common host cell factor(s) required for Rev and Rex function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Y. F., Hanly S. M., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Structure-function analyses of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev RNA response elements: insights into the mechanism of Rex and Rev action. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballaun C., Farrington G. K., Dobrovnik M., Rusche J., Hauber J., Böhnlein E. Functional analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex-response element: direct RNA binding of Rex protein correlates with in vivo activity. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4408–4413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4408-4413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd H. P., Huckaby G. L., Ahmed Y. F., Hanly S. M., Greene W. C. The type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) Rex trans-activator binds directly to the HTLV-I Rex and the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus Rev RNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Berger J., Hauber J. Functional mapping of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev RNA binding domain: new insights into the domain structure of Rev and Rex. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):7051–7055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.7051-7055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein S., Pirker F. P., Hofer L., Zimmermann K., Bachmayer H., Böhnlein E., Hauber J. Transdominant repressors for human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 rev function. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.81-88.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Identification of sequences important in the nucleolar localization of human immunodeficiency virus Rev: relevance of nucleolar localization to function. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.881-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. S., Fisk G. J., Hauber J., Usman N., Daly T. J., Rusche J. R. Characterization of HIV-1 REV protein: binding stoichiometry and minimal RNA substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1577–1583. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Derse D., Athanassopoulos A., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Cross-activation of the Rex proteins of HTLV-I and BLV and of the Rev protein of HIV-1 and nonreciprocal interactions with their RNA responsive elements. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco L. D., Harper D. S., Keene J. D. Leucine periodicity of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) A' protein is implicated in snRNP assembly via protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1578–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Rimsky L. T., Malim M. H., Kim J. H., Hauber J., Duc Dodon M., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Comparative analysis of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory proteins and their RNA response elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1534–1544. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer L., Weichselbraun I., Quick S., Farrington G. K., Böhnlein E., Hauber J. Mutational analysis of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I trans-acting rex gene product. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3379–3383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3379-3383.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., Bond B. L., McDonald D., Klein N. P., Parslow T. G. Effector domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev and human T-cell leukemia virus type I Rex are functionally interchangeable and share an essential peptide motif. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6001–6007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6001-6007.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires the binding of multiple Rev monomers to the viral RRE: implications for HIV-1 latency. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90158-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Fenrick R., Cullen B. R. Immunodeficiency virus rev trans-activator modulates the expression of the viral regulatory genes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):181–183. doi: 10.1038/335181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., McCarn D. F., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Mutational definition of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev activation domain. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4248–4254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4248-4254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermer B., Felber B. K., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Identification of trans-dominant HIV-1 rev protein mutants by direct transfer of bacterially produced proteins into human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2037–2044. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Dodon M. D., Dixon E. P., Greene W. C. Trans-dominant inactivation of HTLV-I and HIV-1 gene expression by mutation of the HTLV-I Rex transactivator. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):453–456. doi: 10.1038/341453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Hauber J., Dukovich M., Malim M. H., Langlois A., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Functional replacement of the HIV-1 rev protein by the HTLV-1 rex protein. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):738–740. doi: 10.1038/335738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomin L., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Different sites of interaction for Rev, Tev, and Rex proteins within the Rev-responsive element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6010–6017. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6010-6017.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unge T., Solomin L., Mellini M., Derse D., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. The Rex regulatory protein of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I binds specifically to its target site within the viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7145–7149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Regulation of HIV and HTLV gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]