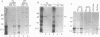Abstract
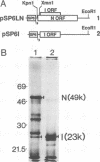
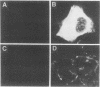
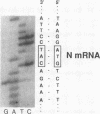
For animal RNA viruses that replicate through an RNA intermediate, reported examples of bicistronic mRNAs with overlapping open reading frames in which one cistron is contained entirely within another have been made only for those with negative-strand or double-stranded genomes. In this report, we demonstrate for the positive-strand bovine coronavirus that an overlapping open reading frame potentially encoding a 23-kDa protein (names the I [for internal open reading frame] protein) and lying entirely within the gene for the 49-kDa nucleocapsid phosphoprotein is expressed during virus replication from a single species of unedited mRNA. The I protein was specifically immunoprecipitated from virus-infected cells with an I-specific antipeptide serum and was shown to be membrane associated. Many features of I protein synthesis conform to the leaky ribosomal scanning model for regulation of translation. This, to our knowledge, is the first example of a bicistronic mRNA for a cytoplasmically replicating, positive-strand animal RNA virus in which one cistron entirely overlaps another.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S., Kienzle T. E., Lapps W. E., Brian D. A. Sequence and expression analysis of potential nonstructural proteins of 4.9, 4.8, 12.7, and 9.5 kDa encoded between the spike and membrane protein genes of the bovine coronavirus. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90513-Q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi H., Bishop D. H. Comparison of the sequences and coding of La Crosse and snowshoe hare bunyavirus S RNA species. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1155–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1155-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Massie B., Briedis D. J. Expression of bicistronic measles virus P/C mRNA by using hybrid adenoviruses: levels of C protein synthesized in vivo are unaffected by the presence or absence of the upstream P initiator codon. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4059–4069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4059-4069.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J., Smeekens S., Rottier P. Sequence of the nucleocapsid gene from murine coronavirus MHV-A59. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):883–891. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Foulds I. J., Brown T. D. Sequences of the nucleocapsid genes from two strains of avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):573–580. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzilowicz C. J., Weiss S. R. In vitro synthesis of two polypeptides from a nonstructural gene of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90293-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. A., Richardson C., Kolakofsky D. Ribosomal initiation at alternate AUGs on the Sendai virus P/C mRNA. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):684–687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.684-687.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus X protein. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2869–2874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus Y proteins in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot R. J., Andeweg A. C., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Sequence analysis of the 3'-end of the feline coronavirus FIPV 79-1146 genome: comparison with the genome of porcine coronavirus TGEV reveals large insertions. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst H., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus hemagglutinin mRNA codes for two polypeptides in overlapping reading frames. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):48–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Lambert D. M., Wechsler S. L., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus mRNA encoding the P and C proteins. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):46–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieco F., Burgyan J., Russo M. The nucleotide sequence of cymbidium ringspot virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6383–6383. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Translational modulation in vitro of a eukaryotic viral mRNA encoding overlapping genes: ribosome scanning and potential roles of conformational changes in the P/C mRNA of Sendai virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91774-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne P. Q., Knorr D. A., Hillman B. I., Morris T. J. The complete genome structure and synthesis of infectious RNA from clones of tomato bushy stunt virus. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M. A., Brian D. A. A PCR-enhanced method for determining the 5' end sequence of mRNAs. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Aug;1(1):43–45. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M. A., Brian D. A. Sequencing PCR DNA amplified directly from a bacterial colony. Biotechniques. 1991 Jul;11(1):30–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M. A., Sethna P. B., Brian D. A. Bovine coronavirus mRNA replication continues throughout persistent infection in cell culture. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4108–4114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4108-4114.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogue B. G., King B., Brian D. A. Antigenic relationships among proteins of bovine coronavirus, human respiratory coronavirus OC43, and mouse hepatitis coronavirus A59. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamahora T., Soe L. H., Lai M. M. Sequence analysis of nucleocapsid gene and leader RNA of human coronavirus OC43. Virus Res. 1989 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90048-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapke P. A., Brian D. A. Sequence analysis of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus nucleocapsid protein gene. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90102-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kienzle T. E., Abraham S., Hogue B. G., Brian D. A. Structure and orientation of expressed bovine coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase protein. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1834–1838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1834-1838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Bando H., Tsurudome M., Kawano M., Nishio M., Ito Y. Sequence analysis of the phosphoprotein (P) genes of human parainfluenza type 4A and 4B viruses and RNA editing at transcript of the P genes: the number of G residues added is imprecise. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90413-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
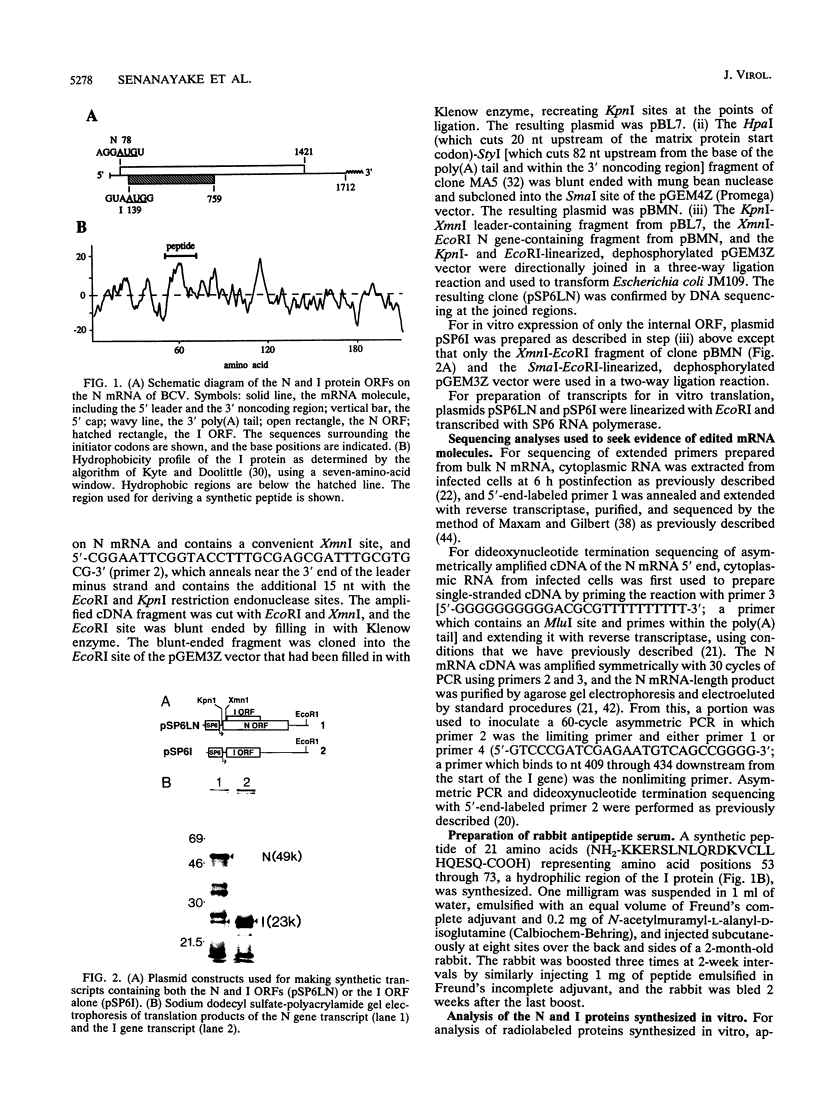
- Lapps W., Hogue B. G., Brian D. A. Sequence analysis of the bovine coronavirus nucleocapsid and matrix protein genes. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90312-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Perlman S., Weinstock G., DeVries J. R., Budzilowicz C., Weissemann J. M., Weiss S. R. Detection of a murine coronavirus nonstructural protein encoded in a downstream open reading frame. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90631-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. X., Cavanagh D., Green P., Inglis S. C. A polycistronic mRNA specified by the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90423-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. X., Inglis S. C. Identification of two new polypeptides encoded by mRNA5 of the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):342–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90094-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk D., Sánchez A., Banerjee A. K. Messenger RNA encoding the phosphoprotein (P) gene of human parainfluenza virus 3 is bicistronic. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):318–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Bredenbeek P. J., Noten A. F., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Sequence of mouse hepatitis virus A59 mRNA 2: indications for RNA recombination between coronaviruses and influenza C virus. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90512-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Curran J., Pelet T., Kolakofsky D., Ray R., Compans R. W. The P gene of human parainfluenza virus type 1 encodes P and C proteins but not a cysteine-rich V protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3406–3410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3406-3410.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto T., Arpin M., Gaetani S. Use of proteases for the study of membrane insertion. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:121–150. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. RNA editing by G-nucleotide insertion in mumps virus P-gene mRNA transcripts. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4137–4145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4137-4145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelet T., Curran J., Kolakofsky D. The P gene of bovine parainfluenza virus 3 expresses all three reading frames from a single mRNA editing site. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):443–448. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochon D. M., Johnston J. C. Infectious transcripts from cloned cucumber necrosis virus cDNA: evidence for a bifunctional subgenomic mRNA. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):656–665. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90899-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. S., Kamahora T., Lai M. M. Sequence analysis of the nucleocapsid protein gene of human coronavirus 229E. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):142–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna P. B., Hofmann M. A., Brian D. A. Minus-strand copies of replicating coronavirus mRNAs contain antileaders. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.320-325.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. W., Choppin P. W., Lamb R. A. A previously unrecognized influenza B virus glycoprotein from a bicistronic mRNA that also encodes the viral neuraminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4879–4883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus JHM: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA that encodes nucleocapsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5045–5054. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Lamb R. A., Paterson R. G. Two mRNAs that differ by two nontemplated nucleotides encode the amino coterminal proteins P and V of the paramyxovirus SV5. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):891–902. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(88)91285-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S., Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Editing of the Sendai virus P/C mRNA by G insertion occurs during mRNA synthesis via a virus-encoded activity. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.239-246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]