Abstract
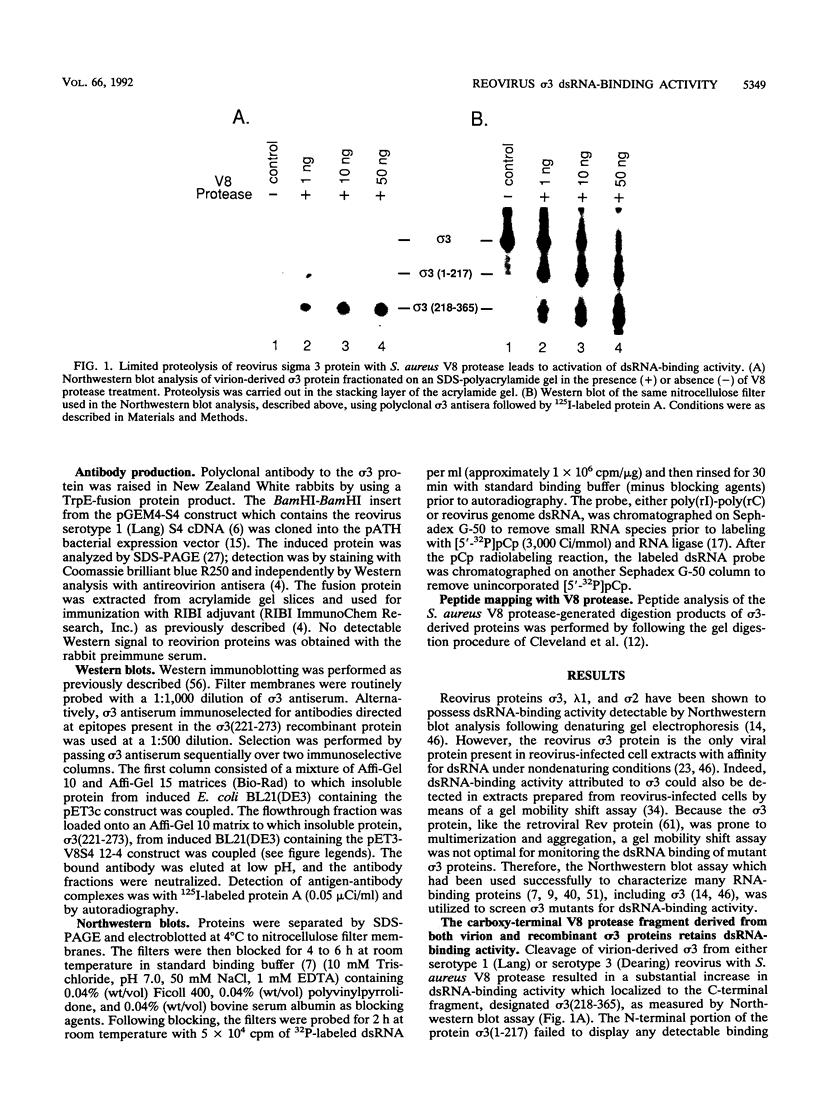
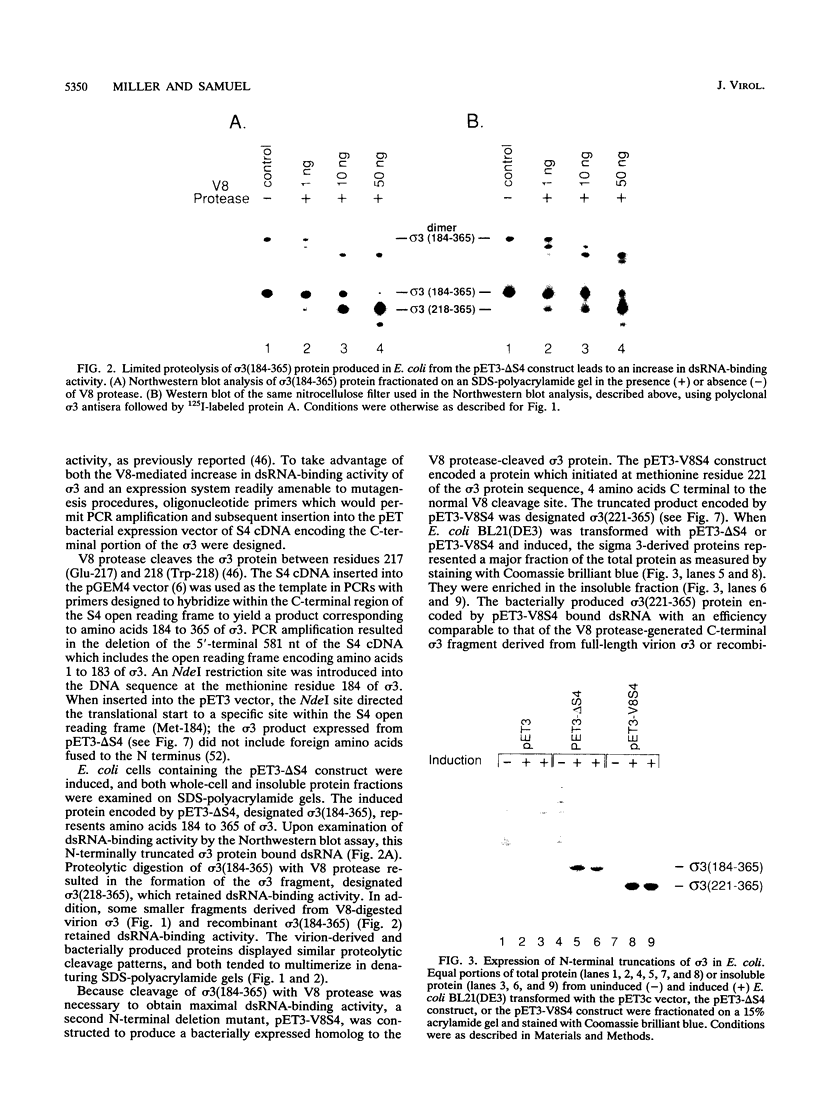
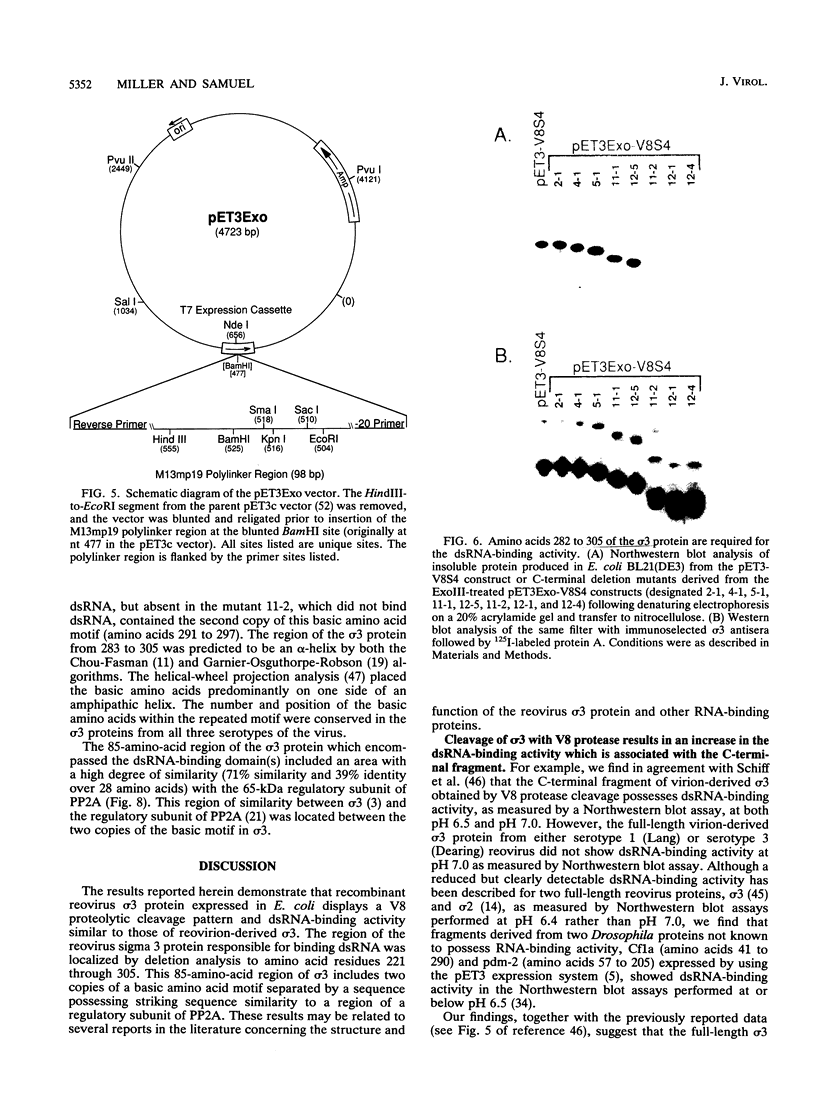
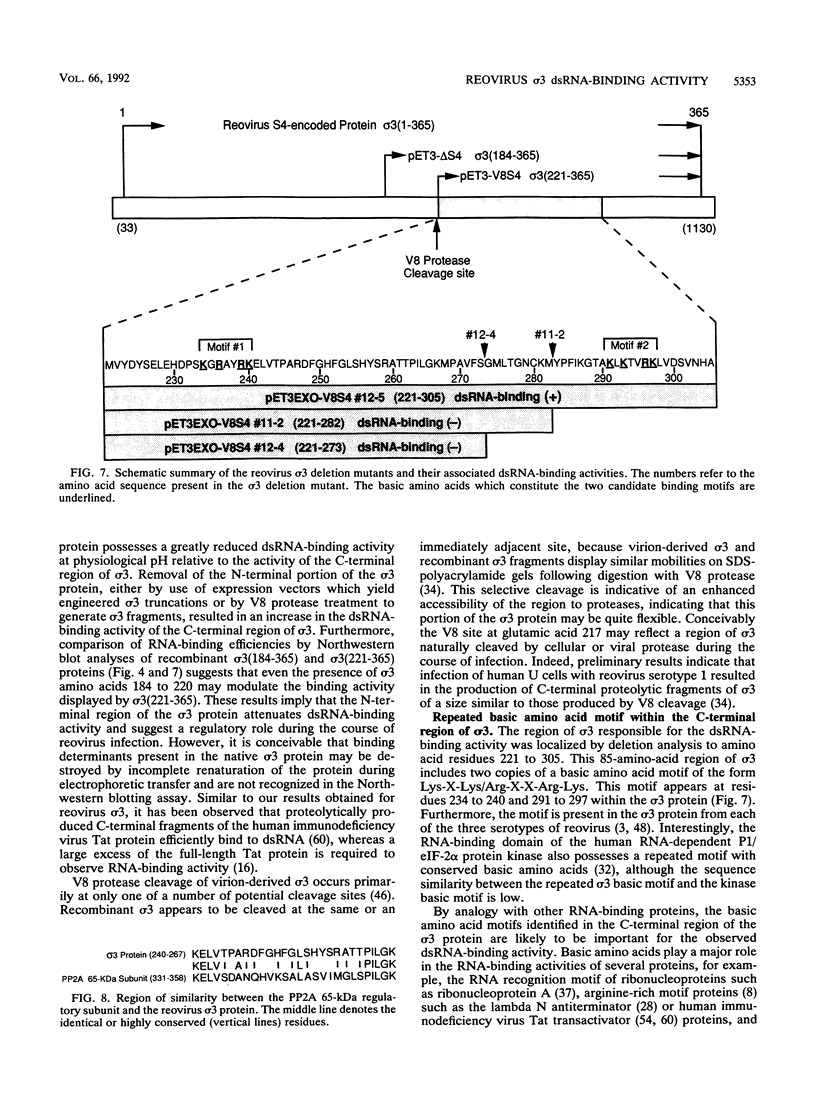
The reovirus capsid protein sigma 3 was examined for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding activity by Northwestern (RNA-protein) blot analysis. Treatment of virion-derived sigma 3 protein with Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease led to an increase in the dsRNA-binding activity associated with the C-terminal fragment of the protein. Recombinant C-terminal fragments of the sigma 3 protein were expressed in Escherichia coli from the S4 cDNA of reovirus serotype 1. These truncated sigma 3 proteins displayed proteolytic processing and dsRNA-binding activity similar to those observed for native, virion-derived sigma 3 protein as measured by Northwestern blot analysis. Construction of a modified pET3c vector, pET3Exo, allowed the production of 3'-terminal deletions of the S4 cDNA by using exonuclease III and rapid screening of the induced truncated sigma 3 proteins. An 85-amino-acid domain within the C-terminal portion of the sigma 3 protein which was responsible for dsRNA-binding activity was identified. The 85-amino-acid domain possessed a repeated basic amino acid motif which was conserved in all three serotypes of reovirus. Deletion of one of the basic motifs, predicted to be an amphipathic alpha-helix, destroyed dsRNA-binding activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Klett H., Schonberg M., Christman J., Levin D. H., Silverstein S. C. Mechanism of reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.684-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Fields B. N. Role of the S4 gene in the establishment of persistent reovirus infection in L cells. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):605–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater J. A., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Molecular cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence of the reovirus serotype 1 Lang strain s4 mRNA which encodes the major capsid surface polypeptide sigma 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli B. A., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: expression of reovirus S1-encoded sigma 1NS protein in transfected and infected cells as measured with serotype specific polyclonal antibody. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):698–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90541-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billin A. N., Cockerill K. A., Poole S. J. Isolation of a family of Drosophila POU domain genes expressed in early development. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. F., Holmes K. V. RNA-binding proteins of bovine rotavirus. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.561-568.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. F., Baker S. C., Soe L. H., Kamahora T., Keck J. G., Makino S., Govindarajan S., Lai M. M. Human hepatitis delta antigen is a nuclear phosphoprotein with RNA-binding activity. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2403–2410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2403-2410.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Isolation and partial characterization of an Mr 60,000 subunit of a type 2A phosphatase from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7267–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch D., Safer B. Purification and properties of eIF-2 phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7918–7924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermody T. S., Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Coombs K. M., Fields B. N. The S2 gene nucleotide sequences of prototype strains of the three reovirus serotypes: characterization of reovirus core protein sigma 2. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5721–5731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5721-5731.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Prakash O., Stamatos N. M. Small reovirus particle composed solely of sigma NS with specificity for binding different nucleic acids. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):115–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.115-124.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Adams-Pearson C., Maurer F., Müller P., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3166–3173. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Joklik W. K. Reovirus-coded polypeptides in infected cells: isolation of two native monomeric polypeptides with affinity for single-stranded and double-stranded RNA, respectively. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamibayashi C., Estes R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. C. Subunit interactions control protein phosphatase 2A. Effects of limited proteolysis, N-ethylmaleimide, and heparin on the interaction of the B subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13251–13260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux R., Lemay G., Millward S. The viral protein sigma 3 participates in translation of late viral mRNA in reovirus-infected L cells. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2472–2479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2472-2479.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin K. H., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. purification and characterization of the small-sized class mRNAs of reovirus type 3: coding assignments and translational efficiencies. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack S. J., Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Multiplication rate but not yield of reovirus serotypes 1 and 3 correlates with the level of virus-mediated inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins S. G., Frana M. F., McGowan J. J., Boyle J. F., Holmes K. V. RNA-binding proteins of coronavirus MHV: detection of monomeric and multimeric N protein with an RNA overlay-protein blot assay. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):402–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90305-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 in interferon-treated human cells by a ribosome-associated kinase processing site specificity similar to hemin-regulated rabbit reticulocyte kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):600–604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Co M. S., Brown E. G., Fields B. N. Distinct binding sites for zinc and double-stranded RNA in the reovirus outer capsid protein sigma 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger L. S., Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Translational effects and sequence comparisons of the three serotypes of the reovirus S4 gene. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Baric R. S., Nelson G. N., Soe L. H., Welter L. M., Deans R. J. Specific interaction between coronavirus leader RNA and nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4288–4295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4288-4295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturzenbecker L. J., Nibert M., Furlong D., Fields B. N. Intracellular digestion of reovirus particles requires a low pH and is an essential step in the viral infectious cycle. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2351–2361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2351-2361.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Venkatesh L., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Functional substitution of the basic domain of the HIV-1 trans-activator, Tat, with the basic domain of the functionally heterologous Rev. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90242-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomis D. C., Doohan J. P., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: cDNA structure, expression, and regulation of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase from human cells. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90732-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulker N., Zhang X., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. I. Characterization of a 54-kDa protein induced by gamma interferon with properties similar to a cytoskeletal component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16798–16803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Graaf M., Kroon G. J., Hemminga M. A. Conformation and mobility of the RNA-binding N-terminal part of the intact coat protein of cowpea chlorotic mottle virus. A two-dimensional proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90111-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Ampe C., Schultz S. C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Fragments of the HIV-1 Tat protein specifically bind TAR RNA. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1281–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.2205002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Hope T. J., Parslow T. G., Green M. R. Oligomerization and RNA binding domains of the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein: a dual function for an arginine-rich binding motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7734–7738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J. Multiple forms of SS leads to DS RNA polymerase activity in reovirus-infected cells. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):313–315. doi: 10.1038/247313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf M., Hemminga M. A. Conformational studies on a peptide fragment representing the RNA-binding N-terminus of a viral coat protein using circular dichroism and NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 15;201(2):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]