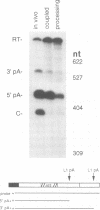
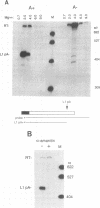
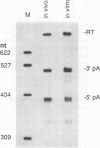
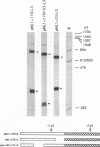
Abstract
The adenovirus major late transcription unit encodes five poly(A) sites whose use during infection is regulated. Early in the infection, the 5'-most site, L1, is used preferentially, whereas late in infection, all sites are used equivalently. Previous in vivo experiments indicated that regulatory sequences flank the AAUAAA and GU-rich elements of the L1 poly(A) site. We have developed an in vitro coupled transcription-processing system for studying the function of these regulatory sequences in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. The in vitro analysis using this system shows that predominant use of the L1 poly(A) site, as mediated by the upstream regulatory sequence, is independent of transcription. Furthermore, the reaction conditions are favorable to both 3'-end processing and splicing, making this system generally useful for the study of posttranscriptional processes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G., Babiss L. E. DNA template effect on RNA splicing: two copies of the same gene in the same nucleus are processed differently. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3457–3465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Persson H. Controls of RNA splicing and termination in the major late adenovirus transcription unit. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):420–426. doi: 10.1038/292420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Hanson P. I., Polvino-Bodnar M., Zempsky W., Ward D. C. The terminal regions of adenovirus and minute virus of mice DNAs are preferentially associated with the nuclear matrix in infected cells. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4344–4353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4344-4353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Efficient polyadenylation within the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat requires flanking U3-specific sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3340–3343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3340-3343.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Alwine J. C. Efficiency of utilization of the simian virus 40 late polyadenylation site: effects of upstream sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4248–4258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Falck-Pedersen E., Imperiale M. J. Sequences regulating temporal poly(A) site switching in the adenovirus major late transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5977–5984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Imperiale M. J. Sequences upstream of AAUAAA influence poly(A) site selection in a complex transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4951–4961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Kilpatrick J. E., Imperiale M. J. Involvement of long terminal repeat U3 sequences overlapping the transcription control region in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mRNA 3' end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1624–1630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J. Regulation of poly(A) site selection in adenovirus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):532–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.532-541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Chebli K., Himmelspach M., Stévenin J. Modulation of alternative splicing of adenoviral E1A transcripts: factors involved in the early-to-late transition. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1847–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales K. H., Birk J. M., Imperiale M. J. Analysis of adenovirus type 2 L1 RNA 3'-end formation in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1464–1468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1464-1468.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Ricci W. M., Finn L. A. Alternative splicing of tropomyosin pre-mRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1627–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Structure and organization of the gene coding for the DNA binding protein of adenovirus type 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4439–4457. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. Rna synthesis in isolated nuclei processing of adenovirus serotype 2 late messenger rna precursors. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):581–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Ohshima Y. Short donor site sequences inserted within the intron of beta-globin pre-mRNA serve for splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4484–4491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifflin R. C., Kellems R. E. Coupled transcription-polyadenylation in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19593–19598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miralles V. J. Termination of transcription in an 'in vitro' system is dependent on a polyadenylation sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3593–3599. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moen P. T., Jr, Fox E., Bodnar J. W. Adenovirus and minute virus of mice DNAs are localized at the nuclear periphery. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):513–520. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Control of adenovirus E1B mRNA synthesis by a shift in the activities of RNA splice sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):966–972. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyne G., Pichard E., Bernhard W. Localization of simian adenovirus 7 (SA 7) transcription and replication in lytic infection. An ultracytochemical and autoradiographical study. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa M., Rose S. D., Berget S. M. In vitro polyadenylation is stimulated by the presence of an upstream intron. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1552–1559. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawar S., Ahmed C. M., Watkins R., Zain S. Efficient coupled transcription and mRNA splicing in vitro using plasmids derived from early region 3 of adenovirus 2 and a nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Pruzan R., Aloni Y. Elements involved in an in vitro block to transcription elongation at the end of the L1 mRNA family of adenovirus 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1783–1790. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R., Ganem D. Sequences 5' to the polyadenylation signal mediate differential poly(A) site use in hepatitis B viruses. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):764–776. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon H., Brodmann P., Hohn T. A dissection of the cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation signal. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Ho W. Y., Freimuth P., Shenk T. Adenovirus terminal protein mediates both nuclear matrix association and efficient transcription of adenovirus DNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1197–1208. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt P., Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Stévenin J. Alternative splicing of E1A transcripts of adenovirus requires appropriate ionic conditions in vitro. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90659-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Four factors are required for 3'-end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1711–1724. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valsamakis A., Zeichner S., Carswell S., Alwine J. C. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 polyadenylylation signal: a 3' long terminal repeat element upstream of the AAUAAA necessary for efficient polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton T. H., Moen P. T., Jr, Fox E., Bodnar J. W. Interactions of minute virus of mice and adenovirus with host nucleoli. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3651–3660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3651-3660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. A., Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):215–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. L., Hsu M. T. Linear adenovirus DNA is organized into supercoiled domains in virus particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3535–3550. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. L., Hsu M. T. Psoralen-cross-linking study of the organization of intracellular adenovirus nucleoprotein complexes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1227-1234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younghusband H. B., Maundrell K. Adenovirus DNA is associated with the nuclear matrix of infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):705–713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.705-713.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]