Abstract
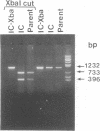
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a positive-stranded enveloped RNA virus that belongs to the family Flaviviridae. Genomic JEV RNA is approximately 11 kb long and encodes 10 proteins, 3 structural and 7 nonstructural. A full-length cDNA copy of the JEV genome was constructed by in vitro ligation of two cDNA fragments which encode the 5' (nucleotide positions 1 to 5576) and 3' (nucleotide positions 5577 to 10976) halves of the genome. T7 RNA polymerase transcripts of the ligated full-length cDNA template were infectious when transfected into BHK-21 cells. To identify the recombinant virus, a silent mutation was introduced into the clone encoding the 3' half of the genome, which abolished an XbaI site at nucleotide position 9131. Virus recovered by transfection with the transcripts contained this silent mutation, confirming its identity. Recombinant and parent viruses were identical with respect to growth and plaque production in BHK-21 cells, envelope protein expression in C6/36 cells, and neurovirulence and immunogenicity in mice. Repeated attempts to obtain infectious RNA by transcription from full-length JEV genome cDNA templates cloned into plasmid vectors were unsuccessful. Synthesis of infectious JEV RNA from in vitro-ligated JEV cDNA templates will be useful for molecular and genetic studies of flavivirus replication and virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease domain in flaviviruses and pestiviruses. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):637–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., McWilliam S. M., Butler H. C., Gibbs A. J., Weiller G., Herring B. L., Hemsley A. C., Aaskov J. G., Yoksan S., Bhamarapravati N. Comparison of a dengue-2 virus and its candidate vaccine derivative: sequence relationships with the flaviviruses and other viruses. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90460-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. E. From the World Health Organization. Current approaches to the development of dengue vaccines and related aspects of the molecular biology of flaviviruses. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1105–1111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Weir R. C., Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Rice C. M. Evidence that the N-terminal domain of nonstructural protein NS3 from yellow fever virus is a serine protease responsible for site-specific cleavages in the viral polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. R., Tesh R. B., Rico-Hesse R. Genetic variation of Japanese encephalitis virus in nature. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2915–2922. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu P. W., Westaway E. G. Characterization of Kunjin virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: reinitiation of synthesis in vitro. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):330–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90275-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Powell N., Greenwald G. F., Willis L. V., Johnson B. J., Smith J. F., Johnston R. E. Attenuating mutations in the E2 glycoprotein gene of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus: construction of single and multiple mutants in a full-length cDNA clone. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):20–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90114-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. B., Brinton M. A. Dissociation of NS5 from cell fractions containing West Nile virus-specific polymerase activity. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3641–3644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3641-3644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE J. H., LEE L. H. A serological investigation of six encephalitis viruses isolated in Malaya. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Oct;35(5):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Dalrymple J. M., Strauss J. H., Rice C. M. Comparison of the virulent Asibi strain of yellow fever virus with the 17D vaccine strain derived from it. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2019–2023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Nomoto A., Watanabe K., Mori T., Takezawa T., Aizawa C., Takegami T., Hiramatsu K. Molecular cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of Japanese encephalitis virus Beijing-1 strain. Virus Genes. 1988 Jun;1(3):305–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00572709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoke C. H., Nisalak A., Sangawhipa N., Jatanasen S., Laorakapongse T., Innis B. L., Kotchasenee S., Gingrich J. B., Latendresse J., Fukai K. Protection against Japanese encephalitis by inactivated vaccines. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 8;319(10):608–614. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809083191004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura N., Kohara M., Abe S., Komatsu T., Tago K., Arita M., Nomoto A. Determinants in the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus Sabin 1 RNA that influence the attenuation phenotype. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1302–1309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1302-1309.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura-Kuroda J., Yasui K. Topographical analysis of antigenic determinants on envelope glycoprotein V3 (E) of Japanese encephalitis virus, using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):124–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.124-132.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Hasegawa H., Oyama T., Tamai T., Kusaba T. Antigenic analysis of Japanese encephalitis virus by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.117-123.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Almond J. W., Racaniello V. R. A mouse model for poliovirus neurovirulence identifies mutations that attenuate the virus for humans. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2917–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2917-2920.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Zhao B. T., Hori H., Bray M. Infectious RNA transcribed from stably cloned full-length cDNA of dengue type 4 virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobigs M., Marshall I. D., Weir R. C., Dalgarno L. Murray Valley encephalitis virus field strains from Australia and Papua New Guinea: studies on the sequence of the major envelope protein gene and virulence for mice. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90678-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobigs M., Usha R., Nestorowicz A., Marshall I. D., Weir R. C., Dalgarno L. Host cell selection of Murray Valley encephalitis virus variants altered at an RGD sequence in the envelope protein and in mouse virulence. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90029-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAda P. C., Mason P. W., Schmaljohn C. S., Dalrymple J. M., Mason T. L., Fournier M. J. Partial nucleotide sequence of the Japanese encephalitis virus genome. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitayaphan S., Grant J. A., Chang G. J., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the virulent SA-14 strain of Japanese encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, SA-14-14-2. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90519-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Okada T., Kondo A., Suzuki M., Kobayashi M., Oya A. Immunotyping of different strains of Japanese encephalitis virus by antibody-absorption, haemagglutination-inhibition and complement-fixation tests. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(4):547–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno Y., Okamoto Y., Yamada A., Baba K., Yabuuchi H. Effect of current Japanese encephalitis vaccine on different strains of Japanese encephalitis virus. Vaccine. 1987 Jun;5(2):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polo J. M., Davis N. L., Rice C. M., Huang H. V., Johnston R. E. Molecular analysis of Sindbis virus pathogenesis in neonatal mice by using virus recombinants constructed in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2124-2133.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Lenches E. M., Strauss J. H. Flavivirus enzyme-substrate interactions studied with chimeric proteinases: identification of an intragenic locus important for substrate recognition. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4749–4758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4749-4758.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Grakoui A., Galler R., Chambers T. J. Transcription of infectious yellow fever RNA from full-length cDNA templates produced by in vitro ligation. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):285–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Linares A., Cahour A., Després P., Girard M., Bouloy M. Processing of yellow fever virus polyprotein: role of cellular proteases in maturation of the structural proteins. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4199–4209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4199-4209.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiyoshi H., Mori C., Fuke I., Morita K., Kuhara S., Kondou J., Kikuchi Y., Nagamatu H., Igarashi A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Japanese encephalitis virus genome RNA. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Czaya G., Färber P. M., Hegemann J. H. In vitro synthesis of West Nile virus proteins indicates that the amino-terminal segment of the NS3 protein contains the active centre of the protease which cleaves the viral polyprotein after multiple basic amino acids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):851–858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Flavivirus replication strategy. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:45–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]