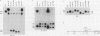Abstract
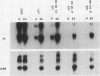
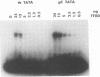
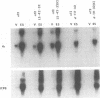
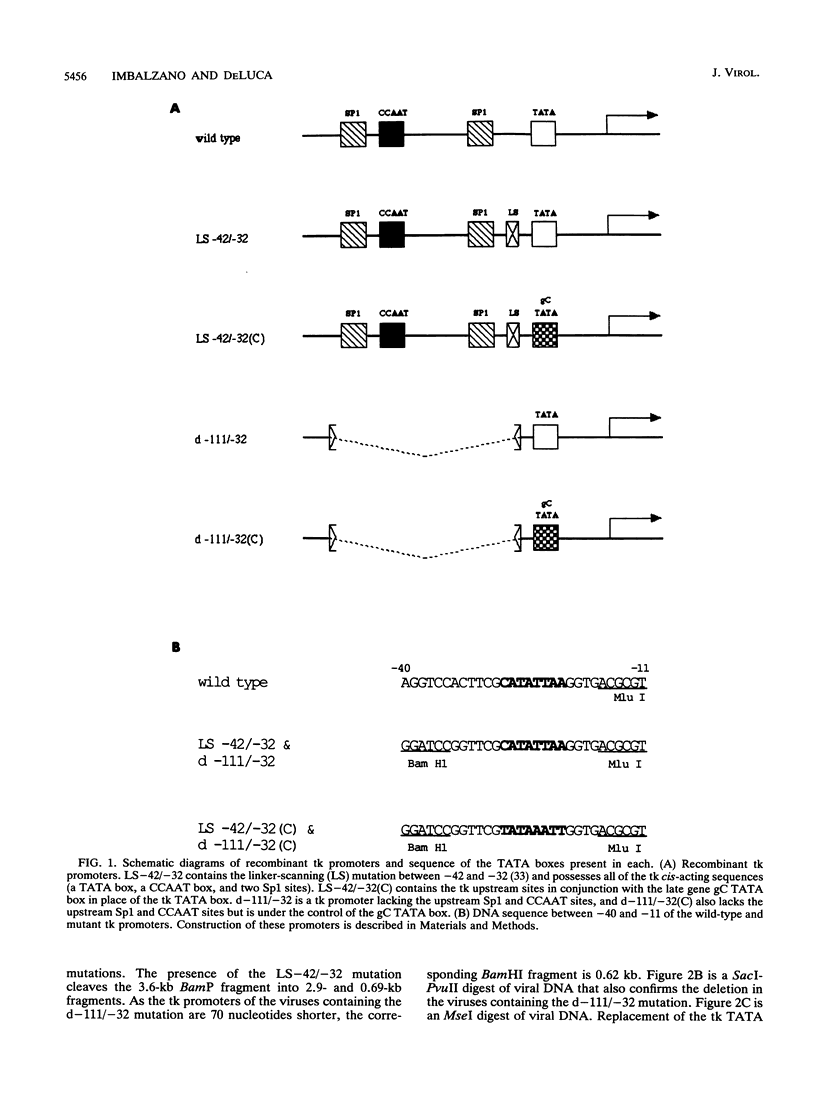
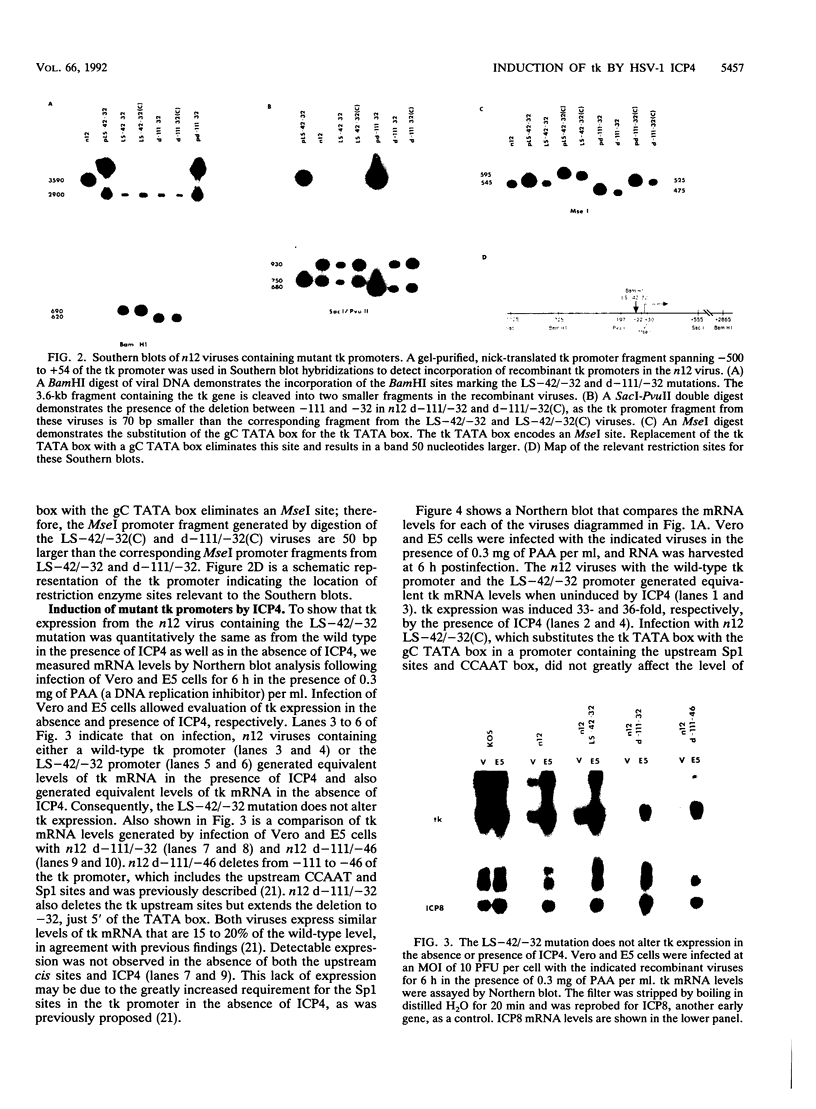
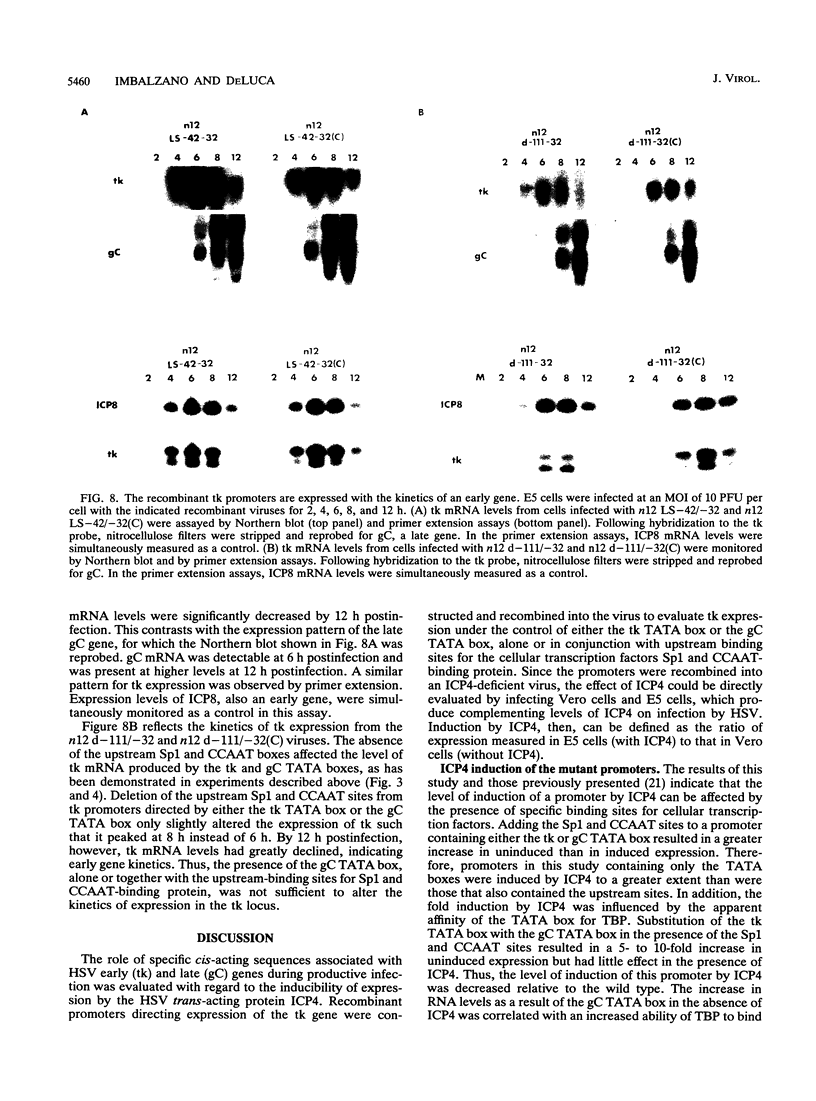
The role of cis-acting promoter elements associated with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) early and late genes was evaluated during productive infection with regard to activation of gene expression by the HSV-1 transactivator ICP4 and control of temporal regulation. A set of recombinant viruses was constructed such that expression of an HSV-1 early gene, thymidine kinase (tk), was placed under the control of either the tk TATA box or the TATA box from the late gene, glycoprotein C (gC), in the presence or absence of the upstream Sp1 and CCAAT sites normally found in the tk promoter. The presence of Sp1 sites in the promoter or replacement of the tk TATA box with the gC TATA box resulted in a decreased activation of tk mRNA expression by ICP4. Substitution of the A + T-rich region from the gC TATA box in the context of the remainder of the surrounding tk sequences resulted in a promoter that bound recombinant TATA-binding protein (TBP) better at lower concentrations than the wild-type tk promoter did. These results indicate that tk promoters that are better able to utilize TBP are less responsive to ICP4 activation and suggest that activation by ICP4 involves the general transcription factors that interact with TBP or TBP itself. Additionally, all of the viruses expressed tk at early times postinfection, indicating that cis-acting promoter elements that control the level of expression of HSV-1 early and late genes do not determine temporal regulation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abmayr S. M., Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. The pseudorabies immediate early protein stimulates in vitro transcription by facilitating TFIID: promoter interactions. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):542–553. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni J., Coen D. M. Examination of the roles of transcription factor Sp1-binding sites and an octamer motif in trans induction of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4088–4092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4088-4092.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. DNA nucleotide sequence analysis of the immediate-early gene of pseudorabies virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4637–4646. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Courtney M. A., Schaffer P. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants in herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 permissive for early gene expression. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):767–776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.767-776.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activities of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP4 genes specifying nonsense peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4491–4511. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical and functional domains of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.732-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ElKareh A., Murphy A. J., Fichter T., Efstratiadis A., Silverstein S. "Transactivation" control signals in the promoter of the herpesvirus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1002–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Maguire K., Kralli A., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Weinmann R. Direct interaction between adenovirus E1A protein and the TATA box binding transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5124–5128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbalzano A. N., Coen D. M., DeLuca N. A. Herpes simplex virus transactivator ICP4 operationally substitutes for the cellular transcription factor Sp1 for efficient expression of the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):565–574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.565-574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbalzano A. N., Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Functional relevance of specific interactions between herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 and sequences from the promoter-regulatory domain of the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2620–2631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2620-2631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Everett R. D. The control of herpes simplex virus type-1 late gene transcription: a 'TATA-box'/cap site region is sufficient for fully efficient regulated activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8247–8264. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Pei R., Berk A. J. Cloning of a transcriptionally active human TATA binding factor. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1646–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.2194289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibler P. K., Duncan J., Keith B. D., Hupel T., Smiley J. R. Regulation of herpes simplex virus true late gene expression: sequences downstream from the US11 TATA box inhibit expression from an unreplicated template. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6749–6760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6749-6760.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. The Zta trans-activator protein stabilizes TFIID association with promoter DNA by direct protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2441–2454. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Roizman B. Activation of herpes simplex virus 1 gamma 2 genes by viral DNA replication. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Roizman B. Delineation of regulatory domains of early (beta) and late (gamma 2) genes by construction of chimeric genes expressed in herpes simplex virus 1 genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Silverstein S. J. Interaction of cell and virus proteins with DNA sequences encompassing the promoter/regulatory and leader regions of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9402–9412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 ts mutants by marker rescue: correlation of the physical and genetic maps. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. Mutational dissection of the HSV-1 immediate-early protein Vmw175 involved in transcriptional transactivation and repression. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):186–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. The regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein Vmw175 required for site specific DNA binding closely correspond to those involved in transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11005–11025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Preston V. G., Everett R. D. A mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early polypeptide Vmw175 binds to the cap site of its own promoter in vitro but fails to autoregulate in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):851–861. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Abnormal properties of an immediate early polypeptide in cells infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):357–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.357-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. A second-site revertant of a defective herpes simplex virus ICP4 protein with restored regulatory activities and impaired DNA-binding properties. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):787–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.787-795.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Activities of heterodimers composed of DNA-binding- and transactivation-deficient subunits of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):299–307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.299-307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., Imbalzano A. N., DeLuca N. A. Separation of primary structural components conferring autoregulation, transactivation, and DNA-binding properties to the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3714–3728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3714-3728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Johnson D. C., Pizer L. I., Everett R. D. The ICP4 binding sites in the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D (gD) promoter are not essential for efficient gD transcription during virus infection. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):623–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.623-631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffy K. R., Weir J. P. Upstream promoter elements of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein H gene. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):972–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.972-975.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L., Knipe D. M. Mapping of the transcriptional initiation site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP8 gene in infected and transfected cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.615-620.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Everett R. D., Wilcox K. W., Beard P., Pizer L. I. ICP4-binding sites in the promoter and coding regions of the herpes simplex virus gD gene contribute to activation of in vitro transcription by ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2510–2520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2510-2520.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder D. G., Pizer L. I. Role for DNA-protein interaction in activation of the herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D gene. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4661–4672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4661-4672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus is a general transactivator but stimulates only suboptimally utilized promoters. A clue to specificity? J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlcek C., Paces V., Schwyzer M. Nucleotide sequence of the pseudorabies virus immediate early gene, encoding a strong transactivator protein. Virus Genes. 1989 Aug;2(4):335–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00684041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Narayanan P. R. Expression of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C gene requires sequences in the 5' noncoding region of the gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.445-449.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]