Abstract
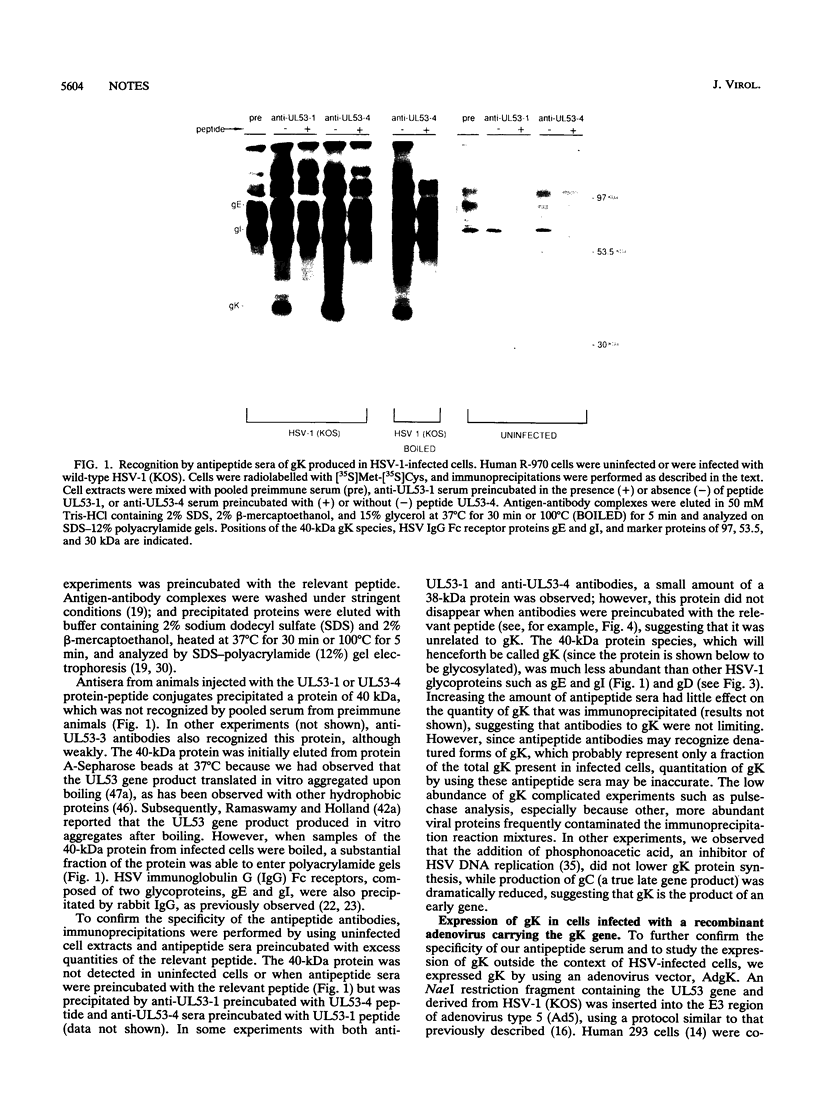
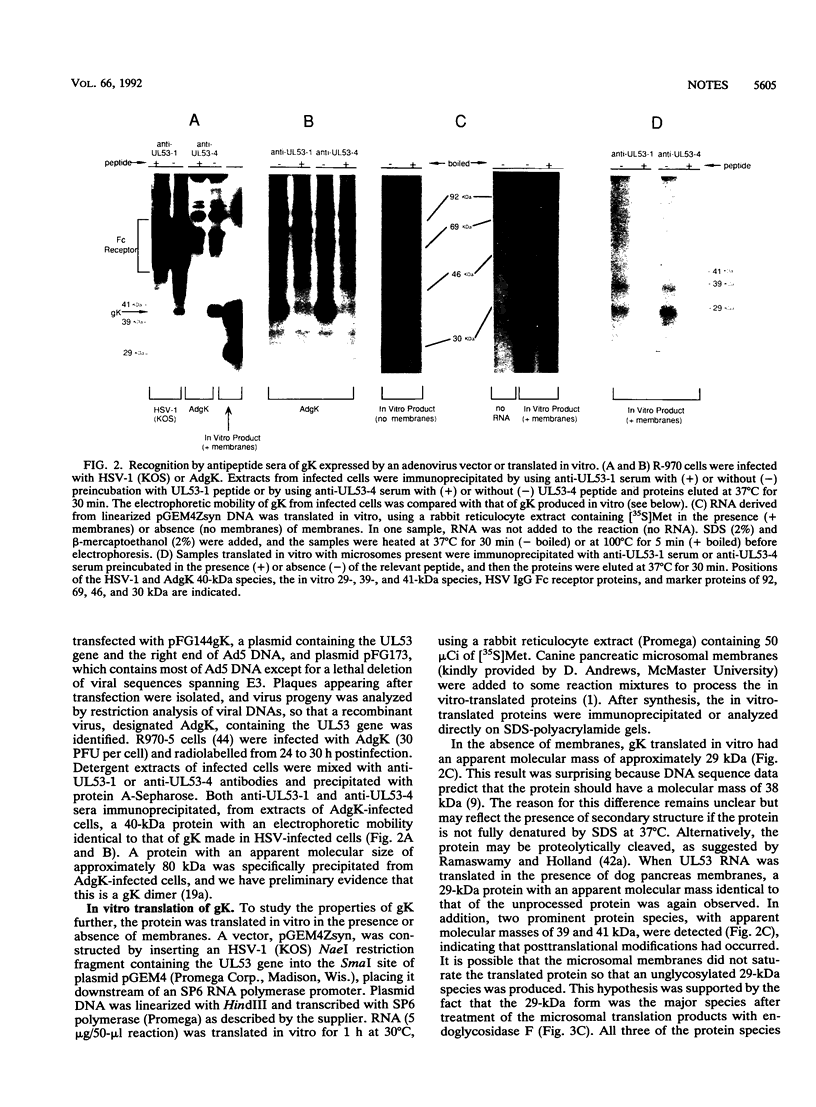
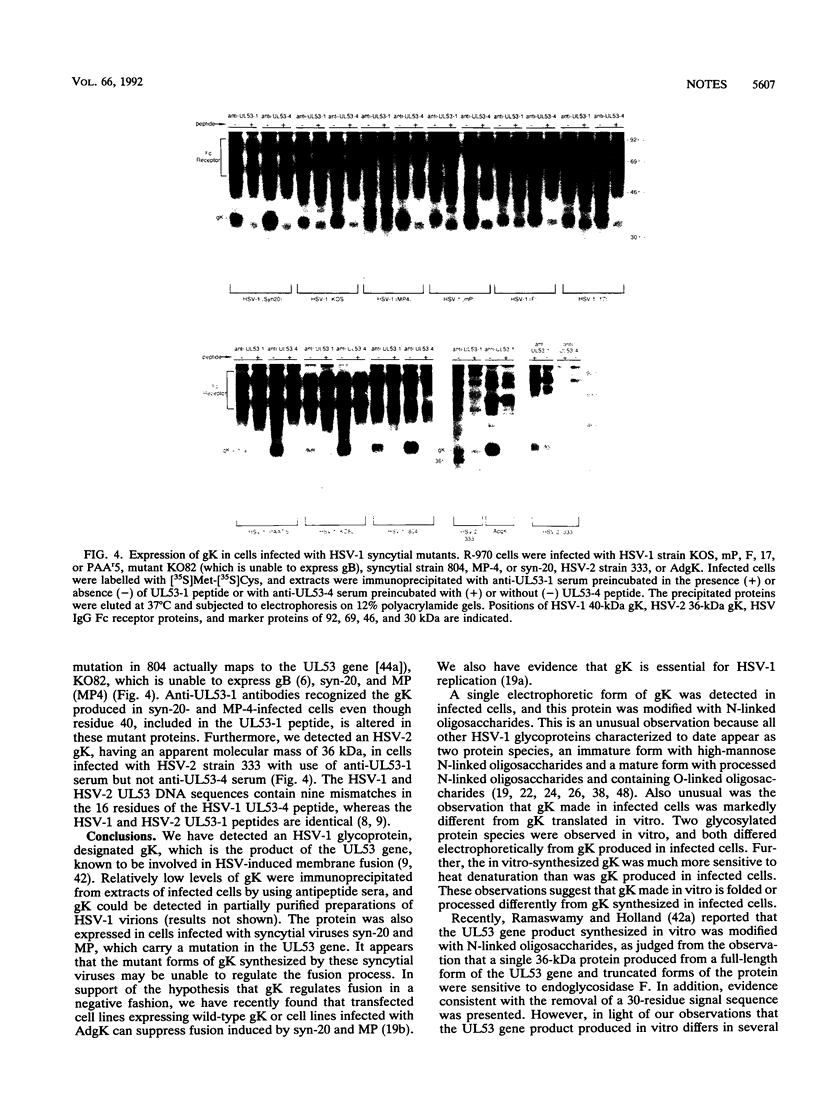
Antipeptide sera were used to identify a novel glycoprotein encoded by the UL53 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). The UL53 gene product is thought to play a central role in regulating membrane fusion because mutations giving rise to the syncytial phenotype, wherein cells are extensively fused, frequently map to this gene. A single 40-kDa protein, designated gK (the ninth HSV-1 glycoprotein to be described), was detected with antipeptide sera in cells infected with both wild-type and syncytial strains of HSV-1 which were labelled with [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine or with [3H]glucosamine, and this protein was sensitive to treatment of cells with tunicamycin. With all other HSV glycoproteins studied to date, at least two glycosylated species, often differing substantially in electrophoretic mobility, have been observed in infected cells; thus, gK is unusual in this respect. The 40-kDa gK protein was also immunoprecipitated from cells infected with a recombinant adenovirus vector carrying the UL53 gene. Two glycosylated species of 39 and 41 kDa were produced when UL53 mRNA was translated in vitro in the presence of microsomes, and these proteins differed from gK produced in infected cells not only because they possessed different electrophoretic mobilities but also because they were unable to enter gels after being heated. In addition, a 36-kDa protein was detected in extracts from cells infected with HSV-2 with use of these sera.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. Examining protein translocation in cell-free systems and microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):960-2, 964-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines J. D., Ward P. L., Campadelli-Fiume G., Roizman B. The UL20 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes a function necessary for viral egress. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6414–6424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6414-6424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond V. C., Person S. Fine structure physical map locations of alterations that affect cell fusion in herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Genetic studies with herpes simplex virus type 1. The isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants, their arrangement into complementation groups and recombination analysis leading to a linkage map. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):329–346. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence of a region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB glycoprotein gene: mutations affecting rate of virus entry and cell fusion. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., Warner S. C., Zhou J. H., DeLuca N. A. Linker-insertion nonsense and restriction-site deletion mutations of the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.714-721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Arsenakis M., Farabegoli F., Roizman B. Entry of herpes simplex virus 1 in BJ cells that constitutively express viral glycoprotein D is by endocytosis and results in degradation of the virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.159-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Bzik D. J., Bond V. C., Person S., Snipes W. Nucleotide sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) affecting virus entry, cell fusion, and production of glycoprotein gb (VP7). Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):411–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DebRoy C. Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type-2 syn gene that causes cell fusion. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90043-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debroy C., Pederson N., Person S. Nucleotide sequence of a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene that causes cell fusion. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):36–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester A., Farrell H., Wilkinson G., Kaye J., Davis-Poynter N., Minson T. Construction and properties of a mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 with glycoprotein H coding sequences deleted. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):341–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.341-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B. The isolation and properties of a variant of Herpes simplex producing multinucleated giant cells in monolayer cultures in the presence of antibody. Am J Hyg. 1959 Sep;70:208–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. D., Coen D. M., Fisher B. L., Weisslitz M., Randall S., Almy R. E., Gelep P. T., Schaffer P. A. Generation of genetic diversity in herpes simplex virus: an antimutator phenotype maps to the DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke T., Graham F. L., Lulitanond V., Johnson D. C. Herpes simplex virus IgG Fc receptors induced using recombinant adenovirus vectors expressing glycoproteins E and I. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90507-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B., Prusiner S. B., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for a secretory form of the cellular prion protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8110–8115. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson L., Browne H., Wargent V., Davis-Poynter N., Primorac S., Goldsmith K., Minson A. C., Johnson D. C. A novel herpes simplex virus glycoprotein, gL, forms a complex with glycoprotein H (gH) and affects normal folding and surface expression of gH. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2240–2250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2240-2250.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. G., Martin S. L., Coen D. M. A conserved open reading frame that overlaps the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene is important for viral growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1839–1843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1839-1843.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Burke R. L., Gregory T. Soluble forms of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bind to a limited number of cell surface receptors and inhibit virus entry into cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2569–2576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2569-2576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Feenstra V. Identification of a novel herpes simplex virus type 1-induced glycoprotein which complexes with gE and binds immunoglobulin. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2208–2216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2208-2216.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Frame M. C., Ligas M. W., Cross A. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus immunoglobulin G Fc receptor activity depends on a complex of two viral glycoproteins, gE and gI. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1347-1354.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Ghosh-Choudhury G., Smiley J. R., Fallis L., Graham F. L. Abundant expression of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gB using an adenovirus vector. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90613-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Wittels M., Spear P. G. Binding to cells of virosomes containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and evidence for fusion. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):238–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.238-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D mediates interference with herpes simplex virus infection. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):819–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.819-827.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. N., Rothman J. E., Lingappa V. R., Blobel G., Lodish H. F. Membrane assembly in vitro: synthesis, glycosylation, and asymmetric insertion of a transmembrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Devillers-Thiery A., Blobel G. Nascent prehormones are intermediates in the biosynthesis of authentic bovine pituitary growth hormone and prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Schaffer P. A. Expression of the syncytial (syn) phenotype in HSV-1, strain KOS: genetic and phenotypic studies of mutants in two syn loci. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):686–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. A., Efstathiou S., Elliott M. L., Jamieson F. E., McGeoch D. J. Investigation of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes encoding multiply inserted membrane proteins. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minson A. C., Hodgman T. C., Digard P., Hancock D. C., Bell S. E., Buckmaster E. A. An analysis of the biological properties of monoclonal antibodies against glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus and identification of amino acid substitutions that confer resistance to neutralization. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1001–1013. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Blomberg J., Lycke E. O-glycosidic carbohydrate-peptide linkages of Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01320247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Immunoglobulin G(Fc)-binding receptors on virions of herpes simplex virus type 1 and transfer of these receptors to the cell surface by infection. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.512-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Person S., Knowles R. W., Read G. S., Warner S. C., Bond V. C. Kinetics of cell fusion induced by a syncytia-producing mutant of herpes simplex virus type I. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.183-190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Lee G. T., Shapira S. K., Spear P. G. Fine mapping of mutations in the fusion-inducing MP strain of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Spear P. G. The single base pair substitution responsible for the Syn phenotype of herpes simplex virus type 1, strain MP. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy R., Holland T. C. In vitro characterization of the HSV-1 UL53 gene product. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90024-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Person S., Keller P. M. Genetic studies of cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.105-113.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S., Cho H. Y., Huebner R. J. Non-producer human cells induced by murine sarcoma virus. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jan 15;15(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH K. O. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE ENVELOPE AND THE INFECTIVITY OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:814–816. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza J. C., Hardwick K. G., Dean N., Pelham H. R. ERD2, a yeast gene required for the receptor-mediated retrieval of luminal ER proteins from the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1349–1357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90698-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]