Abstract
Mutagenesis of promoter sequences and oligonucleotide competition assays have been used to demonstrate the late-phase-specific stimulation of the adenovirus type 2 major late promoter is mediated by functionally redundant elements located between positions +75 and +125. These octamer motif-related sequences are recognized by multiple factors.
Full text
PDF



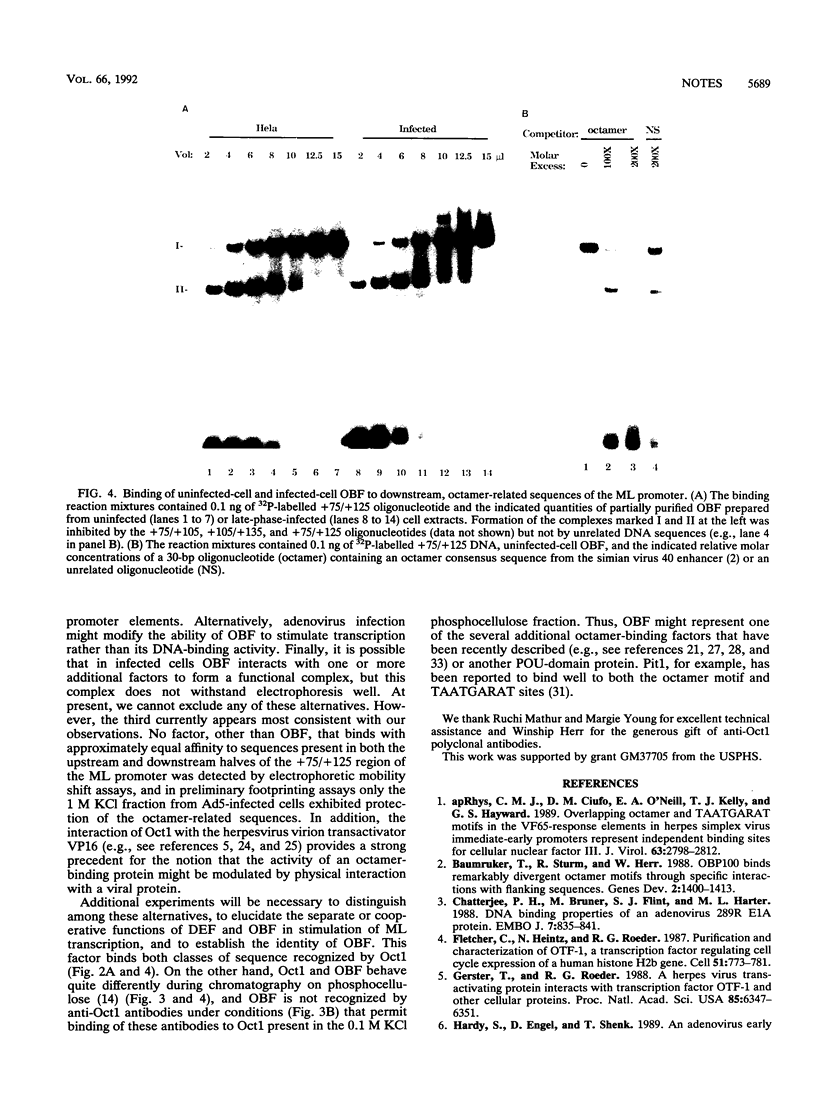

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Bruner M., Flint S. J., Harter M. L. DNA-binding properties of an adenovirus 289R E1A protein. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):835–841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. The adenovirus early region 4 open reading frame 6/7 protein regulates the DNA binding activity of the cellular transcription factor, E2F, through a direct complex. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1699–1710. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. Replication-induced stimulation of the major late promoter of adenovirus is correlated to the binding of a factor to sequences in the first intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3771–3786. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Durr P., Mondésert G., Kédinger C. Replication-dependent activation of the adenovirus major late promoter is mediated by the increased binding of a transcription factor to sequences in the first intron. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5124–5132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5124-5132.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai Y., Chen H., Flint S. J. Anatomy of an unusual RNA polymerase II promoter containing a downstream TATA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2884–2897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schreiber E., Müller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2001–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Elements modulating the block of transcription elongation at the adenovirus 2 attenuation site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9785–9790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Flint S. J. Specific transcription of an adenoviral gene that possesses no TATA sequence homology in extracts of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11527–11533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Lee W., Berk A. J. High-level transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter requires downstream binding sites for late-phase-specific factors. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.51-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Pausing and premature termination of human RNA polymerase II during transcription of adenovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5931–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton M. J., Baim S. B., Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. The adenovirus E4 17-kilodalton protein complexes with the cellular transcription factor E2F, altering its DNA-binding properties and stimulating E1A-independent accumulation of E2 mRNA. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2345–2359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2345-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer D., Graus A., Kraay R., Langeveld A., Mulder M. P., Grosveld G. The octamer binding factor Oct6: cDNA cloning and expression in early embryonic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7357–7365. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Hemstrom C., Virtanen A., Nevins J. R. An adenovirus E4 gene product trans-activates E2 transcription and stimulates stable E2F binding through a direct association with E2F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. K., Hawley D. K. In vitro analysis of a transcription termination site for RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5782–5795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- apRhys C. M., Ciufo D. M., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Overlapping octamer and TAATGARAT motifs in the VF65-response elements in herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters represent independent binding sites for cellular nuclear factor III. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2798–2812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2798-2812.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]