Abstract
Purpose
In order to discover diagnostic biomarkers associated with early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), we searched for autoantibodies preferentially present in stage I patients compared to patients with advanced stage disease. Here we describe an autoantibody against complement factor H (CFH) and its association with early stage NSCLC.
Experimental Design
Immunoblots were used to detect autoantibodies in the sera of stage I NSCLC patients. An autoantibody recognizing a 150 kDa protein was discovered and the protein was identified by mass spectrometry. The association of the autoantibody with early stage disease was suggested by the results of immunoblot analysis with sera from 28 stage I patients and 28 stage III/IV patients. This association was confirmed by protein microarray of sera from 125 NSCLC patients of all stages as well as 125 age, gender, and smoking history matched controls.
Results
The immunoreactive protein was identified as CFH. By immunoblot analysis, anti-CFH autoantibody was found in 50% of stage I NSCLC patients and 11% of late stage NSCLC patients (P=0.003). By protein microarray analysis, patients with stage I NSCLC had a significantly higher incidence of anti-CFH antibody than those with late stage NSCLC (P=0.0051). The percentage of sera with a positive level of CFH autoantibody was 30.4% in stage I, 21.1% in stage II, 12.5% in stage III, 7.4% in stage IV and 8.0% in the control group.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that in patients with NSCLC, CFH autoantibody is a molecular marker associated with early stage disease.
Keywords: Lung Cancer, Metastasis, Complement Factor H, Autoimmunity
Introduction
Patients with NSCLC typically present with advanced stage disease and almost all will eventually die with metastasis. Even patients classified as having stage I disease have a 5-year survival rate of less than 60%, suggesting undetected micrometastasis at the time of presentation (1, 2). Unfortunately, attempts to improve outcome through early detection efforts using chest radiographs, sputum cytology, and more recently, low-dose computed tomography (CT), have failed to demonstrate a reduction in mortality. New strategies that make use of our continually improving understanding of oncogenesis and the process of metastasis are needed if early detection efforts are to be successful.
One approach to early detection is the discovery of novel biomarkers that could not only identify patients with lung cancer, but assist in appropriate staging. Autoantibodies are one class of potentially useful serum biomarkers as there is a low incidence of cancer-associated autoantibodies in healthy individuals (3). In addition, the autoantibody response elicited against a tumor associated antigen may elucidate a unique therapeutic target, albeit in a select group of cancer patients. Here we report the discovery of an autoantibody to complement factor H (CFH), one of the complement inhibitory proteins on tumor cells, and demonstrate its association with early stage NSCLC.
Material & Methods
Patient samples
This study was approved by the Duke University Institutional Review Board. All cancer patients selected for entry into the study met the following criteria: 1) a new diagnosis of histologically confirmed NSCLC, 2) no prior treatment including surgery, chemotherapy or radiation for lung cancer, and 3) no other known malignancy. We selected control sera from our repository from age, gender and smoking history matched individuals with no cancer who had a chest CT for a variety of thoracic indications, including interstitial lung disease, cardiovascular abnormalities, asthma, possible pulmonary embolism, and sickle cell disease.All sera were collected following informed consent and stored in a serum repository at −80 °C. Patient demographics for each portion of the study are described below.
Immunoblot analyses
The source of antigen for autoantibody discovery was pooled serum from late stage (i.e., stage III and IV) NSCLC patients. This serum pool was depleted of albumin and IgG using a commercial kit (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ), and 400 μg of protein was loaded into a single preparative lane of a polyacrylamide gel and separated by SDS-PAGE, carried out under reducing conditions. The proteins were then transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane and the membrane inserted into a Surf-Blot apparatus (Idea Scientific Company, Minneapolis, MN). The Surf-Blot apparatus creates channels that permit the screening of up to 21 different serum samples. The membrane was probed with individual serum samples (diluted 1:1000) from each of 10 stage I NSCLC patients, as described previously (4). The stage I NSCLC patients included 4 males and 6 females, with a mean age of 66.6 years (range 57-72 years), and all were disease free at least 2 years after diagnosis and treatment.
For confirmatory CFH immunoblot analysis, 0.5 μg/well of purified human CFH (Complement Technology Inc., Tyler, TX), was probed with multiple serum samples in the manner described above. We randomly selected from our repository sera from 28 patients with stage I NSCLC: 14 males and 14 females, with a mean age of 65.5 years (range 51-78 years). In addition, we randomly selected from the repository sera from 28 patients with stage III or IV NSCLC: 16 males and 12 females, with a mean age of 64.0 years (range 41-83 years). Sera from 12 age, gender, smoking history matched individuals with no cancer (“high risk control subjects”) were also examined.
Identification of the immunoreactive protein
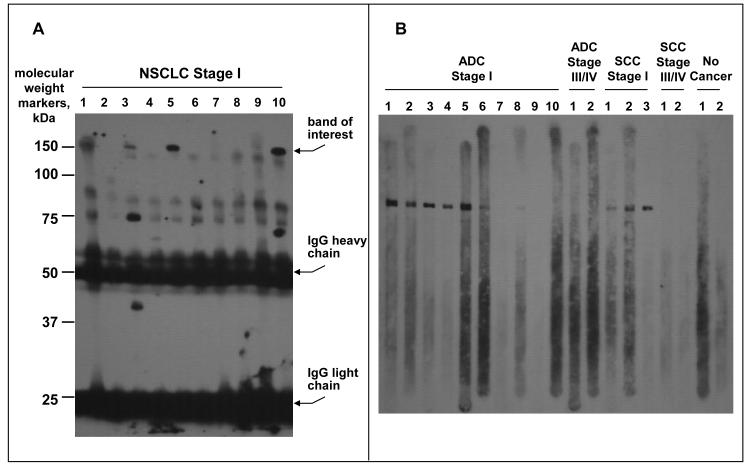
The pool of sera from patients with late stage disease, depleted of albumin and IgG, was run in two adjacent lanes of an SDS-PAGE gel under non-reducing conditions. Non-reducing conditions were necessary since the abundant serum protein alpha-2 macroglobulin runs at approximately the same molecular mass as the band of interest under reducing conditions, but at ~320 kDa under non-reducing conditions (5). Immunoblot analysis of one lane with serum #5 from Fig. 1A was used to identify a Coomassie blue stained band in the other lane. The proteins in the band were then subjected to in-gel tryptic digestion and identified by MALDI-TOF peptide fingerprint analysis and MS/MS sequencing. Of the proteins identified from the band, purified CFH was the only one that demonstrated immunoreactivity with serum #5.
Fig. 1.
Immunoblots probed with NSCLC patient sera. A, Pooled serum blot: Ten individual serum samples from patients with stage I NSCLC were used to probe a blot containing the pooled sera from 5 late stage NSCLC patients. B, CFH blot: Individual stage I, stage III/IV and normal serum samples were used to probe a blot containing purified CFH.
CFH Microarray
Purified CFH was reduced and denatured in 6 M urea, 1.5% (w/v) CHAPS, 12 mM mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine and 100 mM iodoacetamide for 30 minutes. It was then exchanged into Dulbecco’s PBS (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD) using Zeba Spin desalting columns according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Pierce, Rockford, IL), lyophilized and resuspended in deionized water to a concentration of 0.3 mg/ml. Microarray construction and testing was performed by ArrayIt Corporation (Sunnyvale, CA). Arrays were printed on SuperEpoxy 2 Microarray slide substrate using a Spotbot microarrayer with a 946MP3 printing pin at 50 % humidity. Volume printed was 1 nl per spot. Spots of human IgG and CY3 fluorescent dye were used as positive controls. After activation and inhibition of nonspecific binding, arrays were incubated with serum (diluted 1:300), with each serum sample tested on triplicate spots of CFH. Bound IgG was detected with mouse antihuman IgG, conjugated to AlexaFluor 488, at 1 μg/ml. Arrays were read by ArrayIt InnoScan® 710. Data quantification was performed with Mapix Quantification Software (Innopsys, Carbonne, France).
For the microarray assay, 125 sera from 65 males and 60 females with all stages of NSCLC were selected, as well as 125 controls matched by age, gender, and smoking history. Mean age and smoking history for the cancer and control study groups were 60.1 years (range 25-80), 40.2 pack years, and 60.4 years (20-81), 38.3 pack years, respectively (see Table 1). All cancer patients selected for entry into the study met the criteria for inclusion as described above. We then matched control patients from our repository, having had a thoracic CT for a variety of indications as described above, but without a history of cancer.
Table 1.
Age, gender, smoking history, cancer stage and histology of 125 NSCLC patients and matched controls selected for the microarray portion of the study.
| Demographic | Cancer (n = 125) | Control (n = 125) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.0 ± 10.2 | 60.4 ± 10.4 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 65 | 65 |
| Female | 60 | 60 |
| Smoking History (pack years) |
40.2 ± 30.7 | 38.3 ± 29.1 |
| Stage | ||
| I | 47 | |
| II | 19 | |
| III | 32 | |
| IV | 27 | |
| Histology | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 66 | |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 1 | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 32 | |
| Large cell carcinoma | 7 | |
| BAC | 1 | |
| NSC carcinoma, unspecified | 18 |
Statistical analysis of microarray data
Microarray data analysis was performed with Excel (Microsoft) or JMP (SAS, Cary, NC) software. The median spot pixel intensity minus background was used as the fluorescence intensity for each spot. Each data point on an array was normalized to the mean of triplicate spots of purified human IgG on the same array. Outliers were identified using Dixon’s Q-test at the 95% confidence interval (6).
We used two different methods to define positivity for the CFH autoantibody. First, we defined a positive autoantibody response as one that produced a mean fluorescence intensity of two standard deviations (2SD) above the mean of the control group. We also established a cutoff value for a positive autoantibody response using receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis. Using both criteria for defining autoantibody positivity, Student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance between early and late stage disease.
Results
Discovery and confirmatory immunoblots
We hypothesized that patients with NSCLC express proteins that stimulate antibody production. We further hypothesized that early stage patients may possess antibodies that play an inhibitory role in cancer progression, and therefore be less prevalent in late stage patients. Such a finding would have implications for cancer detection and therapeutic intervention. To test our hypothesis that early stage lung cancer patients produce autoantibodies, we conducted an initial screen of individual sera from patients with stage I NSCLC, whose cancers were non-recurrent 2 years after treatment. We discovered that 4 of 10 sera contained an antibody that recognized a 150 kDa protein present in a pool of serum from late stage patients (Fig. 1A). The immunoreactive 150 kDa protein was identified as CFH.
We next tested the hypothesis that the CFH autoantibody found in stage I lung cancer patients would be less prevalent in advanced stage patients by performing an immunoblot of purified CFH with sera from 28 stage I patients, 28 stage III/IV patients, and 12 control patients without cancer. A representative sample of the results is shown (Fig. 1B). Sera were considered CFH-autoantibody positive or negative based on visual assessment of CFH immunoblots. Overall, 14 of 28 non-recurrent stage I NSCLC patients (50%) were positive for the CFH autoantibody, including 10 of 17 adenocarcinoma patients (ADC) and 4 of 11 squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) patients. In contrast, only 3 of 28 late stage NSCLC patients had detectible autoantibody (10.7%) including 2 of 16 with ADC and 1 of 12 with SCC. The difference in the incidence of CFH autoantibody in early vs. late stage NSCLC was statistically significant (P=0.003). None of the 12 individuals without cancer had the CFH autoantibody.
Microarray
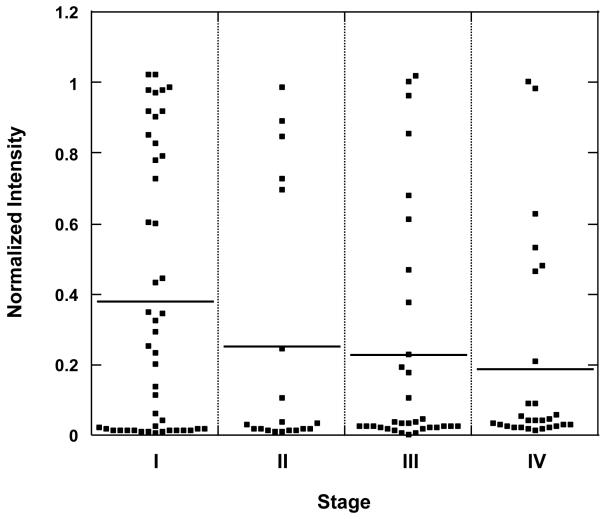
Protein microarrays were used to confirm the association of CFH autoantibody to early stage NSCLC. Sera from 125 patients at all stages of NSCLC were randomly selected from our serum repository. Sera from an equal number of age, gender and smoking history matched control patients were also selected to define the prevalence of the CFH autoantibody in a non-cancer population. These sera were tested on CFH-imprinted microarrays and fluorescence data were obtained. After normalization, the mean spot intensity was obtained for each sample. The distributions of spot intensity, separated by cancer stage, are shown (Fig. 2). The mean spot intensity of stage I sera (0.38) was significantly greater than that of late stage disease (0.23 in stage III and 0.19 in stage IV, P=0.031 and 0.011, respectively).
Fig. 2.
Distribution of microarray spot intensity for CFH autoantibody shown by stage (stage I [n=46], stage II [n=19], stage III [n=32], stage IV [n=27]). The horizontal line represents the median spot intensity for each stage.
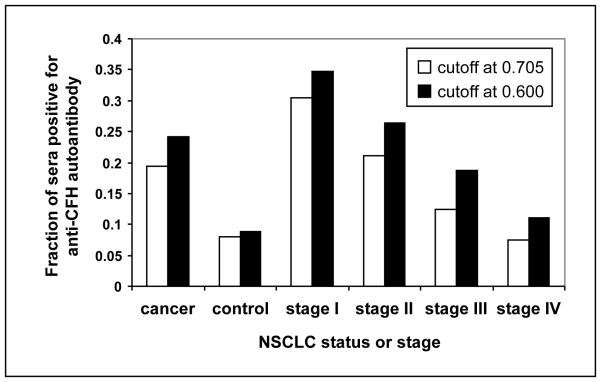
We defined a CFH autoantibody-positive serum as one that gave an intensity value that was 2SD greater than the mean spot intensity of CFH autoantibody in control sera (cutoff = 0.705) (6-8). The percentage of sera with a positive level of CFH autoantibody was highest in stage I and lowest in stage IV (P=0.0051): 30.4% in stage I, 21.1% in stage II, 12.5% in stage III, and 7.4% in stage IV (Fig. 3). The percentage of sera with a positive level of CFH autoantibody in the control group was 8.0%, also significantly lower than that of stage I (P=0.0001).
Fig. 3.
Fraction of sera in all stages of cancer (cancer) vs. control and by stage with a positive level of CFH autoantibody in the microarray. For definition of positivity, the cutoff point is defined as 2SD greater than the mean spot intensity for CFH autoantibody of the control group (0.705), or as the optimal cutoff value determined from ROC analysis (0.600).
Alternatively, we used ROC analysis to define a positive autoantibody cutoff point of 0.600. When this definition of positivity was used, the percentage of sera with a positive level of CFH autoantibody was again highest in stage I and lowest in stage IV (P=0.0073): 34.8% in stage I, 26.3% in stage II, 18.8% in stage III, and 11.1% in stage IV (Fig. 3). The percentage of sera with a positive level of CFH autoantibody in the control group was 8.8%, also significantly lower than that of stage I (P<0.0001).
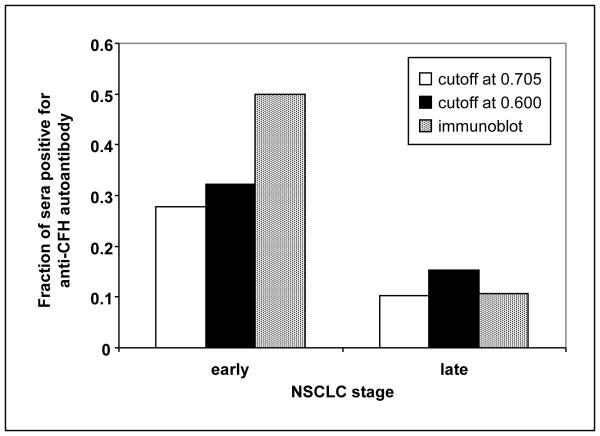
Lastly, the microarray data were reanalyzed such that stage I and II made up an “early stage” group and III and IV made up the “late stage” group (Fig. 4.) Again, there was a significant difference between the percent of positives in these two groups using both the 2SD and ROC cutoff points for the microarray data (P=0.0119 and 0.0250, respectively).
Fig. 4.
Fraction of sera in early (I/II) and late (III/IV) stage NSCLC with a positive level of CFH autoantibody in the microarray. The cutoff points for positivity are as described in the legend to Fig. 3. For comparison, the proportion of sera in each group defined as positive from a visual assessment of immunoblots is shown.
Discussion
Lung cancer is a diverse disease and a significant public health issue, with approximately 159,000 deaths and 219,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States in 2009, according to the American Cancer Society. There is no currently accepted screening method for lung cancer and over 75% of lung cancer patients present with advanced stage disease when therapeutic options are limited (7). Even those patients who present with clinical stage I lung cancer have at best a 60% 5-year survival rate, suggesting that at least 40% of all patients classified as stage I have undetectable metastatic disease at the time of presentation (1, 2). Unfortunately, there is no way to identify which patients will develop recurrence and will need adjuvant therapy. The current approach that assigns treatment for NSCLC patients based on histology and stage, and then follows response and alters therapy based on RECIST criteria is inadequate (8).
These issues underscore the need for substantial improvement in diagnostic techniques and more accurate molecular classifications of NSCLC. A non-invasive serum test that could complement imaging, with the potential to suggest the appropriate therapy, would have a tremendous impact on clinical management and outcomes. Complementary or alternative strategies for early detection and targeted therapy selection have recently focused on the development of tumor biomarkers. As tumors are heterogeneous within the patient population, multiple markers may be required to encompass all NSCLC patients.
Detection of tumor autoantibodies is one approach that could be used for cancer detection or staging (9-13). Tumors secrete proteins needed for tumor development and progression. Additionally, proteins are shed into the circulation from tumor cells undergoing necrosis. Tumor-derived proteins could provoke an immune response if the proteins possess mutations or post-translational modifications, or if abnormal protein folding exposes a cryptic epitope. The immune response is amplified even when the antigens are low abundance proteins. Furthermore, as antibodies are relatively stable, they may be detected long after a response is first elicited by a tumor antigen. An autoantibody could provide evidence of the existence of an antigen that is expressed early in tumor development, or a protein that has a short half-life in the blood.
Several studies have demonstrated the association of autoantibodies with early versus late stage cancer (3). For instance, autoantibodies to MUC1 were associated with early stage breast, gastric and ovarian cancers as well as with survival (14-17). Autoantibodies to annexin I, 14-3-3 theta and LAMR1 were shown to precede the onset of symptoms and diagnosis of NSCLC (18). Conversely, autoantibodies to p53 are associated with high grade tumors and poor survival (19). The current study, for the first time, describes CFH autoantibodies as associated with early stage NSCLC.
By immunoblot and microarray analyses, we uncovered a relationship between CFH autoantibodies and cancer stage: a significantly higher number of stage I patients had autoantibodies to CFH as compared to stage IV and high risk controls. One possible explanation for this finding is that the level of CFH autoantibodies rises during early stages of lung cancer and wanes in later stages, perhaps because of a reduction in immune competence as disease progresses. Another intriguing possibility is that the presence of CFH autoantibodies may have prevented early stage tumors from progressing into more advanced tumors. The host immune response to tumors is thought to be primarily mediated by cellular immunity (20). A humoral response to tumors has been recognized but its effectiveness in combating tumor growth or metastasis is unknown (21). Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies are used to treat some tumors, and it may be possible that some patients whose tumors do not metastasize have generated autoantibodies that block one of the critical steps in metastasis formation. Therefore, CFH autoantibodies may have value not only in a panel of diagnostic cancer biomarkers, but the autoantigen (i.e., CFH) may be a possible therapeutic target.
The primary function of CFH is to inhibit the alternative pathway of complement-mediated lysis by accelerating the removal of C3b and the inactivation of the C3 convertase C3bBb (22). It has been shown that neutralizing antibodies to complement inhibitory proteins increase C3b deposition on cell lines that express and bind these proteins, and inactivation of multiple complement inhibitory proteins is needed for cytotoxicity (23-25) Previous studies have described CFH autoantibodies in patients with hemolytic uremia syndrome (HUS) (26). None of the patients in the current study had any renal disease, suggesting that the CFH autoantibody in lung cancer patients recognizes a different epitope from that recognized in HUS. The CFH autoantibody may be part of a more complex host defense mechanism resulting in limiting tumor growth and suppression of metastasis. If this is the case, it follows that some high-risk patients may be protected from the development of wide spread disease by CFH autoantibodies. This may partially explain the incidence of CFH autoantibodies in control sera. Further studies are needed to elucidate the functional role of the CFH autoantibody, and to determine if antibodies against CFH protein, or against a combination of complement inhibitory proteins, could protect against metastasis.
The host immune response to malignancy presents a challenging opportunity for both diagnostics and the discovery of novel molecular targets. The present data suggest that autoantibodies against CFH may address both of these issues, but further studies are needed to define the true clinical utility of this target.
Translational Relevance.
Accurate staging of lung cancer provides prognostic information and guides treatment, but unfortunately the current TNM system is suboptimal. New diagnostic strategies with molecular markers could potentially complement and improve on this traditional anatomic staging system. The current translational study explored the humoral response in patients with NSCLC in an effort to discover diagnostic autoantibodies associated with early stage disease, with the additional benefit that the autoantigens could be novel therapeutic targets. We found and focused on an autoantibody to complement factor H (CFH) and showed that it is strongly associated with early stage NSCLC. These data suggest that this marker may be useful in conjunction with other autoantibodies as a diagnostic panel, and raises the possibility that CFH may be a therapeutic target.
Acknowledgments
We thank Irina Kusmartseva for expert technical assistance.
This study was partially supported by NCI grant 5RO1-CA109384-03.
References
- 1.Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:706–14. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31812f3c1a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Groome PA, Bolejack V, Crowley JJ, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: validation of the proposals for revision of the T, N, and M descriptors and consequent stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:694–705. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31812d05d5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reuschenbach M, Doeberitz M von Knebel, Wentzensen N. A systematic review of humoral immune responses against tumor antigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58:1535–44. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0733-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hoagland LF, 4th, Campa MJ, Gottlin EB, Herndon JE, 2nd, Patz EF., Jr Haptoglobin and posttranslational glycan-modified derivatives as serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2007;110:2260–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sayegh R, Awwad JT, Maxwell C, Lessey B, Isaacson K. Alpha 2-macroglobulin production by the human endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:1021–6. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.3.7533769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dean RB, Dixon WJ. Simplified Statistics for Small Numbers of Observations. Anal Chem. 1951;23:636–8. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hayat MJ, Howlader N, Reichman ME, Edwards BK. Cancer Statistics, Trends, and Multiple Primary Cancer Analyses from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Oncologist. 2007;12:20–37. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-1-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Birchard KR, Hoang JK, Herndon JE, Jr., Patz EF., Jr Early changes in tumor size in patients treated for advanced stage nonsmall cell lung cancer do not correlate with survival. Cancer. 2009;115:581–6. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tan HT, Low J, Lim SG, Chung MC. Serum autoantibodies as biomarkers for early cancer detection. Febs J. 2009;276:6880–6904. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sahin U, Tureci O, Schmitt H, et al. Human neoplasms elicit multiple specific immune responses in the autologous host. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:11810–3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anderson KS, LaBaer J. The sentinel within: exploiting the immune system for cancer biomarkers. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:1123–33. doi: 10.1021/pr0500814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Caron M, Choquet-Kastylevsky G, Joubert-Caron R. Cancer immunomics using autoantibody signatures for biomarker discovery. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:1115–22. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R600016-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Salazar L, Disis ML. Antibodies to human tumor oncoproteins in cancer patients. In: Stauss H, Kawakami Y, Parmiani G, editors. Tumor Antigens Recognized by T Cells and Antibodies. Taylor and Francis; New York: 2003. pp. 172–90. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kurtenkov O, Klaamas K, Mensdorff-Pouilly S, et al. Humoral immune response to MUC1 and to the Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) glycotope in patients with gastric cancer: relation to survival. Acta Oncol. 2007;46:316–23. doi: 10.1080/02841860601055441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kurtenkov O, Klaamas K, Rittenhouse-Olson K, et al. IgG immune response to tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TF, Tn, alphaGal) in patients with breast cancer: impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and relation to the survival. Exp Oncol. 2005;27:136–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Richards ER, Devine PL, Quin RJ, et al. Antibodies reactive with the protein core of MUC1 mucin are present in ovarian cancer patients and healthy women. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1998;46:245–52. doi: 10.1007/s002620050484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.von Mensdorff-Pouilly S, Verstraeten AA, Kenemans P, et al. Survival in early breast cancer patients is favorably influenced by a natural humoral immune response to polymorphic epithelial mucin. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:574–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.3.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Qiu J, Choi G, Li L, et al. Occurrence of autoantibodies to annexin I, 14-3-3 theta and LAMR1 in prediagnostic lung cancer sera. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5060–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Soussi T. p53 Antibodies in the sera of patients with various types of cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1777–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Finn OJ. Human tumor immunology at the molecular divide. J Immunol. 2007;178:2615–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.2615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI, Trapani JA. A fresh look at tumor immunosurveillance and immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:293–9. doi: 10.1038/86297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.de Cordoba S Rodriguez, Esparza-Gordillo J, de Jorge E Goicoechea, Lopez-Trascasa M, Sanchez-Corral P. The human complement factor H: functional roles, genetic variations and disease associations. Mol Immunol. 2004;41:355–67. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Varsano S, Rashkovsky L, Shapiro H, Ophir D, Mark-Bentankur T. Human lung cancer cell lines express cell membrane complement inhibitory proteins and are extremely resistant to complement-mediated lysis; a comparison with normal human respiratory epithelium in vitro, and an insight into mechanism(s) of resistance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998;113:173–82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ajona D, Hsu YF, Corrales L, Montuenga LM, Pio R. Down-regulation of human complement factor H sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to complement attack and reduces in vivo tumor growth. J Immunol. 2007;178:5991–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.9.5991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Junnikkala S, Jokiranta TS, Friese MA, et al. Exceptional resistance of human H2 glioblastoma cells to complement-mediated killing by expression and utilization of factor H and factor H-like protein 1. J Immunol. 2000;164:6075–81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.6075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dragon-Durey MA, Loirat C, Cloarec S, et al. Anti-Factor H autoantibodies associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:555–63. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004050380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]