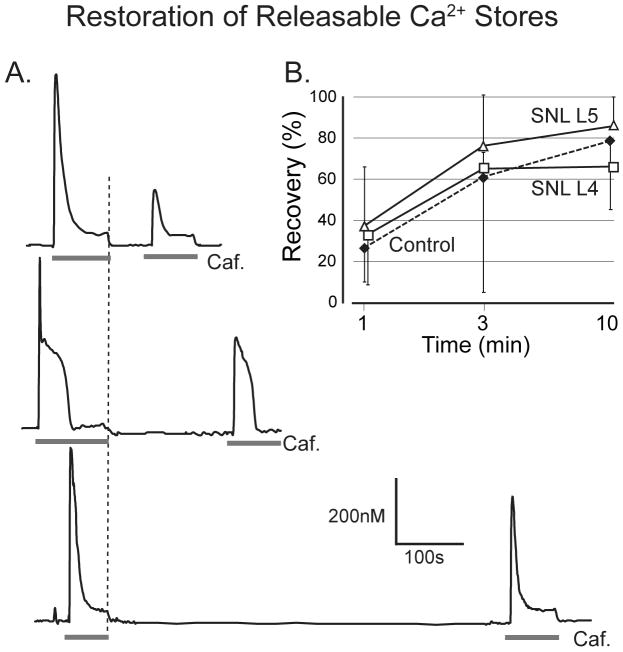
Figure 5.
Recovery of caffeine-induced Ca2+ release during rest. A. A second application of caffeine (Caf., 20mM) at intervals of 1, 3, and 10min following the offset of the previous application (dotted line) shows progressive recovery of transient area in three different neurons. B. Proportionate recovery is comparable in control neurons and in fourth lumbar (L4) and L5 neurons after spinal nerve ligation (SNL). Two-way ANOVA shows a significant main effect for time interval, but not for injury. Groups at each data point include 4 to 14 neurons. Error bars show standard deviation.