Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A., HUMPHREY J. H., PORTER R. R. On the origin of the multiple forms of rabbit gamma-globulin. Biochem J. 1956 Jul;63(3):412–419. doi: 10.1042/bj0630412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., ANKER H. S. Kinetics of amino acid incorporation into serum proteins. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):283–293. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUEMER H. D. Formation of hippuric acid from phenylalanine labelled with carbon-14 in phenylketonuric subjects. Nature. 1961 Jan 7;189:63–64. doi: 10.1038/189063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
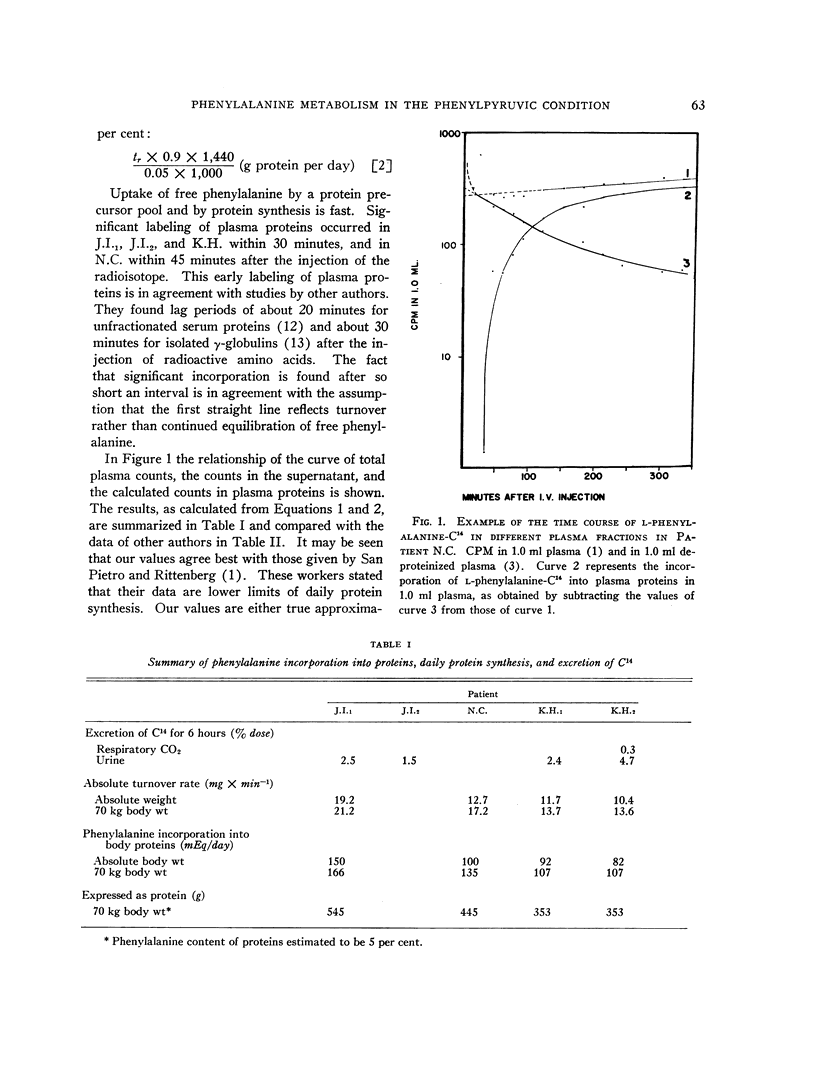
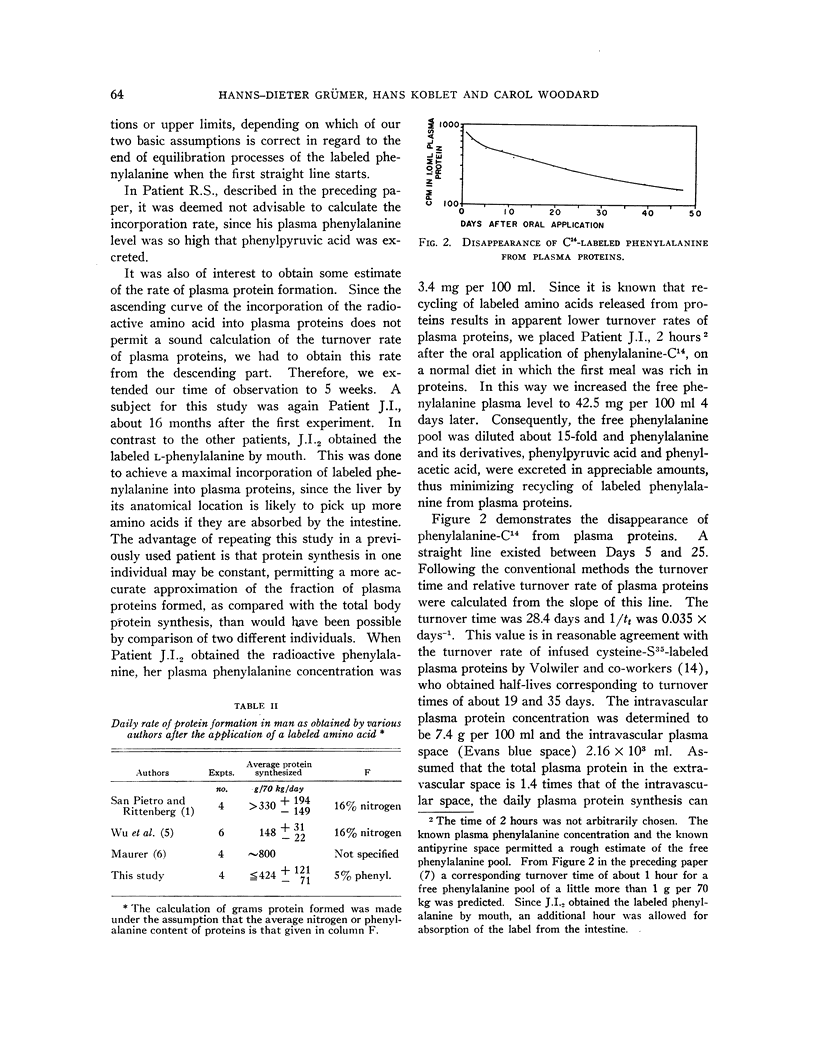
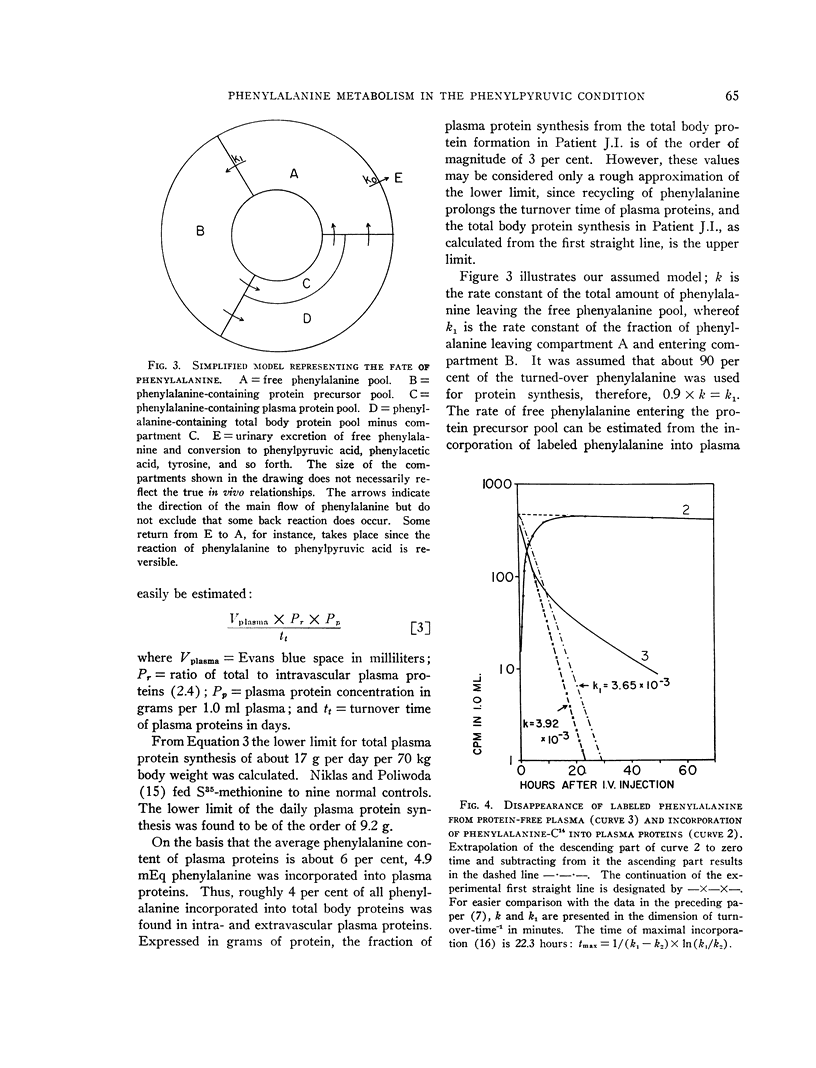
- GRUMER H. D., KOBLET H., WOODARD C. Phenylalanine metabolism in the phenylpyruvic condition. I. Distribution, pool size, and turnover rate in human phenylketonuria. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1758–1765. doi: 10.1172/JCI104399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAN PIETRO A., RITTENBERG D. A study of the rate of protein synthesis in humans. II. Measurement of the metabolic pool and the rate of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):457–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., BESSMAN S. P. The hydroxylation of phenylalanine and antipyrine in phenylpyruvic oligophrenia. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):961–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLWILER W., GOLDSWORTHY P. D., MACMARTIN M. P., WOOD P. A., MACKAY I. R., FREMONT-SMITH K. Biosynthetic determination with radioactive sulfur of turn-over rates of various plasma proteins in normal and cirrhotic man. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):1126–1146. doi: 10.1172/JCI103162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU H., BISHOP C. W. Pattern of N15-excretion in man following administration of N15-labeled glycine. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Jan;14(1):1–5. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU H., SENDROY J., Jr, BISHOP C. W. Interpretation of urinary N15-excretion data following administration of an N15-labeled amino acid. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Jan;14(1):11–21. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU H., SENDROY J., Jr Pattern of N15-excretion in man following administration of N15-labeled L-phenylalanine. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Jan;14(1):6–10. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILVERSMIT D. B. The design and analysis of isotope experiments. Am J Med. 1960 Nov;29:832–848. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


