Abstract
We report a case of Hymenolepis diminuta infection in a 2-year-old child living in a suburban area of Catania, Italy. This case was initially referred to us as Dipylidium caninum infection, which was not cured after being treated twice with mebendazole. However, by analyzing the clinical presentation and stool samples we arrived to the diagnosis of H. diminuta infection. The case presented with atypical allergic manifestations which had never been reported as clinical features of symptomatic H. diminuta infection; remittent fever with abdominal pain, diffuse cutaneous itching, transient thoracic rash, and arthromyalgias. The patient was treated with a 7-day cycle of oral niclosamide, which proved to be safe and effective. This case report emphasizes that a correct parasitological diagnosis requires adequate district laboratories and trained personnel. In addition, we recommend the importance of reporting all H. diminuta infection cases, in order to improve knowledge on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment protocols.
Keywords: Hymenolepis diminuta, cestode infection, treatment, intestinal helminthiasis
INTRODUCTION
Hymenolepis diminuta is a rat tapeworm whose diffusion throughout the world as a human infection is today rare even in developing countries. The definitive hosts of this helminth are usually rats and other rodents, while humans can only accidentally enter into the life cycle of this tapeworm by ingesting infected arthropods containing in their body cavity the helminth's cysticercoid larvae [1]. The great majority of the reported human infections derive from mass stool screenings in different populations or field surveys in tropical and subtropical areas. Infection is mainly asymptomatic, though rarely symptoms, such as itching, abdominal pain, and mild diarrhea, have been reported.
CASE DESCRIPTION
In December 2007, a 2-year-old boy, who had recently moved to a suburban area near the town of Paternò (20,000 inhabitants in eastern Sicily) after having always lived in a metropolitan area, was referred to the Outpatient Clinic of the Paediatric Unit in the University Hospital of Catania, Italy. He had a 6-month history of remittent fever and occasional emission of suspect tapeworm proglottids in his stool.
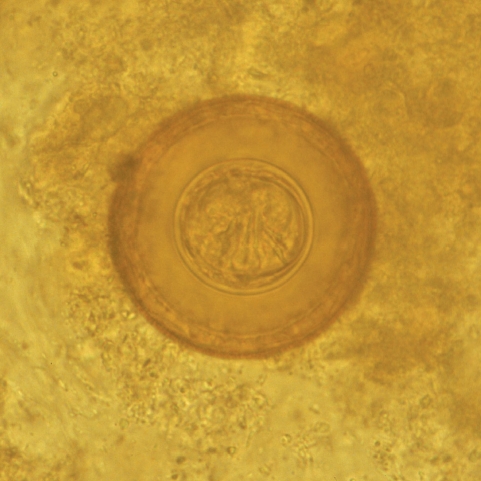
Before the child being referred to the Outpatient Clinic of the Paediatric Clinic of the University Hospital of Catania, the proglottids and several stool samples had been examined in a private laboratory and the child was diagnosed with Dipylidium caninum infection. Therefore, he was treated by his general practitioner with mebendazole for 3 days, without achieving clinical remission. A second stool examination, carried out in the same private laboratory after 20 days, revealed the presence of the same parasite, which led to a further treatment with a prolonged cycle of mebendazole (3 days per week for 3 consecutive months). One month after the end of the latest therapeutic cycle, the child was brought to the parasitological laboratory of the University Hospital in Catania, presenting remittent fever (maximum peak 37.7℃), abdominal pain, diffuse cutaneous itching, transient thoracic rash, and arthromyalgias. Blood and urine examinations together with abdominal ultrasound scan were performed without showing any abnormal results. Also, the parasitological examination of concentrated stool samples was negative. Two weeks later, while the same symptoms were persisting, the child emitted again proglottids in his stool. A parasitological examination of a concentrated stool sample performed in our laboratory revealed numerous spherical eggs, 70 mm in diameter, which lacked polar filaments, and presented a thick-shelled outer membrane and a thin inner membrane containing 6 hooklets (Fig. 1) [2]. The child was admitted as an inpatient in our Paediatric Unit and treated with oral niclosamide (1 g on the first day and 500 mg/day for the following 6 days) [3]. Within a week from the start of niclosamide treatment, fever, arthralgias and diffuse itching completely recovered.
Fig. 1.
H. diminuta egg found in the patient's stool. The egg contains 6 central hooklets but no polar filaments 13 × 13 mm (600 × 600 DPI).
Parasitological stool examinations performed in our laboratory 1, 7, 15, and 30 days after the end of the treatment were negative for H. diminuta eggs. In addition, the child maintained completely asymptomatic.
DISCUSSION
The natural reservoir and definitive host of H. diminuta is represented by rats and other rodents, while coprophilic arthropods, such as fleas, lepidoptera, and coleoptera, act as intermediate hosts when, by eating H. diminuta eggs emitted in the rodent's stool, they develop into cysticercoid larvae in their body cavity. If the infected arthropod is eaten by the definitive host, the ingested cysticercoid is introduced into the bowels of the rodent and develops to an adult worm whose eggs are discharged in the rodent's feces [1]. In addition, it has been recently demonstrated that a further mechanism of egg dispersal is represented by a beetle-to-beetle transmission of H. diminuta, which occurs in natural environments as a way for the helminth to wide its diffusion [4].
Humans can only accidentally enter into the life cycle of H. diminuta, acting as definitive hosts when they ingest infected arthropods containing its cysticercoid larvae, which is the reason why this infection in humans is so uncommon [1]. At present, only a few hundred cases have been reported globally, the majority of which concerned with children who are more likely to accidentally ingest the helminth larvae [5-21]. However, surveys concerning the parasitization rates of different populations revealed a prevalence range between 0.001% and 5.5% of the total population [9-11,22-24]. H. diminuta differs from a related species, Hymenolepis nana, whose eggs are more frequently found in the human stool, since the latter can be transmitted through a person-to-person mechanism and hence does not necessarily require an intermediate host [1].
With regard to the case described in our report, its rarity resides into 3 different reasons: firstly, up to now only 2 clear-cut clinically symptomatic cases of H. diminuta infection have been reported in Italy, the last having been described 5 years ago [20]. Similar to the last case reported in Italy, the house where the child lived (in a peripheral but not a rural area), its surroundings, and the places he attended were inspected but no evidence of rodents or fleas has been found.
Secondly, this case atypically presented as a fever of unknown origin and, as far as we know, fever has never been reported as a clinical feature of symptomatic H. diminuta infection. In addition to the remittent fever, other atypical allergic manifestations, like abdominal pain, diffuse cutaneous itching, transient thoracic rash, and arthromyalgias, were present. Allergic symptoms are often present in chronic worm infections, lead by a constant state of immune activation characterized by a dominant Th2 type of cytokine profiles and high IgE levels [25,26]. However, eosinophilia is usually not observed in infections with helminths that reside in the lumen of the human gut as H. diminuta. Nevertheless, helminth infections may affect the expression of an allergic disease, and in certain situations, they may be associated with increased, decreased, or no risk of atopic conditions [27,28].
Thirdly, in our case, the infection was misdiagnosed as D. caninum in a private laboratory, leading to a delayed diagnosis as well as to an inadequate repeated treatment with mebendazole. This fact confirms that a parasitological diagnosis cannot be performed everywhere but requires adequate district laboratories with well trained personnel.
As refers to therapy, actually there is no strong supportive evidence for its role either because of the lack of controlled studies or because there is some evidence that many infected and untreated individuals become spontaneously asymptomatic by time. Nevertheless, praziquantel is considered the drug of choice for the treatment of H. diminuta infection. However, its safety in children is far from being adequately demonstrated. In the case here described, we decided to use oral niclosamide, which seemed to be equally effective and relatively non-toxic as previously reported [3,6,20].
Finally, we agree with Marangi et al. [20] and Tena et al. [21] who both recommended the necessity to report any case of H. diminuta infection in order to improve knowledge on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment protocols.
References
- 1.De Carneri F. Elminti. Classe Cestoda. Ordine Cyclophillidea. Famiglia Hymenolepididae. Parassitologia generale e umana. 13th ed. Milano, Italy: Casa Editrice Ambrosiana; 2004. pp. 307–309. [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization. Tavole OMS per la diagnosi delle parassitosi intestinali. Editoriale Fernando Folini. 1996. tavola 2. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jones WE. Niclosamide as treatment for Hymenolepis diminuta and Dipylidium caninum infection in man. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979;28:300–302. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pappas PW, Barley AJ. Beetle-to-beetle transmission and dispersal of Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda) eggs via the feces of Tenebrio molitor. J Parasitol. 1999;85:384–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cohen IP. A case report of Hymenolepis diminuta in a child in St. James Parish, Jamaica. J La State Med Soc. 1989;141:23–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hamrick HJ, Bowdre JH, Church SM. Rat tapeworm: Hymenolepis diminuta infection in a child. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990;9:216–219. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199003000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kan SK, Kok RT, Marto S, Thomas I, Teo WW. The first report in Hymenolepis diminuta infection in Sabah, Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75:609. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Levi MH, Raucher BG, Teicher E, Sheehan DJ, McKitrick JC. Hymenolepis diminuta: one of three pathogens isolated from a child. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987;7:255–259. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lo CT, Ayele Y, Birrie H. Helminth and snail survey in Harerge region of Ethiopia with special reference to schistosomiasis. Ethiop Med J. 1989;27:73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McMillan B, Kelly A, Walker JC. Prevalence of Hymenolepis diminuta infection in man in the New Guinea Highlands. Trop Geogr Med. 1971;23:390–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mercado A, Arias B. Taenia sp. and other intestinal cestode infections in individuals from public outpatient clinics and hospitals from the northern section of Santiago, Chile (1985-1994) Bol Chil Parasitol. 1995;50:80–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Scaglione L, Troielli F, Ansaldi E, Orsi PG, Garavelli PL. Hymenolepis diminuta: a rare helminthiasis in humans. Description of a clinical case. Minerva Med. 1990;81:65–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Guevara D, Dominguez J. Un nuevo caso en Espana de parassitismo humano por Hymenolepis diminuta. Rev Iber Parasitol. 1955;1995:59. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tesjaroen S, Chareonlarp K, Yoolek A, Mai-iam W, Lertlaituan P. Fifth and sixth discoveries of Hymenolepis diminuta in Thai people. J Med Assoc Thai. 1987;70:49–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Varghese SL, Sudha P, Padmaja P, Jaiswal PK, Kuruvilla T. Hymenolepis diminuta infestation in a child. J Commun Dis. 1998;30:201–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Edelman MH, Springarn CL, Nauenberg WG, Gregory C. Hymenolepis diminuta (rat tapeworm) infection in man. Am J Med. 1965;38:951–953. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gonzalez N, Molinas MA, Leon J. Casos humanos de Hymenolepis diminuta. Rev Parasitol Microbiol II. 1967;1:58–60. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ratliff CR, Donalson L. A human case of Hymenolepis diminuta in Alabama. J Parasitol. 1965;51:808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sane SY, Irani S, Jain N, Shah KN. Hymenolepis diminuta: a rare zoonotic infection report of a case. Indian J Pediatr. 1984;51:743–745. doi: 10.1007/BF02776395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Marangi M, Zechini B, Fileti A, Quaranta G, Aceti A. Hymenolepis diminuta Infection in a child living in the urban area of Rome, Italy. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:3994–3995. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3994-3995.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tena D, Perez Simon M, Gimeno M, Perez Pomata MT, Illescas S, Amondarain I, Gonzalez A, Dominguez J, Bisquert J. Human infection with Hymenolepis diminuta: case report from Spain. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:2375–2376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.8.2375-2376.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foresi C. Data on the epidemiology of hymenolepiasis in Italy. Arch Ital Sci Med Trop Parassitol. 1967;48:251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Naquira C, Delgado E, Tantalean M, Naquira F, Elliot A. Prevalencia de enteroparasitos en escolares de los distritos de San Juan y Magdalena. Rev Peru Med Trop. 1973;2:37–40. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Panpiglione S, Visconti S, Pezzino G. Human intestinal parasites in Subsaharan Africa II. Sao Tome and Principe. Parassitologia. 1987;29:15–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Robinson TM, Nelson RG, Boyer JD. Parasitic infection and the polarized Th2 immune response can alter a vaccine-induced immune response. DNA Cell Biol. 2003;22:421–430. doi: 10.1089/104454903767650685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Palmer LJ, Celedon JC, Weiss ST, Wang B, Fang Z, Xu X. Ascaris lumbricoides is associated with increased risk of childhood asthma and atopy in rural China. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1489–1493. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2107020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cooper PJ, Chico ME, Bland M, Griffin GE, Nutman TB. Alllergic symptoms, atopy, and geohelminth infections in a rural area of Ecuador. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:313–317. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200211-1320OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wiwanitkit V. Overview of Hymenolepis diminuta infection among Thai patients. Med Gen Med. 2004;6:7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]